FAQ for CD-Recordable and CD-R Drives. What is CD-R writing speed? How to burn audio CDs
Despite the emergence of modern car audio systems, due to their very high cost, the demand for familiar car radios among drivers remains at the same level. In this regard, the question of how to burn music to a disc for a radio tape recorder is always relevant, so that it can be read correctly and does not create problems while listening to music files.
What should be remembered before burning files to a radio CD?
To do this, first of all, you need to choose a suitable disc for recording, and also carefully study the instructions for the radio tape recorder, which should indicate which file formats the device can read. Based on this information, as well as choosing the appropriate computer program for burning, you can correctly burn music to a CD for the radio.
Choosing file formats for recording
The most common formats that can be recorded on CD are CDA, WAV, MP3. CDA. But to play them on the radio, there must be appropriate decoders. In order not to spoil the disc and not be left without musical accompaniment during a long trip, it is better to study the parameters of the device in advance. But you should also be aware of the peculiarities of the process of recording a CD.

What is the best way to record music for the radio - CD or DVD?
The standard way to burn a disc for a CD-recorder is to select a regular CD-R blank onto which, using special program burn music files are recorded. But, contrary to popular belief, you can also record DVDs for a car radio, which have a number of advantages over conventional CDs. If a regular CD can record a maximum of 800 megabytes of information, but in fact - 750 (which corresponds to 75 minutes of playing music files), then a DVD disc can record up to 8.5 GB of music (as well as other information - for information). If the car radio reads the DVD format, then it is more advisable to use it for recording music files.
The next thing to remember when choosing a media for recording music for a car radio is the possibility of multiple burns for recording. You can choose both a regular CD-blank, to which mp3 files are recorded once, and CD-RW, where you can record, erase and rewrite files up to 50 times.
So how do you burn a CD-R disc to your radio?
Have you bought a suitable disc for recording and have a folder with mp3 files ready? Then all you still need is to install on your computer suitable program for burning a CD. Sometimes even this is not required if your PC has a CD burner. But in most cases, you will need one of any programs that are freely available for download on the Internet. It could be Ashampoo burning Studio, CDBurnerXP and other programs. One of the most popular and most frequently used programs due to its intuitive interface is the Nero program.

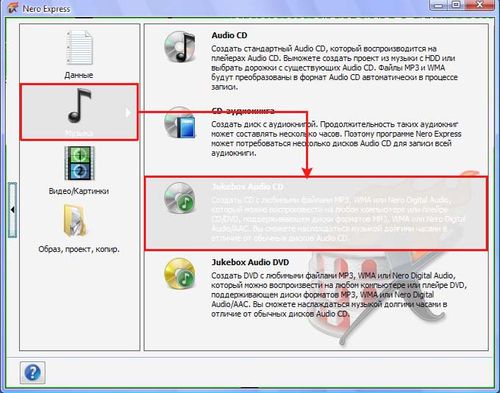
Let's look at the process of burning a CD using the example of Nero Express.
For Nero, as well as for other programs for recording audio and video CDs, the burning process includes the standard steps for choosing a file format (music, video, document). We need Music / Audio CD format. If you are going to burn a disc for an mp3 radio, then select the appropriate Music / MP3 Disc format. Having selected it, you need to go to the field for adding audio files in root folder CD using the Add button. By clicking on it, you will open the path to your audio files.
You can do it easier and drag the selected files from the open folder just into the add field. When adding music, you can change the sequence of files by simply dragging them up or down relative to each other - they will be recorded in the established order.
Having selected the files to burn, click the Next button, after which you will go to the field for selecting the device for recording (this will be your CD-R or DVD), as well as the speed of the recording process. Burn speed is a very important point in this matter, because if set incorrectly, the CD may be unreadable. The standard setting is 8x speed. Having selected all the parameters, you can go directly to the burning process by clicking on the Burn button. After a while, your disc will be ready, and the computer itself will eject it from the drive after burning.
Possible problems when recording and playing music files from a CD on a radio tape recorder
Sometimes, even by strictly following the instructions of the program, while sitting in the car, you may find that the device does not want to read the disc. There may be several reasons for this, let's name the most common of them:
- The radio tape recorder does not have an appropriate decoder for the recorded file formats, or simply does not "read" them;
- The CD is “full” (for example, if you burned to CD-R music for all 80 minutes, and the recommended volume should not exceed 75 minutes);
- The writing speed was too high (the recommended value for most CDs is 8x);
- There is a conflict between the "old" and "new" CD-ROM file reading system.
How else can you record music for your car radio?
In addition to CD-disks, you can record music for a car radio and on a regular USB flash drive. If your radio has a slot for reading USB drives, you can select it to play audio files. In this case, the process of burning files will be easier than for a CD, because it doesn’t need special utilities and additional devices. In order to write files to a USB flash drive for a radio tape recorder, simply select them in a folder on your computer and copy them to the clipboard, and then move them to the root folder of the flash drive using the Ctrl + V hotkey combination.
In contact with
If you are wondering how to burn music to a disc in mp3 or audio disc format using a free program that can burn CD and DVD discs, then this article is about this. If your computer does not have a paid Nero program or some other alternative program, then the problem can be solved. You have already learned how to write information on blank disks without special programs, using standard Windows tools in my lesson: "". If you haven't read it yet, then it's time to do it. Using the link above, you will learn how to record music, video or something else, without installing programs.
Unfortunately, you cannot burn files and folders this way in Windows XP to a DVD disc. This can be done using a special program that has the function of burning to DVD discs. What should those who do not have it do? Everything is simple enough. There are free programs that are no worse than the well-known Nero program. In addition to pluses, the Nero program has many minuses. This program is paid, takes up a lot of space on the computer, includes unnecessary functions.
Free disc burning software takes up little space on your computer and has the most essential functions for working with discs. The size installation file small, since the developers do not create additional functions, but create those that will be needed. Unfortunately, many free programs also have a number of disadvantages. I tried to find a free CD burning software for you and DVD discs, in which I practically did not find any obvious drawbacks, we can say that it is one of the best free programs that are not distributed for money. I would also like to please Russian-speaking users that the program is completely in Russian and you will not have any difficulties in installing or using it.
I present to you a free program that is designed for writing data to discs - CDBurnerXP... From the name of the program, you will think that it only works in Windows system XP, but I want to please you that it also works great on Windows 7 and 8.
Installing CD Burner XP
You can download CDBurnerXP from my blog here. After clicking on the link, indicate where you want to save the CDBurnerXP program on your computer. The volume of this program is quite small, downloading such a file will take a little time. These pluses only confirm that the developers have tried their best to create it.
After downloading the files, open it double click left mouse button. The welcome window of the installation wizard will open, in this window we can familiarize ourselves with the version of the program (4.4.0.2838). Then, in the window that appears, click the "Next" button.
Now select "I accept all terms of the agreement", and then click the "Next" button again.
You will be prompted for the path to install the program. We do not change anything and just click the "Next" button.
In the next window, uncheck the "Languages" checkbox and select the installation of only the Russian language "Russian (Russia)", click the "Next" button. In the next window, all the checkmarks are as needed, just click the "Install" button. If you need the * .iso extension to associate with CDBurnerXP, then check the corresponding box “Associate ISO files(.iso) with CDBurnerXP ". By the way, if you need to open ISO image, then you do not need to write it to disk, but you can simply open: "".
Now you need to wait a little for the program to install into your computer. Uncheck the box "Run CDBurnerXP", then click the "Finish" button. If you leave the check mark, then after clicking the Finish button CDBurnerXP will open.
The icon appears on the desktop. This will be yours free program for burning CDs and DVDs.
Open the program icon on the CDBurnerXP desktop. You will be prompted to select the language first if you have installed all the additional components, otherwise the program will open immediately. If it immediately displays "Russian", then click "OK". If suddenly the required language is determined incorrectly, then you need to select it from the specified list.
Now you will learn how to record music to disc. First, the program will offer to select the type of data to be burned (Data disc; Video DVD; Audio disc; Burn ISO image; Copy disc; Erase disc). A widely used recording item is “Data Disc”. With it, you can write various data to disk, almost anything you want. Such a disk will open on any computer. There are descriptions under each item that can help you write.
We need to understand how to record music on a disc, and therefore I will not tell you how this or that information is recorded. We need 2 points:
- Data disc. When choosing this option, you need to record music for mp3 players. Nowadays, all new players recognize the mp3 format. With this option, you will be able to burn about 100-200 songs to a disc.
- Audio disc. But there are also old players that cannot read the mp3 format and therefore must be recorded as an audio CD.
From the above, you need to decide which disc you want to burn. I can only say one thing, that when recording an audio disc (item 2), about 20 songs are recorded on 1 disc.
Let's say your player reads mp3 format. It is necessary to click on the inscription in the "Data disc" menu, and then on the "OK" button. A new window will open, where the upper part of this window is designed to find music on your computer that needs to be burned to disk. The bottom part (empty) is needed to drag music there and to display it.
When adding music, pay attention to the strip that is at the very bottom. open window... She shows how much more free space on disk.
Let's repeat the steps, at the top you open the place where the music is located. Then you need to left-click on the tracks that you want to burn to disk, then, without releasing the mouse, pull them down.
After you have already dragged the necessary data that you want to burn to the disk to the bottom of the window, click the "Burn" button.
Note: in this moment we are looking at how to burn music to CD / DVD R, but you can also burn any data: videos, folders, files, etc.
After that, a window will appear in which you need to select the item how exactly you need to burn the disc. If you select the "Leave disc open" option, then after recording on this disc you can then add something else, in some programs that are designed to burn discs, this method is called "multisession".
If you click on the "Finalize disc" item, then it will not be possible to add anything to your disc. After you click on the appropriate item, the recording procedure will begin. Using this program as an example, you now know how to burn music to disc.
To understand what multisession is, I will give a small example. Let's say I have a file with a size of 150 mb., I burn it to a CD disk, which can be written to 700 mb ... , 300 mb.
Wait for the end of the recording. When writing files, it is advisable not to open or copy those files that are written to disk in real time. After your disc is burned, you can close the program. Now you have learned how to quickly and easily burn to a blank disc using CDBurnerXP. Everything is simple enough even for beginners.
Usually, tunes are burned to CD R discs, so I showed you how to burn music to CD R discs, although this procedure is no different from DVD discs.
| Mobile devices
All DVDs say 4.7 GB in size. But Nero sees it as 4.3 GB (4.7 billion). What is the problem? Or do you need to use overburn? What are the risks of using overburn? And I would like to know about the "+ \ -" technologies, in terms of which is better - DVD-R or DVD + R? Or at least what's the difference? Prompt links on these issues.
Gennady answers:
The problem is with the marketing of the disc manufacturers (as well as the manufacturers of hard drives), they think that 1 GB is 1000 MB, not 1024. The actual size of a DVD-5 disc: 4.37 GB - Nero says it’s right! Briefly about the "+ \ -" technologies: the minus is more suitable for recording DVD-Video, it is compatible with a large number of stationary DVD players (older players may not understand the "plus" format), and the plus is more suitable for recording data, because ... by its structure, it is less prone to errors and failures.
Khailov Konstantin Yurievich answers:
Everything is written correctly on the disk. Do not forget that there are 1024 kilobytes in 1 megabyte. This is where the difference comes from. Further. There is no fundamental difference between "+" and "-" technology. Previously, it was believed that "-" plays better on home DVD-players, while "+" has better recording quality (data is stored more reliably). Over time, manufacturers have improved these technologies and now there is no difference. So for an amateur. It is better not to use Overburn, because it often happens that this disc will be readable for you, but not on other slightly older drives. In general, the meaning of this technology is to reduce the length of the notch ( simple language speaking).
Neo answers:
Real size DVD disc is 4.7, but you can only write 4.44. The fact is that the recording of the system track, which is needed for its recognition in the DVD-player, requires space, and therefore the capacity of the disc from this is less ... On the question of plus or minus DVD. Plus or minus DVD. Let's start with the fact that there is no definite answer to the question, as, in fact, there is no answer to many other questions related to DVD. This is such a mysterious and enigmatic format. For example, the development of the DVD standard began in September 1995, and a group of 10 very large corporations was engaged in it: Hitachi, JVC, Matsushita, Mitsubishi, Philips, Pioneer, Sony, Thomson, Time Warner and Toshiba (all together they made this called the DVD Consortium, which then, in 1997, became the current DVD Forum). However, despite such a number of participants, the abbreviation DVD itself does not have an exact transcript. You can read it as a Digital Video Disc or Digital Versatile Disc. It is quite possible that this is caused by the competition that arose from the very beginning of the development of the format. The fact is that initially there were two groups of developers. One was headed by Sony and Philips and they worked on MMCD (Multimedia Compact Disc). The other included Toshiba and Time Warner, their development was called SD (Super Disc). It was only under external pressure that the companies merged into the aforementioned DVD Consortium and adopted a common DVD standard. Fortunately, the great battle Betamax vs. VHS was still fresh in the memory, and no one wanted two competing standards. Incidentally, the aforementioned external pressure was directed by IBM, for which special thanks go to her. Five types of DVDs were originally standardized: DVD-ROM, DVD-Video, DVD-Audio, DVD Recordable (DVD-R), and DVD RAM. DVD-ROM and DVD-Video appeared on the market in 1996 and still exist in the same form. However, of greater interest are the recorded DVD-R discs and DVD RAM. DVD-R discs originally entered the market in 1997 and were 3.95 billion bytes (or 3.68 GB) in size. In 1999, the DVD-R 2.0 specification was adopted, according to which the volume of the recordable disc increased to 4.37 GB and thus became equal to the stamped DVD-ROM. Since then, the DVD-R standard has remained largely unchanged. As for DVD-RAM, it was conceived as a rewritable format. DVD-RAM discs are based on the technology of recording with a change in the phase of the material (as in CD-RW) with some elements borrowed from the technology of magneto-optical discs. DVD-RAM entered the market in 1998 and for some time remained the only rewritable DVD. Initially, their capacity was 2.4 GB, but then also increased to the standard 4.37 GB. However, DVD-RAMs were quite inconvenient to use (in particular, due to the mandatory protective cartridge), so very soon they had an alternative in the form of DVD-RW. This format was developed by Pioneer on the basis of the already existing DVD-R and was originally called DVD-R / W or DVD-ER (that is, erasable). The first DVD-RW readers and discs appeared on the market in 1999 (at first they were sold exclusively in Japan and did not enter the world market until two years later, in 2001). Price DVD-RW disc was then about $ 30. The capacity of DVD-RW was from the very beginning equal to a standard DVD disc, that is, 4.37 GB. DVD-RW is based on the same phase change recording technology as CD-RW discs. However, with the advent of CD-RW as an alternative to DVD-RAM, the development of DVD standards has not ended. The fact is that initially all the above-mentioned formats were created specifically for video recording. Almost simultaneously with the advent of DVD-RAM, a group of companies that included Sony, Philips, Hewlett-Packard, Ricoh and Yamaha organized the DVD + RW Compatibility Alliance to develop and promote the alternative DVD + RW rewritable DVD format, respectively. Moreover, in order not to aggravate the conflict within the DVD Forum, this format was originally declared as intended solely for storing computer data. What caused the creation of the DVD + RW Alliance by companies that were already members of the DVD Forum? Mostly patent controversy. Virtually all of the major participants held their own set of patents for optical media technology. Accordingly, each participant tried to include their own technologies in the standard and exclude the technologies of competitors. Therefore, when the DVD + RW format did hit the market in 2001, it turned out to be incompatible with either DVD-RAM or DVD-RW. And this despite the fact that the basic technology used in them is the same - changing the phase of the working substance and a laser with a wavelength of 650 nm. In the wake of DVD + RW, the DVD + R write-once format eventually emerged. It happened in 2002, after which, in fact, the main confrontation between the two recorded formats + and - R / RW began. So what is the difference between these formats? But in general, from the user's point of view, nothing. There are undoubtedly technical differences in the principle of track tracking, addressing and marking. These differences make + and - drives completely incompatible with each other. But enough time has passed since the release of DVD + RW / DVD + R, so that all modern drives understand both, which is usually indicated in the specifications. As far as DVD players are concerned, older ones (and certainly those made before 2002) may not understand DVD + RW / DVD + R discs. But all modern technology reads both equally well. We can say that the standard with the "plus" is more modern and therefore better. But practice shows that in three years of coexistence, "plus" and "minus" have reached a certain parity. In addition, the next generation of optical discs is already on the horizon - BluRay, which in a few years will begin to replace DVD and finally transfer this issue to the category of academic.
Shurovik answers:
Remember, decimal GB is 1000 MB and binary is 1024. Divide 4.700.000.000 B by 1024 three times to get the capacity in binary GB. It turns out 3.78 GB. That's all right. For the home user, there is no difference between "+" and "-" drives. Unless "+" disks are read on old drives. And their write speed is higher.
Victor answers:
Go to www.cd4user.net. By the way, they have a good mailing list on these issues.
Vladimir answers:
Overburn cannot be used on DVD. 2-3 MB of additional weather on DVD will not do, and if more, then the disc will go to waste.
Vasily answers:
A small correction for Shurovik: divide 4,700,000,000 B by 1024 3 times - you get 4.38 GB.
What is CD Recordable?
Recordable CDs or CD-Rs are optical discs produced using a technology that allows the user to independently create their own CD in one of the electronic formats... In terms of its internal structure, a CD-R is a conventional compact disc, in which the reflective layer is made mainly of gold or silver film, and between it and the polycarbonate base there is a recording layer (dye layer) made of organic material, which changes the degree of reflection when heated. During the recording process, the laser beam heats up the selected points of the layer, which darken and stop transmitting light to the reflective layer, forming areas similar to pits. The production is based on the technology of making discs for write once (WORM - Write Once, Read Many), standardized by Philips and Sony and described in the corresponding documentation (Orange Book, Part II).
What contrast CD-R from a rewritable CD-RW disc?
Rewritable discs use an intermediate layer of organic film, which changes its phase state from amorphous to crystalline under the influence of a beam, and vice versa, as a result of which the transparency of the layer changes. The fixation of changes in state occurs due to the fact that the material of the recording layer, when heated above the critical temperature, passes into an amorphous state and remains in it after cooling, and when heated to a temperature significantly below the critical temperature, it restores the crystalline state. CD-RW discs can withstand thousands to tens of thousands of rewriting cycles. However, their reflectivity is significantly lower than stamped and single-shot CDs, which makes them difficult to read in conventional drives. To read CD-RWs, a drive with Auto Gain Control is formally required, although some conventional CD-ROM drives and consumer players can read them on a par with regular discs.
What are they used for? CD-R disc and?
The same information structure is organized on CD-R as on stamped discs - TOC and a set of tracks different types... It allows the user to create CDs of all industry standards, including audio discs (CD-DA), video discs (Video CD), data discs (CD-ROM), photographs (Photo CD). CD-R discs allow you to store a fairly substantial amount of information: up to 700 MB of data, which corresponds to 80 minutes of high-quality stereo sound.
What explains the different color of the working surface of the discs?
Various materials for the recording and reflective layers. As a recording layer for CD-R discs, the most common organic compounds known under the code names "cyanine" (Cyanine) and "phthalocyanine" (Phtalocyanine). Cyanine has a blue (cyan) color (from which the name of the material is derived, which has nothing to do with cyanides - a chemical derivative of hydrogen cyanide) and is characterized by average resistance to light irradiation and temperature changes. Phthalocyanine has a light green color and is more resistant to external influences.
Gold and silver are used as reflective materials, less often aluminum and alloys. Accordingly, the working surface of the disc with a reflective layer of colorless metal has the color of its recording layer - light green for the combination "phthalocyanine-silver".
What do you need to create your own disc yourself?
In order to record a disc on your own, you must have a blank CD-R disc equipped with a CD recorder (CD Recorder) and the corresponding software.
What is speed CD-R recording?
The term "write speed" defines how quickly data can be written to a CD-R disc. Marking 2x, 4x, 6x, 8x, 12x, 16x, 20x, 24x, 32x, 40x, 48x shows how many times faster the device writes data compared to the single-speed reference. One speed is understood as a data transfer rate equal to 150 Kb / s. Thus, the marking "2x" means that data can be written at a speed of 300 Kb / s, respectively "8x" - 1.2 Mb / s, and "16x" - 2.4 Mb / s. It must be taken into account that real speed may differ depending on the selected recording format, as data is recorded in 2 "048 bytes per block mode, and audio information is recorded in 2" 352 bytes per block mode. That's why real time recordings of one complete disc may differ slightly depending on the format. Typically, CD-ROM drives are labeled with a single number indicating which maximum speed data can be read. In this case, the fastest format for reading is indicated - CD-ROM Mode 1, moreover, moreover, when measured on the outer perimeter of the disk. CD recorders are marked with three digits: the first is the write speed CD-R discs, the second is the rewriting speed (CD-RW discs), the third is the reading speed. Accordingly, marking 16x10x40 for a CD recorder means that it is capable of writing CD-R discs at 2.4 Mb / s, CD-RW discs at 1.5 Mb / s, and reading discs at 6 Mb / s. If the marking consists of two numbers, it means that such a drive cannot work with CD-RW discs.
What is disc-at-once (DAO) disc burning - disc at once?
This is a recording mode when a disc is recorded immediately from beginning to end, without interruptions. Those. the laser beam turns on at the beginning of the disc recording, and turns off only at the end of the recording. First, special information is written to the disk, marking the beginning of the recording (lead-in), then the data itself, and at the end the final information (lead-out). As a rule, the DAO method is preferable if the disc is later transferred to the factory for replication, and the recordable CD-R is the master disc. Recording in DAO mode allows you to avoid bundles of input (run-in) and output (run-out) blocks, which are associated with multisession recording by mastering equipment and make the disc unsuitable for making a matrix from which the circulation will be produced.
What is track-at-once (TAO) disc recording - track at once?
The TAO recording mode allows you to record a disc not immediately from beginning to end, but in several passes: initially, you can record one audio track (track) on a disc, then another, and so on. Accordingly, as many tracks are recorded on the disc, the laser beam will be turned on and off as many times during recording. The switching on and off of the laser is perceived by sound players as a pause between tracks lasting 2 seconds. It should be noted that an audio disc recorded in this way can only be read on a regular CD player after the table of content (TOC) has been written. After TOC has been recorded, it is not possible to add tracks to the disc.
What is session-at-once (SAO) disc burning - session outright?
The SAO recording mode is usually used when recording the CD-Extra format, a format that combines the audio part (CD-DA format) and the software part (CD-ROM format) on a disc. When recording in SAO mode, the laser beam turns on at the beginning of recording the audio part, turns off at the end of recording tracks, then turns on at the beginning of recording a part of data and turns off at the end of the recording. The TAO mode is also applicable for preparing CD-Extra format discs. In this case, during the recording of the audio part, the laser will be turned on / off as many times as there are tracks on the disc.
What is multisession recording mode?
A multisession is a recording mode that allows you to append a CD, that is, add new information to the previously recorded. Each session contains a record of the beginning of the session (lead-in), then the data itself and the final information about the session (lead-out). Unlike disc-at-once recording or injection-molded CD, there can be up to 99 such sessions on one disc.
When recording in multisession mode, information about the structure of previous recordings is copied to the new session and can be corrected. Thus, when recording in multisession mode, the user can destroy information about the structure of already unnecessary or obsolete records without including it in a new table of content (TOC - table of content). This means that it becomes possible to "erase" unnecessary information from the CD, although in fact, it physically continues to remain on the disk and can be restored using a special software.
The disadvantage of the multisession mode is that disk space is wasted, as it separates one session from another. About 13.5 MB (6 "750 blocks) is lost each time. The more sessions recorded on the disc, the more space is wasted for the session separators. Also, some older CD-ROMs (usually before 1994) cannot read multisession discs.
What is finalization and fixation of a CD-R disc?
Finalization is the process that completes the recording of a session, i.e. if a session is written to disk, then it must end with a finalization record representing the table of content (TOC) of the session. If subsequent sessions are recorded on the same disc, then each of them must end with a finalization recording. Finalization is required in order for the CD-ROM drive to read the CD. If the CD is finalized in its entirety, or it would be more correct to say fixed, then it is impossible to add sessions to it, even if there was free space on the disk.
How is audio CD recording done?
Audio discs (CD-DA) are recorded from a set of audio files in the RIFF WAVE format (extension .WAV), the file format is stereo, 16-bit, 44.1 kHz. Each file can be recorded to its own track (TAO mode), or all files can be recorded to one track (DAO mode). In TAO mode, by recording pre-gap zones between tracks, physical gaps appear, audible as two-second pauses in the sound; in DAO mode, files are written end-to-end and produce continuous sound. Regardless of the recording mode, each file is formatted as a separate " sound track", the change of which is marked with the subcode Q, and the addresses are recorded in the TOC.
Since the track size is always a multiple of the frame size (2352 bytes), sound files are rounded up to an integer number of frames by adding zeros (silence) at the end. In the case of continuous sound program obtained by cutting a large sound file multiple parts and recording them in DAO mode, such rounding can lead to noticeable noise.
Why did the drive eject the disc before it finished recording?
The most reliable recording mode is with the preliminary construction of a disk image (image), which is formed in a temporary file before recording is turned on, and then as evenly and consistently as possible is transferred to the disk. In this mode, if there are no other reasons that reduce the performance, practically no performance margin is required.
If the spontaneous interruption of the recording, carried out using this regime, nevertheless happened, then the probable reason most likely could be the following:
There are too many bus processes running on the computer. Most often these are resident antivirus software that track any access to disk drives. It is recommended to deactivate such programs before starting to burn a CD-R disc.
Computer performance is too slow. It is recommended to use utilities to determine the maximum possible speed records. These utilities are usually included with CD-R burning software.
Recorder malfunction: All disc recorders have a limited lifespan and eventually stop working properly.
Disc defects: often found on discs without a label from an unknown manufacturer, or formed on the surface as a result of careless handling and storage without packaging.
Why does the computer "slow down" when recording?
System performance can be reduced by:
Concurrent applications, including system processes such as memory or disk optimizers, file servers, printers, databases, or Email hosted on the recording machine when accessed over the network;
The presence of a passive connection to the network, in which received packets can trigger the triggering of system processes;
Or screen savers, which are automatically activated in the pauses of the user's work;
Excessive fragmentation of source disks, increasing the disk positioning overhead;
Flaw random access memory that causes pumping (swapping) to disk;
Dynamically changing the size of the file cache by the system; in the presence of speed-critical applications, it is recommended to set a constant size (System.ini file, section, MinFileCache / MaxFileCache keys, values in kilobytes);
Frequent system interrupts - from a modem, mouse, printer and other devices;
Operation of other CD-ROM drives (in Windows 95 this is one of the most suboptimal subsystems) or floppy drives;
Finding the recording drive on the same cable with the device from which data (files or image) is received during the recording;
Inappropriate parallel port mode (SPP / Normal instead of EPP) for external CD-R with appropriate adapter;
Frequent and long recalibration of some hard drive models.
If all of the above reasons are eliminated, but the performance is still not enough, all that remains is to reduce the write speed. If the static performance of the system is sufficient for the selected write speed, the process can still be disrupted by short-term data delays as a result of a system crash when starting programs, recognizing inserted floppy disks and CDs, rereading bad sections on the original media, in case of emergency termination of parallel programs, and etc. The safety margin in this case can be roughly estimated by the size of the CD-R buffer, dividing it by the write speed and getting the time for which the data stream can occasionally be painlessly interrupted.
If you burn a 1-16x CD-R disc at 2x and 16x speeds, which copy will be better?
In general, there is no dependence of the write speed on the read speed. Therefore, if the disc is intended for recording in the speed range from 1x to 16x, then you can choose any convenient speed. However, if you go deeply into this issue, then the higher the write speed of the disc, the potentially higher its quality. Rather, with an increase in the write speed, there is a chance to improve several indicators of the disc, including one of the main ones - BLER.
The abbreviation BLER stands for "Block Error Rate" and denotes the frequency of occurrence of blocks of information that have erroneous characters (bytes) detected at the first level of error detection and correction C1. BLER is a parameter that well reflects the quality of a disc as a whole, as it depends on many factors that appear during the manufacturing process of discs.
The Red Book standard defines the maximum BLER<= 220 блоков в секунду. При этом вычисляется среднее значение при измерении на интервалах по 10 секунд. В зависимости от BLER диски делятся на несколько классов (grade) качества:
Grade A (BLER< 6) - диски высокого качества;
Grade B (BLER< 50) - диски хорошего качества;
Grade C (BLER< 100) - диски удовлетворительного качества;
Grade D (BLER< 220) - диски, которые можно использовать, но чтение информации с которых затруднено или велика опасность выхода диска из строя (потеря информации).
Potentially, CD-DA discs can have a higher BLER than CD-ROM discs (it is no coincidence that Red Book allows a fairly high BLER - up to 220). However, the lifespan of an audio disc is usually incomparably longer than a disc with programs - music programs are much less susceptible (or not at all) to obsolescence than modern software. A high BLER indicates not only the danger of data loss, which is incompatible with the long life of the disk, but also about possible reading problems in some drives. Therefore, in practice, the leading CD manufacturers try to manufacture their products with BLER< 50 (Grade B). CD-R технология позволяет легко наладить производство тиражей с BLER < 20 без дополнительных затрат. А если применять только диски известных производителей, то 100% выход дисков высшего класса качества (Grade A) практически обеспечен.
I burned a disc at 2x and it can be read everywhere with me, but a disc recorded at 16x cannot be read anywhere, even on a "native" recorder. What's the matter here?
The aforementioned about some improvement in quality when recording at a higher speed is true only in the case when working equipment is used and the CD-R disc is really intended for recording at high speed.
Manufacturers of high-speed (12x or more) recorders give recommendations on the type of computer and the type of CD-R to be used in order for the disc to be written successfully. If you follow these guidelines, all discs recorded at different speeds will be nearly identical, regardless of write speed. But vendors often claim that their drives are 16x certified, when in fact they are not. In addition, if you have a working recorder (in this regard, the drive is simply "loose") or a recorder installed in a computer case, the cooling of which does not ensure its normal operation, the recording results may not be predictable. That is why, with a serious approach in studio conditions, the quality of the recorded disc is necessarily checked using a CD / CD-R disc analyzer (for example, Clover QA-201D).
Why does the writing software recognize the recorder as a CD-ROM?
Most likely, there are no drivers for this recorder. You need to install them.
Why do some CD-R burning software show an underestimated maximum write speed?
The reason may be the lack of a driver for the drive or an outdated software version that does not support high write speeds. Sometimes it is necessary to "flash" the BIOS of the drive.
Will discs burned at 4x or 8x speeds be read on 20x or 40x speed CD-ROM drives?
Yes, they will. The write speed is independent of the read speed and vice versa.
What's the difference between 74 and 80 minute discs? What drives are the information stored more reliably?
Originally, the Red Book audio CD standard called for CDs that could store 74 minutes of stereo sound. This corresponded to a data volume of 650 MB. Therefore, after CDs began to be used for storing computer data, the question of the maximum capacity did not arise - the same value of 650 MB was adopted. Then the same capacity migrated to the standard CD-R discs.
However, over time, the gigantic value of 650 MB has ceased to be not only gigantic, but simply large. A desire has arisen to increase the capacity of disks for the needs of storing digital video and data. But by the time the question was posed in this way, there were already hundreds of millions of different CD-ROM drives (CD-ROMs, audio and video players) around the world that the newer, larger discs were supposed to be compatible with. The developers took a relatively simple path: they simply "rolled up the spiral" (the path along which the laser beam moves from the center to the edge of the disc) of the injection dies from which CD-Rs are cast, thus obtaining additional capacity. At the same time, compatibility problems did not arise, since the accuracy inherent in the reading drives made it possible to track a "tighter" spiral. At the same time, however, all the leading manufacturers of CD-R discs honestly warned users about some non-standard novelty. But the chase for extra capacity didn't end there. There are discs with a capacity of 90 and even 99 minutes! In the latter case, the spiral was "rolled up" so "tight" that the CD-Rs made in this way were recorded and read only by selected drive models. So, the default is 650MB of disk space. Practice has shown the reliability of using 700 MB disks. To store data on larger disks means to endanger the receipt of the necessary information at the right time, due to the possible incompatibility of the reader and media.
Still I tried to record a 90 minute disc. For some reason, the recorder's drive won't accept it?
Not all recorders are capable of recording discs with a capacity of over 700 MB. Therefore, when recording such discs, it is necessary to use software and a recorder that support a special mode - OverBurning.
They say that over time, information from some CD-R discs ceases to be read. What is the reason, and can you be sure about the readability of my discs?
The largest "damage" that caused a lot of trouble was recorded in the early 90s. The reason was mainly due to two characteristics of the technology for producing compact discs. When reading, the laser beam is reflected from the surface of a special layer. The reflectivity of the laser beam is very important for both CD-ROM drives and the discs themselves. The first problem was the filling of the edges of the disc with varnish. On discs with poorly varnished edges, oxidation affected the reflective layer, which caused problems with reading the discs.
The second problem was caused by the use of paint applied to the outer surface of the disc: it remained chemically active even after being treated with ultraviolet rays. The paint interacted with the reflective layer, which also caused problems with reading discs. CD-ROM manufacturers have taken into account both of these nuances and have made appropriate changes in the production process and material selection.
Disc makers have learned a good lesson from this as well. Please be aware that in-line production of CDs in the factory by injection molding, aluminum is used for the reflective backing, which can corrode over time. In the production of CD-R discs, noble metals such as gold and silver are used for these purposes, which significantly reduces the risk of corrosion and oxidation.
Today, many counterfeit ("pirated", as a rule, no name) CDs are manufactured at factories in violation of the technology. This often leads to the fact that drives fail over time.
What software should you use to burn your CD-R discs?
Indeed, there are a large number of recording software available today: Easy CD, CD Creator, Nero, CD Publisher, Direct CD, WinOnCD, CDRWin (Windows); UniteCD, Disk Juggler, RSJ (OS / 2), etc., the range of application of which is very wide: from primitive copying to professional multi-format disc development. We believe that NERO 5 (Ahead Software) and WinOnCD (versions from 3.7) will be the most successful for most users in terms of ease of use and efficiency.
Why might the files be too small to fit on the disk?
As with magnetic disks, information on CDs is written in blocks - usually 2048 bytes - and each file occupies an integer number of such blocks. On average, the additional consumed volume is approximately equal to half of the block for each file, but this is precisely determined only at the stage of building the image. In addition, the total number of files, directories and the structure of their names affects the size of the table of contents area. Some programs, such as Adaptec Easy CD Creator), calculate the actual volume required in advance. To do this, you need to wait until the optimization is complete, but the total number of blocks may still not be entirely accurate. Others are limited to only summing file sizes. And when the data volume is close to the limit, in the "on-the-fly" recording mode, there may not be enough disk space. As a result, the disc will be damaged. In such cases, it is recommended to first build an image of the recordable disc. The number of blocks required to write an ISO image can be obtained by dividing the image size by 2048 for Mode 1 (CD-ROM) or 2352 for Mode 2 (XA), plus 300 blocks for Pregap / Postgap, plus another 2-5 blocks for minor inaccuracies.
How to copy a disc as accurately as possible?
This is best done either by direct frame-by-frame copying from disk to disk, or by first capturing the disk image to a file. The first method is faster, but requires two drives and is fraught with write failures in the event of read errors and uncalibration of the reading drive. The second is more reliable, it can be performed on a single drive, but it requires significant disk space (up to 650 MB for CD-ROM and up to 780 MB for CD-DA and other disc formats).
Only drives capable of precise positioning and frame joining are suitable for exact copying of CD-DAs.
An intermediate disk image in a file can be obtained, for example, using the SnapShot program from the DAO package. Adaptec CD Copier does not allow creating an image in an "honest" way, however, when using one drive, it is formed in a specified directory as a .TMP file (ISO format), from where it can be renamed after the disc reading phase is completed.
Direct copy or copy-over-image allows you to copy bootable discs as well as a range of non-standard format discs. However, one should not confuse the frame-by-frame reading of the disk image with its rebuilding, which is done, for example, by Adaptec Easy CD Creator by the command "Create Disk Image" - in this case, the TOC is re-formed and the files are placed on the disk, as a result of which the disk is a copy will coincide with the original only in content, but not in structure and format.
How reliable is CD-R discs versus stamped discs?
Since the reflective layer of CD-R discs is usually made of gold and silver, which are less oxidized than aluminum in most stamped discs, they tarnish more slowly than normal discs. However, the material of the CD-R recording layer is more sensitive to light and also susceptible to oxidation.
The most optimistic estimate of the lifetime of phthalocyanine-based discs is about 100 years, however, the actual figures for most modern discs (cyanine and other materials) may be lower, depending on storage conditions, frequent use and transportation.
Multi-colored CD-R discs and discs with a colorless active layer are on sale. How do they differ in quality from regular (familiar) CD-R discs?
Shades of polycarbonate and active dye, which determine the overall color of the working surface, do not affect the quality of recording and disc use, all other things being equal.
 Backlash of the volume and power buttons on the iPhone - a marriage or not?
Backlash of the volume and power buttons on the iPhone - a marriage or not? The network card does not see the cable: instructions for solving the problem What to do if the Internet cable does not work
The network card does not see the cable: instructions for solving the problem What to do if the Internet cable does not work StoCard and Wallet: discount cards from the application
StoCard and Wallet: discount cards from the application