If your connection type is pppoe. See what "PPPoE" is in other dictionaries.
PPPoE (from English. Point-to-point protocol over Ethernet) is network protocol over Ethernet PPP frames. It is typically used by xDSL services. PPPoE provides additional features such as encryption, compression, authentication.
PPPoE- a tunneling protocol that allows you to encapsulate (configure) IP, or other protocols that are overlaid on PPP, over Ethernet connections, but with software features PPP connections. Therefore, this protocol is used for virtual "calls" to neighboring Ethernet machines, as well as for establishing a point-to-point connection used to transport IP packets that works with PPP capabilities.
Due to this, the traditional PPP-oriented software can be used to set up connections that will use a packet-oriented network rather than a serial link, to organize a classic connection with a password and login for Internet connections. In addition, on the other side of the connection, an IP address is assigned only when a PPPoE connection is open, which makes it possible to dynamically reuse IP addresses.
PPPoE functions like this: there is an Ethernet environment, that is, a connection of several network cards addressed by MAC addresses. The headers of Ethernet frames contain the address of the recipient of the frame, the sender of the frame, and the type of the frame itself. One of these cards is listened to by a PPPoE server. The PPPoE server must respond to the broadcast Ethernet frame sent by the client. In turn, the PPPoE server sends a response to the client. If the network contains several PPPoE servers, then each of them sends a response. And then the client needs to select a suitable server and send him a connection request. Then the server sends an acknowledgment to the client, which has unique identifier session, and all further frames in the session will have this identifier. That is, a virtual channel is created between the client and the server, identified by the identifier MAC addresses of the server and client, and the session. After that, a PPP connection is raised in this channel, and IP traffic is packaged into PPP packets.
PPPoE is PPP over Ethernet, a protocol that allows you to send PPP frames directly over Ethernet. The main advantages of PPPoE over traditional IP over Ethernet are that for a connection over local network requires an account on the gateway. This organization of the local network allows you to simplify the control and configuration of billing.
The PPPoE protocol is a complete analog of a dialup connection, differing only in speed - up to 100 Mbps, and the transmission medium - Ethernet. Ethernet uses PPP stack technology, which is not new, as it is already quite common.
PPPoE works on the principle of establishing a point-to-point connection over a common Ethernet environment, therefore, the PPPoE operation process can be divided into two stages. At the first stage, two devices communicate their addresses to each other and establish an initial connection, at the second stage, a PPP session is started.
Advantages and limitations this protocol:
1) Convenience and ease of use.
2) Multiplatform.
3) Simplicity and ease of use.
5) Compared to VPN, no grinding costs are needed.
PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) is a connection protocol over Ethernet. For providers, the main advantage of PPPoE is that they can easily get by with a limited number of IP addresses, simply by assigning them only to users who are connected in this moment. Also, with PPPoE, ISPs can flexibly manage their customer service contingent, and it will be more difficult for individual users to host FTP and Web sites on their servers.
Compared to other types of broadband services, PPPoE has much higher security, which will undoubtedly be appreciated by consumers. After all, it will be more difficult for hackers to identify and hack computers with temporary IP addresses. The user can be inconvenienced by frequent error messages that are issued when the authentication server fails on the part of the provider. Thus, PPPoE cannot seriously affect the connection speed. In essence, using this protocol, a tunnel connection is created between the provider and the subscriber.
You need to authorize PPPoE through CHAP, which means that passwords are always transmitted in encrypted form, and the system records the time the subscriber connected to the network, which makes it easy to check if there are disputes regarding traffic.
PPPoE Protocol Overview PPPoE Active Discovery Request (PADR) PPPoE Active Discovery Session-confirmation (PADS) PPP Session Stage PPPoE Active Discovery Terminate (PADT)
Answer:
PPPoE (English. Point-to-point protocol over Ethernet) is a network protocol for transmitting PPP frames over Ethernet. The protocol is described in RFC 2516.
Network devices ZyXEL (modems, routers, Internet centers) have support for the PPPoE protocol. Using the PPPoE protocol allows multiple users to access the Internet at the same time with only one account. This requires a single PPPoE connection, not multiple connections equal to the number of users.
Consider 2 options for implementing PPPoE:
- Implementation of PPPoE in the device. The ZyXEL device automatically establishes a PPPoE connection for all computers on the local network, establishing only one session. The computers on the local network share the available bandwidth.
- Implementation of PPPoE on a computer. The ZyXEL device acts as a transparent bridge using RFC1483 encapsulation. The device only establishes a DSL connection. To access the Internet, you need to set up a PPPoE connection on each computer. It is possible to carry out several communication sessions using several accounts on the same line.
The first PPPoE implementation using the ZyXEL device. In this case, the device operates in routing mode and is a PPPoE client that sends a connection initiation packet to the PPPoE server to establish a PPPoE connection. With this implementation, only one session is established. All hosts on the local network share the bandwidth of the Internet channel.
The modem first establishes a DSL connection and then automatically establishes a PPPoE connection. The modem receives the IP address from the provider on the DSL port and then routes the traffic. At the same time, it is not necessary to configure a PPPoE connection on each computer on the local network.
The second option for implementing PPPoE on a computer. In this case, the ZyXEL device acts as a transparent bridge and uses RFC1483 encapsulation. To access the Internet, you need to set up a PPPoE connection on each computer. In this case, there are multiple PPPoE sessions within the same virtual circuit.
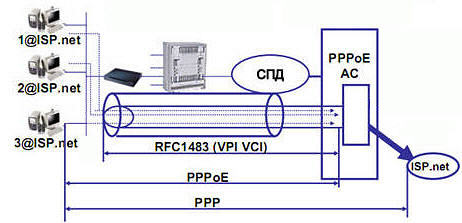
Required additional setting operating system. The modem only establishes a DSL connection with the provider's equipment. In the operating system, you need to create a PPPoE connection for authorization on the provider's server. To access the Internet, the user will need to start a PPPoE connection every time. Information about creating a PPPoE connection in operating systems ah Windows XP/Vista you will find in the footnote to this article.
Overview of the PPPoE protocol
PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) provides access control and billing similar to dial-up services using PPP. PPPoE client and PPPoE server must
be located in the same layer 2 logical segment. A PPPoE session can function both on behalf of each user connected to the xDSL modem (xDSL modem must operate in bridge mode and transparently pass connections), and on behalf of the modem itself (xDSL modem must operate in router mode). DSLAM usually does not recognize PPPoE sessions, it transparently switches Ethernet frames without analyzing their content.
When using PPPoE, it is possible to establish multiple PPP sessions within the same physical connection. Providers often use PPPoE due to the low cost of implementing such solutions. A PPPoE server is also called an Access Concentrator or Broadband Remote Access Server (BBRAS).
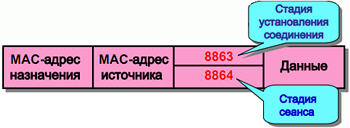
When using the PPPoE protocol, there are two distinct stages that can be called connection establishment stage and session stage.
For the connection establishment stage, the value of the field type equals 8863
, and for the session stage, the field value type equals 8864
.
If a host wants to initiate a PPPoE session, it must first perform a connection establishment procedure in order to determine the Ethernet MAC address of the client device and establish Session ID PPPoE. While PPP operation is peer-to-peer communication, the connection establishment procedure is client-server communication. During the connection establishment process, the host discovers the access concentrator (PPPoE server). Depending on the network topology, a host may access not one, but several PPPoE servers. During the connection establishment stage, the host can discover all kinds of PPPoE servers and then select one of them. If the connection establishment stage is successfully completed, the host and its chosen PPPoE server have the information necessary to establish a point-to-point connection over Ethernet.
After the connection establishment stage is completed, the session stage begins, during which the host receives from the PPPoE server and then the PPP session is established, both the host and the server must allocate the necessary resources for the PPP virtual interface.
PPPoE Encapsulation

Field length Version is 4 bits and its meaning must be equal 0x1
Field length A type is 4 bits and its meaning must be equal 0x1 for this version of the PPPoE specification.
Field length The code is 8 bits (1 byte) and is specified for the PPP connection and session stages.
Field length Session ID is 16 bits (2 bytes). Below is its meaning for connection establishment packets. Within a PPP session, this value remains unchanged.
Field length Length is 16 bits (2 bytes). Its value specifies the length of the PPPoE protocol payload block, excluding the length of the Ethernet or PPPoE headers.
The connection establishment stage is divided into 4 steps:
- The host sends a broadcast request packet to initialize the connection (Code: 0x09).
- One or more PPPoE servers send a response packet (Code: 0x07).
- The host sends a unicast session request packet (Code: 0x19).
- The selected PPPoE server sends a session confirmation packet (Code: 0x65).
The host then transitions to the PPP session stage. At the stage of establishing a connection in all Ethernet frames, the value of the field Medium type equals 0x8863.
To end a session, the PPPoE server or host sends a session end packet (Code: 0xA7).

There are five types of packets sent during the connection establishment stage:
PPPoE Connection Initiation Packet - Active Discovery Initiation ( PADI) (Code: 0x09)
PPPoE - Active Discovery Offer response packet ( PADO) (Code: 0x07)
Connection request packet - PPPoE Active Discovery Request ( PADR) (Code: 0x19)
Session confirmation packet - PPPoE Active Discovery Session-confirmation ( PADS) (Code: 0x65)
Session termination packet - PPPoE Active Discovery Terminate ( PADT) (Code: 0xA7)
PPPoE Package - Active Discovery Initiation (PADI)
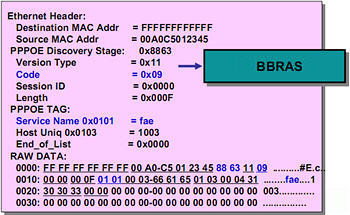
In this packet, the Destination MAC Addr field contains 0xffffffffff, which means broadcast. The host sends a broadcast request packet to initiate a connection.
In field Ether Type costs 0x8863, which means that the parties are in the process of connection establishment.
In field code costs 0x09 which means it is initiation package.
At the stage of establishing a connection session ID always equal 0x00 because the session is not open yet.
V this example Service Name - fae.
Information on how to collect data on all packets passing through a ZyXEL subscriber device (for example, to diagnose the establishment of a PPPoE connection) can be found in the following Knowledge Base article: BZ-1370
PPPoE - Active Discovery Offer (PADO)

In this packet, the Destination MAC Addr is the MAC address of the host, and the Source MAC address (Source MAC Addr) is the address of the Broadband Remote Access Server (BBRAS) that sends the response packet to the host.
In field code costs 0x07 which means it is response packet.
Helpful information PPPoE includes BBRAS information.
PPPoE Active Discovery Request (PADR) Packet
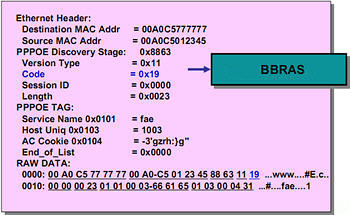
The host sends a request based on the information provided by the BBRAS.
In field code costs 0x19 which means it is Request package.
PPPoE Active Discovery Session-confirmation (PADS) Packet

BBRAS responds to host session confirmation packet.
In field code this package contains 0x65, also the package contains session ID assigned by BBRAS.
PPP session stage
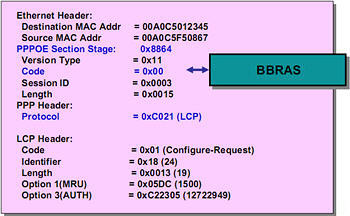
After the connection establishment stage, session stage. Note that now in the field Ether Type contains a value 0x8864. Both participants in a PPPoE connection communicate with each other using session ID The received from the session handshake packet. Protocol top level(PPP) runs over the PPPoE layer and communications begin with the connection establishment phase of the protocol LCP.
At the session stage in the field code packages are always worth 0x00.
PPPoE Active Discovery Terminate (PADT) Packet

If the host or BBRAS wants to terminate the PPPoE connection, it sends session end packet, in field code contained 0xA7, and the value in the field Session ID (Session ID) corresponds to a virtual connection.
Note that the session termination procedure is part of the connection establishment phase, not the session phase, because no data is being transferred.
Note
1. Information on setting up an ADSL modem when using PPPoE encapsulation can be found in the following article: BZ-1894
2. Information on setting up the P-330W router to connect to the Internet via the PPPoE protocol can be found in the following article: BZ-1895
3. When implementing PPPoE on a computer, additional configuration of the operating system is required. To access the Internet, you need to create a PPPoE connection in the operating system and then launch it every time.
To create a PPPoE connection in the operating room Windows system Vista go to Control Panel > Network and Sharing Center and select Setting up a connection or network. Select Internet connection and press the button Further. The wizard will start Internet connection. Select Create a new connection anyway. Then select Create a new connection and press the button Further. Select connection type High speed (with PPPoE). In the next window, enter Username and Password for Internet access provided by the ISP and click the button Connection. To complete the wizard Internet connection press the button close.
To create a PPPoE connection in Windows XP, click Start > Settings > Network connections> New Connection Wizard. Click the button Further to continue working New connection wizards. Select an item Connect to the Internet. In the next window select Establish connection manually. Then select the item Through a high-speed connection requiring a username and password. Next, enter a name for the connection to be created. In the next window, enter Username and Password, provided by the provider for Internet access. To complete the New Connection Wizard, click the button Ready.
Instructions for setting up a PPPoE connection for various operating systems, you can read on our website of the city local area network www.lannur.ru - in the section "Setting up an Internet connection via a PPPoE connection."
Additional Information:
What is PPPoE?
PPPoE (Point-to-point protocol over Ethernet) is a network protocol for transmitting PPP frames over Ethernet. Mainly used by XDSL services. Provides additional features (authentication, compression, encryption).
PPPoE is a tunneling protocol that allows IP, or other protocols that are layered on PPP, to be layered (or encapsulated) over Ethernet connections, but with software-based PPP connections, and is therefore used to make virtual "calls" to neighboring Ethernet -machine and establishes a point-to-point connection that is used to transport IP packets, working with PPP capabilities.
This allows you to use traditional PPP-oriented connection setup software that uses a packet-oriented network (like Ethernet) rather than a serial link to organize a classic connection with a login, password for Internet connections. Also, the IP address on the other side of the connection is only assigned when the PPPoE connection is open, allowing dynamic reuse of IP addresses.
PPPoE is developed by UUNET, Redback Networks and RouterWare. The protocol is described in RFC 2516.
It is worth noting that some hardware vendors (Cisco and Juniper, for example) refer to PPPoEoE (PPPoE over Ethernet), which means PPPoE operating directly over Ethernet or other networks, or linked in Ethernet (Ethernet bridged over) ATM, in order to distinguish from PPPoEoA (PPPoE over ATM), which runs on an ATM virtual circuit according to the RFC 2684 specification and SNAP and encapsulates PPPoE. PPPoEoA is not the same as Point-to-Point Protocol over ATM (PPPoA) - it does not use SNAP.
PPPoE works as follows. There is an Ethernet environment, that is, several connected network cards that are addressed by MAC addresses. Ethernet packet headers contain the packet's sender address, the packet's destination address, and the packet type. One of the cards is listening on a PPPoE server. The client sends a broadcast Ethernet packet, to which the PPPoE server must respond (the packet's sender address is its own MAC address, the packet's destination address is FF:FF:FF:FF:FF and the packet type is PPPoE Discovery).
The PPPoE server sends a response to the client (packet sender address - its own MAC address, packet recipient address - client MAC address and packet type - PPPoE Discovery). If there are several PPPoE servers in the network, then all of them send a response. The client selects a suitable server and sends a connection request to it. The server sends an acknowledgment to the client with a unique session identifier, all subsequent packets in the session will have this identifier.
Thus, a virtual channel is created between the server and the client, which is identified by the session identifier and the MAC addresses of the client and server. Then a PPP connection is raised in this channel, and IP traffic is packed into PPP packets.
Now the same thing, but a little easier:
The PPPoE protocol (abbreviation stands for Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) is required for the user authorization system. This protocol requires the user to confirm his password to establish access to the Internet.
Thus, a feature of this connection method is the built-in authentication procedure, which allows you to correctly track the time of provision and payment for network services. At the conclusion of the contract for the subscriber, Account in the database, i.e. it is assigned: username (login) and password (password).
Why do you need to install this protocol on your computer?
Insofar as PPPoE protocol is an analogue of a dial-up connection, it requires only one IP address, which is available from the Internet only during the established connection, which together significantly reduces the cost of maintaining a permanent connection to the network.
- Advantages of using this protocol
- Simplicity and ease of use.
- Multiplatform.
- High fault tolerance.
- The minimum percentage of channel load compared to other authorization systems.
- No encryption costs (compared to VPN).
In modern life, the PPPoE protocol has become an integral part of the provision of Internet access services by a provider based on xDSL technology. This protocol provides additional features, such as encryption and data compression during transmission, user authentication. This protocol operates in Ethernet networks. In this regard, it is often necessary to purchase a router with support for this protocol. For example, a pppoe router from TP-Link.
Interfaces for connecting routers
As a rule, such modems on the rear panel have several connectors for connecting network cables. One of them is called WAN (global computer network) - it is in this connector that you need to connect the cable going to telephone socket and on to the provider. Other connectors (connectors for power supply and USB port not taken into account) have the same appearance and sizes, but they are grouped separately. They already serve to connect nearby standing computers and devices, and are called LAN (local area network).

The router can be either wired or wifi router pppoe - this has no fundamental differences. Wi-Fi is undoubtedly more convenient, but the price for such modems is somewhat higher than for wired ones.
Router setup. Entering the settings menu
Configuration of almost any modern router is traditionally carried out through a web interface. If we take a TP-LINK router as an example, then to configure it, you need to go to any web browser (for example Internet Explorer), and enter into address bar 192.168.1.1 (this is the standard IP address of all routers, set by the manufacturer). Of course, provided that the router is already turned on and connected to the computer. In this case, a window will appear asking you to enter your login and password to access the device settings. If the router has not been previously used and the factory settings have not changed, then the login and password will be admin and admin, respectively.
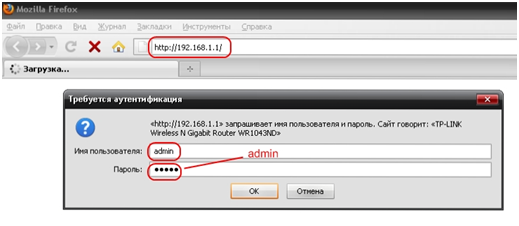
Configuring the WAN interface of the router. Selecting from the PPPoE list
Since the topic concerns the PPPoE standard, we will not consider initial settings, such as changing the password for entering the settings menu, changing the password for connecting to the network, and the like. Let's jump right into the setup. WAN port, which is directly related to the protocol. So, go to the “Network” tab, then in the “WAN” list that appears.
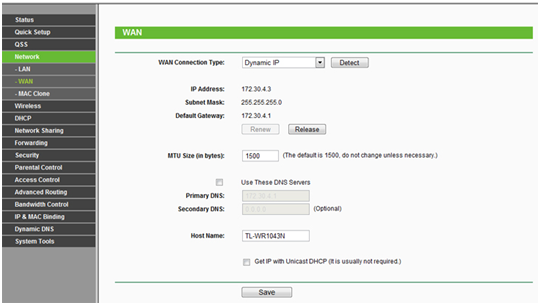
In the upper central part we will see the option "WAN Connection Type", clicking which will expand the list available options connections. Select PPPoE.
Configuring the WAN interface of the router. Entering a username and password
Having selected the PPPoE item, you will need to enter the name in the “User Name” field, and the password provided by your provider in the “Password” field. In the "Confirm Password" field, re-enter the password in order to avoid an error.
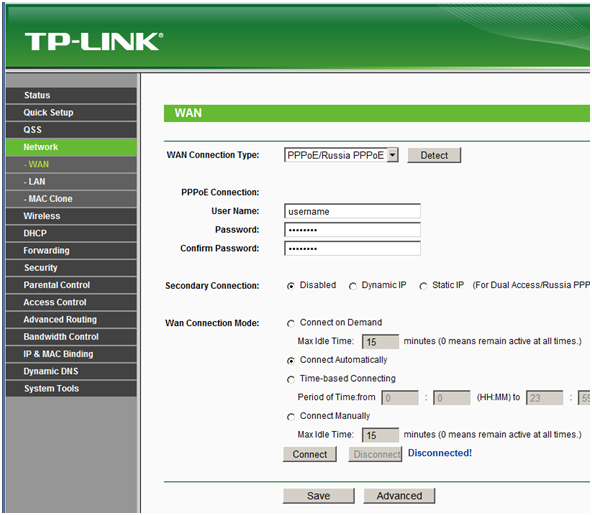
After entering the name and password, select the “Connect Automatically” option just below, which means to establish a connection automatically. It is advisable to use the remaining functions of this section if it is necessary to restrict access to the Internet, for example, strictly at certain hours or to disconnect the connection when the Internet is not used for a long time.
Of course, the appearance or location of the option may differ slightly depending on the router or firmware, but it is always present. Be sure to press the “SAVE” button after making any changes to the router configuration to save our settings. On this pppoe, the router configuration is completed.
It is worth noting that some equipment vendors (Cisco and Juniper, for example) use the term PPPoEoE (PPPoE over Ethernet), meaning PPPoE operating directly over Ethernet or other IEEE 802.3 networks, as well as PPPoE operating over Ethernet bridged over. ATM, to distinguish it from PPPoEoA (PPPoE over ATM), which runs on an ATM virtual circuit according to RFC 2684 and SNAP and encapsulates PPPoE. PPPoEoA is not the same as Point-to-Point Protocol over ATM (PPPoA) because it does not use SNAP.
PPPoE works as follows. There is an Ethernet environment, that is, several connected network cards that are addressed by MAC addresses. Ethernet frame headers contain the frame's sender address, the frame's destination address, and the frame type. One of the cards is listening on a PPPoE server. The client sends a broadcast Ethernet frame, to which the PPPoE server must respond (frame sender address - its own MAC address, frame destination address - FF:FF:FF:FF:FF and frame type - PPPoE Active Discovery Initiation). The PPPoE server sends a response to the client (the frame's source address is its own MAC address, the frame's destination address is the client's MAC address, and the frame type is PPPoE Active Discovery Offer). If there are several PPPoE servers in the network, then all of them send a response. The client selects a suitable server and sends a connection request to it. The server sends an acknowledgment to the client with a unique session ID, all subsequent frames in the session will have this ID. Thus, a virtual channel is created between the server and the client, which is identified by the session identifier and the MAC addresses of the client and server. Then a PPP connection is established in this channel, and traffic is packed into PPP packets.
PPPoE Discovery (PPPoED)
PADI
PADI- PPPoE Active Discovery Initiation.
If a user wants to connect to the Internet via DSL, first his machine must detect an access concentrator (DSL access concentrator or DSL-AC) on the provider side (point of presence (POP)). Communication via Ethernet is only possible via MAC addresses. If the computer does not know the MAC address of the DSL-AC, it sends a PADI packet via Ethernet broadcast (MAC: ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff) This PADI packet contains the MAC address of the machine that sent it.
Example PADI package:
Frame 1 (44 bytes on wire, 44 bytes captured) Ethernet II, Src: 00:50:da:42:d7:df, Dst: ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff PPP-over-Ethernet Discovery Version: 1 Type 1 Code Active Discovery Initiation (PADI) Session ID: 0000 Payload Length: 24 PPPoE Tags Tag: Service-Name Tag: Host-Uniq Binary Data: (16 bytes)
src.(=source) represents the MAC address of the machine that sent the PADI.
Dst.(=destination) is the broadcast Ethernet address.
A PADI package can be received by more than one DSL-AC.
PADO
PADO- PPPoE Active Discovery Offer.
Once the user machine has sent a PADI packet, the DSL-AC responds by sending a PADO packet using the MAC addresses provided by the PADI. The PADO packet contains the DSL-AC's MAC addresses, their names (for example, LEIX11-erx for the T-Com DSL-AC concentrator in Leipzig), and the service name. If more than one DSL-AC responded with a PADO packet, the user machine selects a particular POP from the DSL-AC using the incoming names or service names.
PADO package example:
Frame 2 (60 bytes on wire, 60 bytes captured) Ethernet II, Src: 00:0e:40:7b:f3:8a, Dst: 00:50:da:42:d7:df PPP-over-Ethernet Discovery Version: 1 Type 1 Code Active Discovery Offer (PADO) Session ID: 0000 Payload Length: 36 PPPoE Tags Tag: Service-Name Tag: AC-Name String Data: IpzbrOOl Tag: Host-Uniq Binary Data: (16 bytes)
AC-Name - String Data represents a string AC name, in this case "Ipzbr001" (Arcor DSL-AC in Leipzig).
src. represents the MAC address of the DSL-AC.
The DSL-AC's MAC address also identifies the manufacturer of the DSL-AC (in this case, Nortel Networks).
PADR
PADR stands for PPPoE Active Discovery Request.
As mentioned above, the user machine must select a POP (access point) - this is done using a PADR packet that is sent to the MAC address of the selected DSL-AC.
PADS
PADS- PPPoE Active Discovery Session confirmation.
The PADR packet is confirmed by the concentrator by forwarding the PADS packet, which also contains the Session ID. The connection to the DSL-AC for this access point is now fully established.
PADT
PADT- PPPoE Active Discovery Termination.
This packet terminates the connection to POP. It may be sent either by the user or by the DSL-AC.
Scheme Benefits
- IP headers are ignored in an Ethernet environment. That is, the user can assign an IP address to his network map, but this will not lead to a "collapse" of the network (theoretically, when working with a network hub, there should not be a "collapse" even when the user changes the MAC address to the server address, and when working with a network switch, everything depends on the design of the switch).
- Each connection is separated from the others (works in its own channel).
- Settings (IP address, gateway address, DNS server addresses) can be transmitted by the server.
- A PPP connection is easily authenticated and calculated (for example, using RADIUS).
- PPP connection can be encrypted. For example, when working with a network hub (when all Ethernet traffic can be seen on each network card), it is very difficult to read someone else's IP traffic.
Notes
Links
- RFC 2516- A Method for Transmitting PPP Over Ethernet (PPPoE)
- RFC 3817 - Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) Active Discovery Relay for PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE)
- RFC 4638 - Accommodating a Maximum Transit Unit/Maximum Receive Unit (MTU/MRU) Greater Than 1492 in the Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE)
 Samsung Galaxy S Advance - Specifications Battery life
Samsung Galaxy S Advance - Specifications Battery life Samsung C3322 review: elegant conciseness Specifications samsung c3322
Samsung C3322 review: elegant conciseness Specifications samsung c3322 Nubia Z11 Max - Specifications Various sensors perform various quantitative measurements and convert physical indicators into signals that a mobile device recognizes
Nubia Z11 Max - Specifications Various sensors perform various quantitative measurements and convert physical indicators into signals that a mobile device recognizes