Archive file attribute. How do I select a double-click command? What does the System attribute mean?
ATTRIB command used to change the attributes of one or more files. In order to view the attributes of a particular file, you must click on it right click mouse and select the item properties. For example, let's create on disk "C" text file"Atribut.txt". Right-click on this file and in context menu select the item "Properties".
Read-only file attribute prohibits making changes to it. If this attribute is set (there is a check mark in the “Read-only” field), then the user can open this file, write information to it, but when trying to save, a message will appear that these actions require administrator rights. Although setting this attribute does not allow making changes to the file, this file can be deleted, copied, moved to another location, renamed.
Hidden file attribute makes files invisible in explorer. For example, if you set this attribute (check the "hidden" box), click "Apply" and "Ok", the file will disappear from the explorer (become invisible). To display hidden files in Windows7, you can do the following: go to Explorer, click Organize, then Folder and Search Options, then View. Here you need to check the item "Show hidden files, folders and disks ". Then click "Apply" and "Ok".
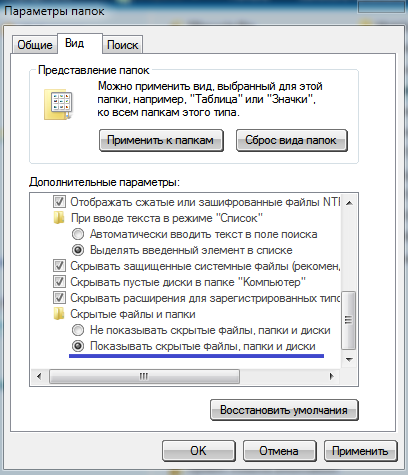
The System attribute is automatically set by the operating system for all important Windows system files. It is impossible to change this attribute through the file properties, since there is no such field (this can be done via command line). System files are automatically set to "Hidden". To display system files in Windows7, you can do the following: go to Explorer, click Organize, then Folder and Search Options, then View. Here you need to check the item "Show hidden files, folders and drives" and uncheck the box next to the item "Show protected system files". Then click "Apply" and "Ok".
![]()
As a result, you will have several new files on the C drive (IO.SYS, MSDOS.SYS, etc.). It is not recommended to enable the display of system and hidden files and folders. there is a high risk of moving or deleting an important file.
When you press the "Other" button in the file properties, a window will open additional attributes.
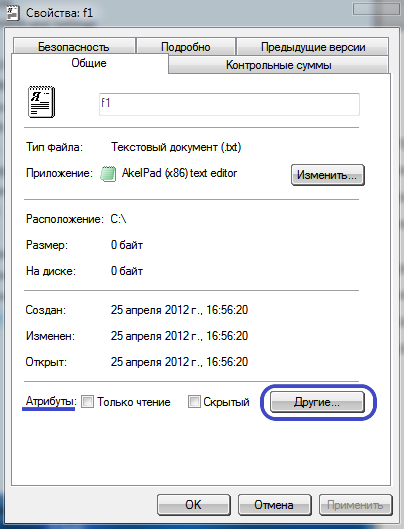
Archive attribute set in the "File ready for archiving" item. If this item is ticked (as in Fig, below), then this file It has archive attribute... The archive attribute is required to create a backup copy of the file when archiving. If the attribute is set, then the program Reserve copy will create a copy of this file and reset the attribute. Accordingly, at the next backup copy of this file will not be made. the archive attribute has been cleared, which means that the file has already been backed up. However, when changes are made to this file, the operating system will automatically set the archive attribute so that a copy of this file will be made the next time it is backed up.
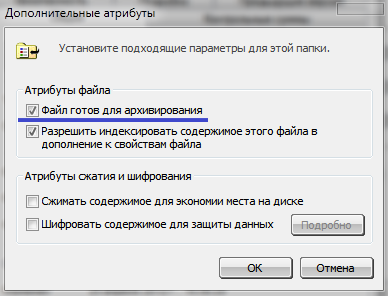
The "indexing" attribute. Above the "File ready for archiving" item is the "Allow indexing of the contents of this file in addition to the file properties" item. By default, this attribute is set for all files. Indexing is necessary for more quick search desired files on your computer. During indexing, the operating system creates special files where it puts the index. When searching desired file it is not searched for on the hard disk, but in the index. Operating system constantly (in background) indexes the most common files.
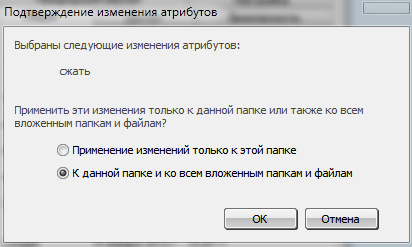
Attribute "Compress content to save disk space" required to compress files and folders. Setting this attribute works by analogy with various archivers (for example, WinRaR). Compression using the attribute does not require unpacking files when working with them, however, the compression ratio is not as high as that of archivers. The names of files and folders with this attribute set are highlighted in blue. When setting this attribute to a folder, you will be prompted to apply compression only to the folder, or to the folder and all its subfolders.
The quality of compression can be viewed in the "properties" of the folder, where the size of the folder will be indicated, and how much space this folder takes on disk.
Attribute "Encrypt content to protect data" allows you to encrypt a file or folder. When this attribute is set, the file or folder will become available only to the user who is logged in with account at which the attribute was set. Other users will not be able to view encrypted folders and files if they do not have a password. The password is generated during the first encryption. Windows will prompt you to create backups your encryption certificate and encryption key. You will need them if you are logged in with a different account. You will need to enter a password to access encrypted folders and files. If you move an unencrypted file to an encrypted folder, it will be automatically encrypted. All encrypted folders and files are highlighted in green.
ATTRIB command makes it possible to change the attributes of a file through the command line. The command has the syntax: ATTRIB [-A] [+ A] [- S] [+ S] [- R] [+ R] [- H] [+ H] [- I] [+ I] [Disk:] [ Path] [File name]. The letters A, S, R, H, I mean respectively: archived, system, read-only, hidden, non-indexed content. The "+" and "-" signs mean setting and unsetting the attribute, respectively.
For example, will create a file "atribut.txt" on the C drive. By default, this file when created has only the archive attribute and the "indexing" attribute set. Let's change the attributes of this file by setting the "Read-only" attribute and unchecking the "archived" attribute: attrib + r –a atribut.txt
As a result, the archive attribute will be removed from the "atribut.txt" file and the attribute "Read Only" will be set.
ATTRIB command / S switch indicates that file attributes are changed not only in the specified directory, but also in all subdirectories. For example, let's create an "atribut" folder on the D drive, inside this folder, create two more folders "atribut1" and "atribut2". Let's create several files in each of these folders. Then the command attrib + r -a d: \ atribut \ *. * / s will change the attributes of all files located in the "atribut" directory and in its "atribut1" and "atribut2" subdirectories.
The ATTRIB command applies not only to files, but also to directories. For example, attrib command+ h d: \ atribut will set the "Hidden" attribute for the "atribut" folder.
Hidden and systemic Windows files
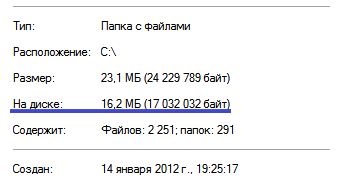
Today we will talk about hidden and system files in Windows, as well as how to work with them. Take pagefile.sys as an example. We know for sure that it should be located at the root of the system drive C, but if we open Windows Explorer, we will not see this file there.
The fact is that the operating system hides some important system files, protecting them from overly curious users. For comparison, this is how the explorer looks like with the display of hidden / system objects enabled.
Attributes
Special metadata is responsible for displaying files and folders in Windows Explorer - attributes... Here is a description of some of them:
H- hidden (hidden). Hides the file, making it invisible in Windows Explorer;
S- system. Tells the OS to treat the file as a system file;
R- read-only. Protects the file from modification, making it read-only;
A- archive. Indicates that the file has been modified since the last backup and is used by backup systems;
I- indexed. Indicates that the contents of the file should not be indexed;
D- directory (directory). Indicates that the object is a directory;
L- link. Indicates that the object is a link.
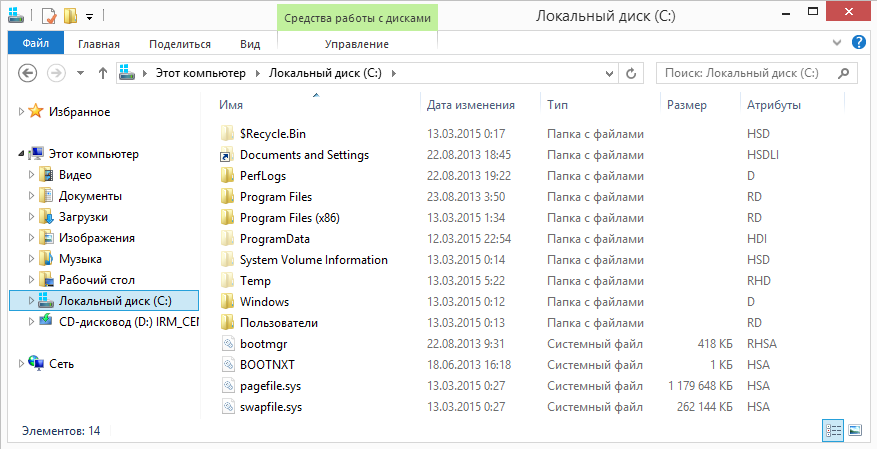
Explorer can show file attributes in the same way as any other properties (type, size, etc.). To do this, click right key mouse on the column name and select the "Attributes" item in the context menu.
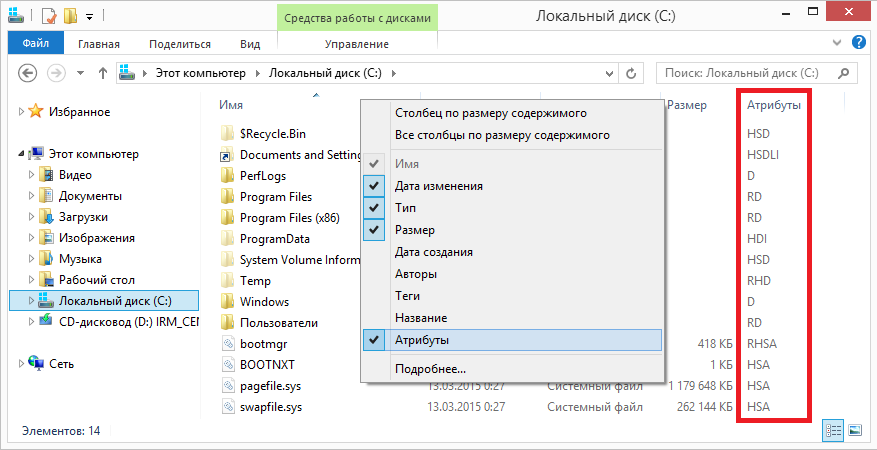
As you can see, all hidden files have H or HS attributes. It is these attributes that affect whether the file will be displayed in the explorer or not. Accordingly, you can see hidden files in two ways - by enabling them to be displayed in Explorer (or another file manager) or by clearing these attributes.
Enabling the display of hidden files
The settings for showing hidden files and folders in Windows Explorer are found in the Folder options snap-in in Control Panel. You can quickly open the snap-in by pressing Win + R and entering the command control folders.
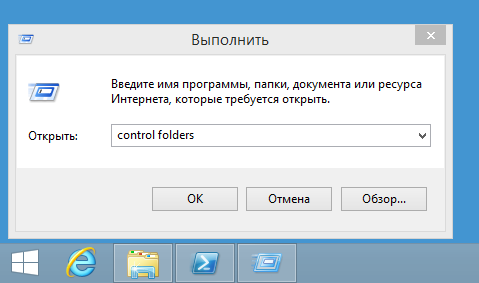
To show hidden files / folders (attribute H), on the "View" tab, in the "Hidden files and folders" field, set the switch to the "Show hidden files, folders and drives" position. To display hidden system files (with HS attributes), you must additionally uncheck the "Hide protected system files" item.
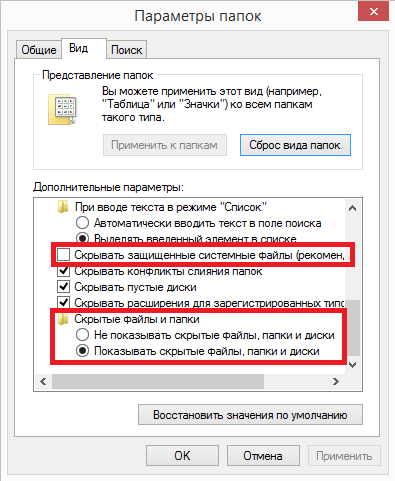
You can also open the Folder Options snap-in directly from Explorer. In Windows XP and Windows 7 (as well as Windows Server 2003 \ 2008 \ 2008R2), to do this, select the "Folder Options" item in the "Tools" menu.
Note. In Windows 7, the menu is hidden, for its appearance you need to press the key Alt.
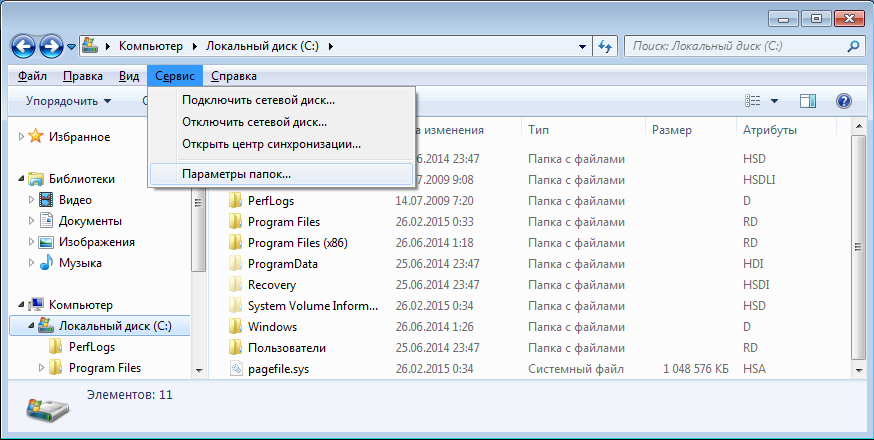
In Windows 8 \ Server 2012, the Ribbon appeared in the Explorer, on which the most needed options were moved. You can quickly turn on the display of hidden files by going to the "View" tab and checking the "Hidden items" item, and you can open the basic snap-in by clicking the "Options" button.
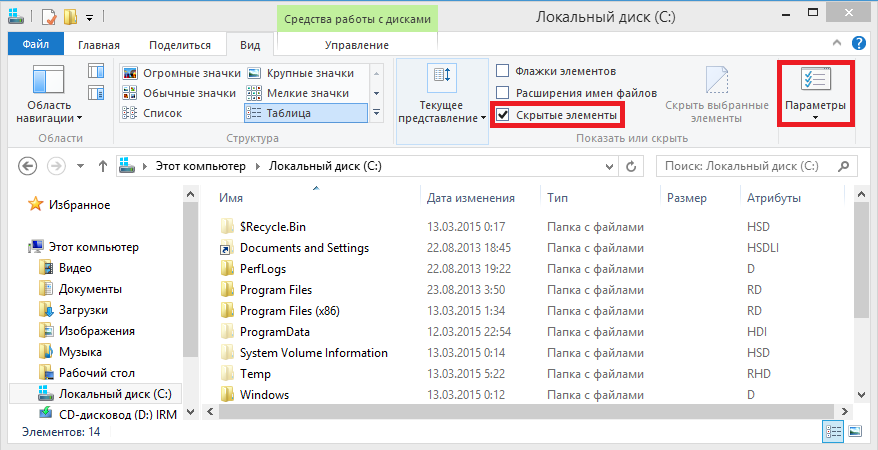
For those who are not looking for easy ways 🙂 it is possible to control the display of hidden \ system files in the explorer with the help of direct editing of the registry. To do this, in the HKCU \ Software \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ Explorer \ Adwanced section, there are two parameters of the Dword type:
Hidden- is responsible for displaying hidden files (0 - do not display, 1 - display);
ShowSuperHidden- is responsible for displaying protected system files (0 - do not display, 1 - display).
If you are using alternative file managers such as FAR or Total commander, then they also have the ability to enable the display of hidden folder files.
In FAR, in order to see hidden content, press F9, go to the "Options" - "Panel settings" section of the menu and check the "Show hidden and system files" item (in the English version Options - Panel settings - Show hidden and system files ). However, most likely nothing of this will be needed, since the display of hidden files is enabled by default in FAR.
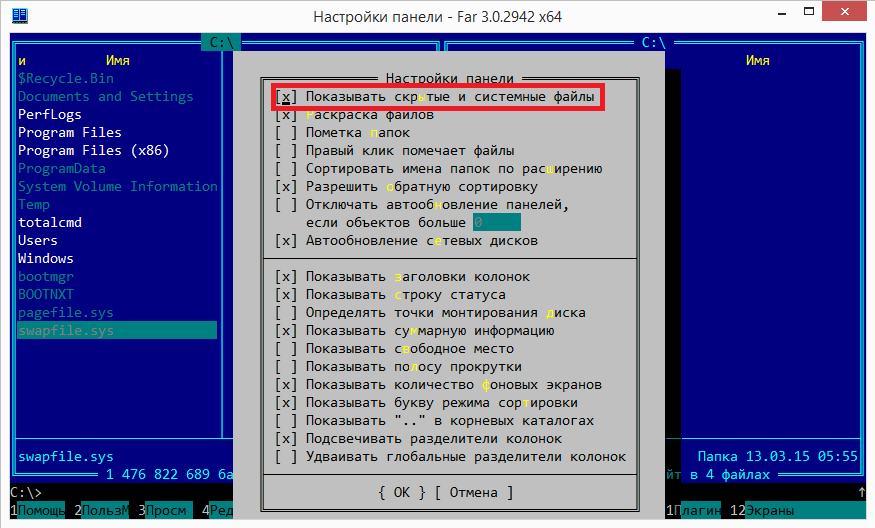
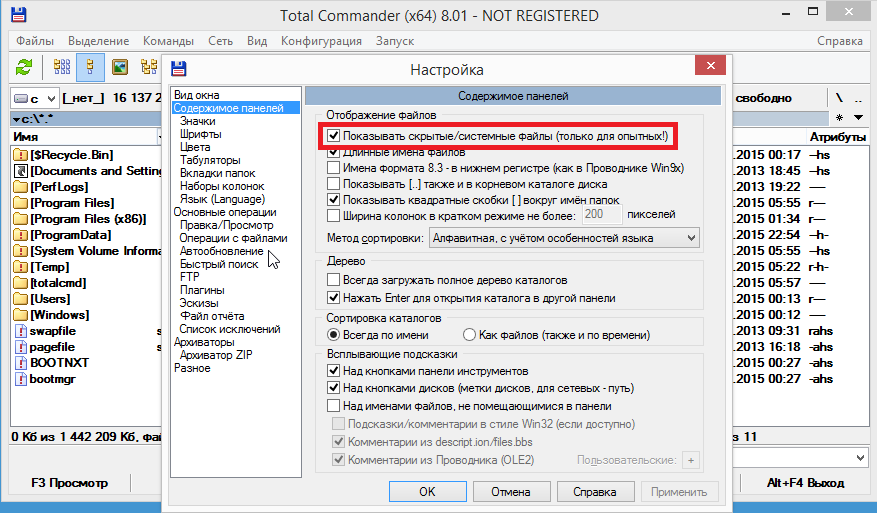
In Total Commander, open the menu "Configuration -" Settings "-" Content of panels "and check the item" Show hidden / system files "(in English. Configuration - Options - Display - Show hidden / system files). Interestingly, Total Commander (unlike FAR) does not enable the display of hidden files by default, and besides, there is a warning in the setting (only for experienced!).
Modifying Attributes
Since the visibility of an object is determined by its attributes, we move on to ways to change them. Some attributes of files / folders can be changed using Explorer. For example, to make a file hidden, just open its properties and check the box next to the corresponding attribute in the "Attributes" field.
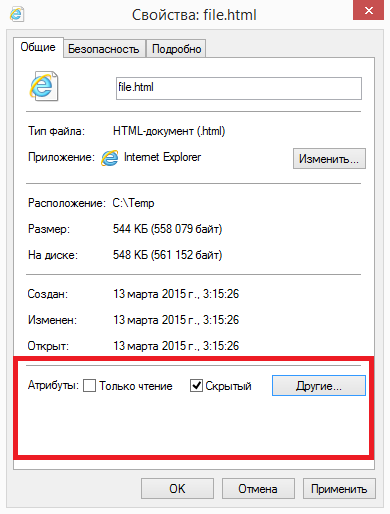
There is also a command line utility for managing attributes in Windows. attrib.exe, which can show and change any attributes of the object. The utility syntax looks like this:
attrib [(+ R | -R)] [(+ A | -A)] [(+ S | -S)] [(+ H | -H)] [FileName]]
+
- setting an attribute;
—
- removal of an attribute;
/ S- apply the command to all files in the current directory and subdirectories;
/ D- apply the command to directories;
/?
- help output.
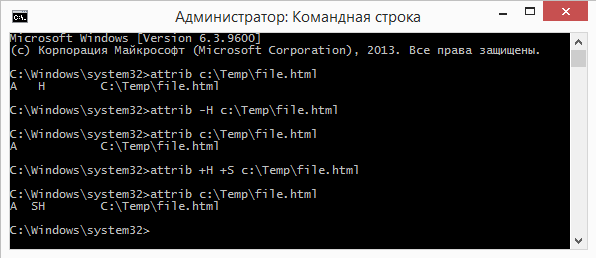
For example, the following command will print the attributes of a file:
attrib ″ C: \ Temp \ file.html ″
This will remove the hidden attribute (-H) from the file:
attrib -H ″ C: \ Temp \ file.html ″
And so let's make it hidden (+ H) and system (+ S):
attrib + H + S ″ C: \ Temp \ file.html ″
Note. Pay attention to the order of operations. The point is that the h and s attributes can only be added together. For example, if you try to add a system attribute to a hidden file, an error will be generated. Therefore, you must first remove the attribute (-H), and then add both attributes (+ H + S).
In Total Commander, to change the attributes, select the file \ folder, then go to the "Files" menu - "Change attributes" and in the "Change attributes" field, put a checkmark in front of the required attributes.
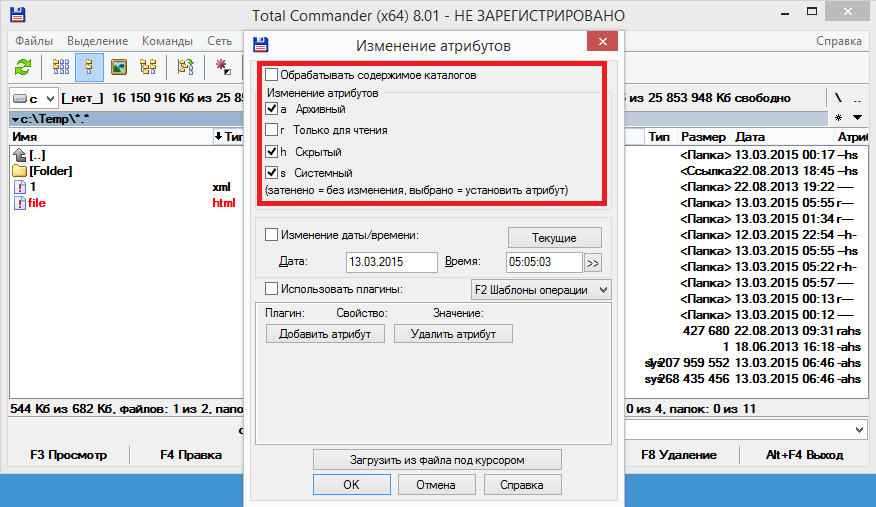
In FAR, it is about the same, only the window for changing attributes is opened with the key combination Ctrl + A(or through the F9 menu - Files - File attributes).
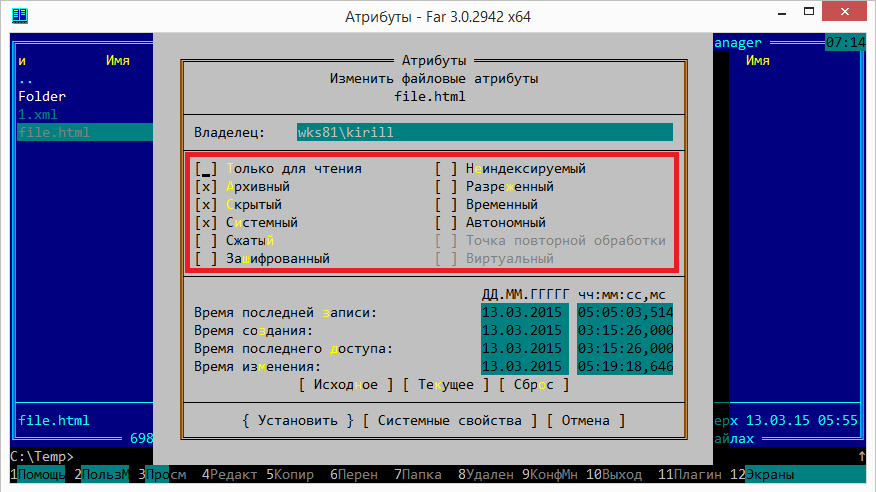
Change prohibition
Let's talk a little about prohibitions. For example, you want to prevent users from changing the settings for displaying hidden files. This can be done using the registry parameter CheckedValue located under HKLM \ Software \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ Explorer \ Advanced \ Folder \ Hidden \ Showall. By default, its value is 1, and if you set it to 0, then enabling the display of hidden files in the folder properties stops working.
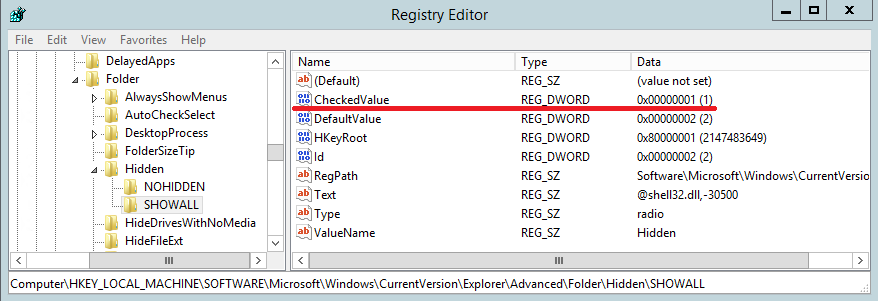
Well, and a more drastic way is to prohibit opening the Folder Properties snap-in. To do this, in the HKCU \ Software \ Microsoft \ Windows \ CurrentVersion \ Policies \ Explorer section, create a parameter of the Dword type with the name NoFolderOptions and assign it the value 1. You can disable the prohibition by setting the parameter NoFolderOptions value 0 or deleting it from the registry.
Note. Both of the above methods work fine, but starting from Windows 8 \ Server 2012, you can change the visibility of hidden files in Explorer using the "Hidden items" checkbox, which is not affected by these settings. Also, prohibitions do not affect the ability of FAR and Total Commander to show hidden objects.
Conclusion
As a conclusion, let me remind you once again that the hidden and system attributes in no way protect files and folders from being changed or deleted, but only affect the visibility of objects in Windows Explorer. It is impossible to fully protect a file using attributes, so other protection mechanisms, such as NTFS rights, encryption, RMS service, and other similar things, must be used to protect important files along with the attributes (or instead of them).
Today I would like to pay attention to what the file attributes are and how to change the file attributes. Before asking myself why I was drawn to such subtleties, let's do one little experiment. Ask someone you know (in ICQ, Skype, social network) one question - "File?".
You can write this in the chat window, by the way, if you do not know how to install Skype, you can read the article: "". So, I bet that in response to the question "File?", 75% of people will answer "Which one?", Hoping to get more information about which file you are interested in. You can explain in detail to your interlocutor exactly what you mean. But in order for the operating system of your computer to receive such information, file attributes are used. Therefore, it will not be superfluous to pay attention to them.
Why are file attributes needed
If you say simply, then this is a parameter that tells the operating system what actions it can take with the file.
There are four main parameters for each file:
- R -readonly (read-only)
- S - system (system)
- H - hidden (hidden)
- A -archive (archived, requiring archiving)
R -readonly ... This parameter, which translates into Russian as "read-only", is responsible for the potential for editing. If its value is "yes", then any attempts to make changes will lead to nothing. The OS simply will not provide an opportunity to save them. This is very useful if several users have access to the file, for example, in the case of shared files on a local network.
S -system ... This parameter unambiguously indicates to the OS that this file is a system file and its presence is required for the stable operation of the application or system. Since the presence of these files is critical when trying to move or delete, Windows will persistently ask you if you really want to do these operations.But, you must remember about the existence of viruses, if a file is marked as a system file, then this is not a reason to think that this is so.
H -hidden ... This parameter is responsible for the visibility of the file to users. Usually they hide service or system files in order to reduce the risk of accidental deletion.
A -archive ... This parameter indicates that the file is compressed.
As you can see, everything is quite simple. It is worth noting that attributes also exist on UNIX-like operating systems. I will not dwell on them because such operating systems are much less common and their users probably know such information. Most likely, you are also interested in the question:
Changing attributes
It is quite easy to do this using the standard Windows explorer... To do this, select the file, open the context menu (it is activated by right-clicking) and select the "Properties" item.
![]()
On the "General" tab, we see two checkboxes that are responsible for assigning the main attributes "Read Only" and "Hidden". You can set the required value by simply ticking the desired item.
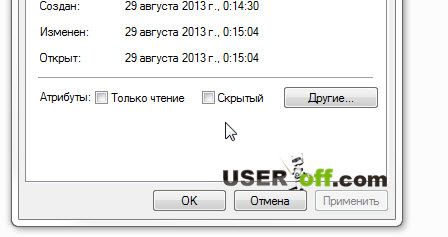
For example, you can set the "Read-only" attribute to any text document. Open the document you just created and type any word. Did you manage to save it?
![]()
By the way, it was because of this situation that I decided to write an article. After all, many novice users do not understand what the catch is.
If you continue your research, you can go to the "Additional" subsection. It contains checkboxes for additional attributes that specify the need for archiving after editing, as well as the need to index the file for faster search.
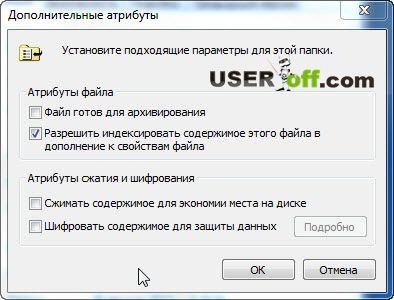
As you can see, the file attributes are a fairly simple thing and it is not difficult to set them. I think I managed to convey to you the information what the file attributes are.
And that's all for today. I would be glad to see your comments 😉.
File attributes
Each file has a number of characteristic properties - attributes... The most important attributes of the file are: name, extension, length, time and date of creation. File name... The name, or the name of the file, just like the name of a person, the name of a document, a book, serves to be able to distinguish one file from another, to point to the desired file.
File extension... In addition to the name, each file may or may not have an extension. The extension is used to characterize the contents of a file in a certain way. For example, the doc and txt extensions indicate that the file contains some kind of document or text, and extension bmp has a file containing an image in bitmap format. The extension, if any, is separated from the file name by a period. In the MS DOS operating system, the extension can contain from one to three characters, for example, otchet4.doc, vedzarpl.txt, picture.bmp, and in Unix systems and Windows 9.x more than three characters are allowed. If there is no extension, then the full stop is not put in the file name. The name, together with the extension, is called the full file name. File length. The next important attribute of a file is its length. The file length is equal to the size of the disk or tape area occupied by the file, and, therefore, is measured in bytes. The value of this attribute is used to determine the possibility of placing a file on a free area of disk media and for some other purposes. File creation time and date... When you first write a file to disk, or when you make changes to the file using the system clock ( special program, which is part of the operating system), the time and date when the file was written to the disk device are automatically recorded. When the computer is turned off, the system clock is supported by special batteries or other power sources.
v operating system MS DOS files have four more attributes - read-only, system, hidden and archive... Each of these attributes has exactly two states - the attribute is enabled or the attribute is disabled. Enabling a read-only attribute(sometimes called the access control attribute) means that the file is not available for making any changes to it. It also makes it more difficult to destroy such a file. After turning off the read-only attribute, the file is available for any operation. System attribute usually only included in the core operating system files. For all other files, the system attribute is usually disabled. Attribute hidden It is included for those files that, when viewing the list of files on the disk device, are not included in this list by the operating system command. The rest of the files have the hidden attribute value turned off. To ensure the reliability of information storage on disk devices, you must have one or two copies of files containing important information. For this, they will organize archive files... When writing a file to an archive, the archive attribute is included. This means that a copy of the latest version of the file is in the archive. When making any changes to such a file, the archive attribute is disabled. This means that the archive contains an outdated version of the file (or the file is not archived at all). Special archiving programs, tracking the value of the archive attribute, can update in the archive only those files in which changes have been made. This allows you to optimize the work of archivers.
Splitting a single file name into its own name and extension exists in almost all operating systems that use the concept of a file and file system... This concept was introduced so that by the name of the file it was possible to immediately determine its purpose: homogeneous documents had the same name extension, and dissimilar documents had different ones. This system continues to be used today.
How does the operating system know which program to use to open the document?
In Windows XP, the file name extension uniquely identifies the document type. The operating system determines the "suitability" of a file for a specific purpose precisely by the extension of its name. Using an "inappropriate" extension prevents the normal use of double-click and context menu and may make the file unavailable for some dialog boxes... In particular, each file name extension is associated with the program used to open the corresponding files.
What is a file type?
Strictly speaking, the file type is the information that is indicated in the Type column when the files are presented in table view. Since the file type is uniquely determined by the extension of the file name, this extension is often used as the file type and they say, for example, about EXE files, about TXT files, and so on. Although the length of a filename extension is not limited to three characters, it is common practice to abide by this limitation; including in order to ensure continuity in relation to earlier operating systems.
What types of files do you need to know about?
As soon as the operating system is installed, a large set of file types recognized by the operating system are automatically registered. For example, files with the .EXE extension are executable program files. Different groups of operating system service files can have the extensions .CPL, .DLL, DRV, SYS, and others. Unformatted text documents have the extension .ТХТ, and formatted documents WordPad and Word have the extension. DOC. WindowsXP recognizes a large number of multimedia document formats: graphic (.BMP, .GIF, JPG, etc.), sound (.WAV, .MRE, etc.), video (.AVI, .QT, .MPG, etc.). Internet documents (Web pages) have the extension .HTM or .HTML. In addition, each program installed on a computer usually supports a number of specific documents. The corresponding file types are registered when this program is installed.
What information is associated with the file type?
Associated with the file type:
The icon corresponding to the given file type;
Application used for such files;
Description (name) of the type;
Standard name extension;
A set of actions that can be performed through the context menu, and one of them is performed in it by a double click.
How can I find out what types of files are registered on the system?
Opening the My Computer window or any<: кно папки, дайте команду Сервис >Folder properties. The Folder Options dialog box can also be opened using the Control Panel. Select the File Types tab. All file types registered by the operating system are listed in the Registered file types list on this tab. Choosing Q;>. any of them, you can see its description in the panel at the bottom 1 && "part of the dialog box.
How do I register a new file type?
Opening the My Computer window or any folder window, go to Tools> Folder Options and select the n "files: s tab. Now you should click on the New button - the Create a new extension dialog box will open. In this window, you need to use a new (or a pre-existing) extension, usually three characters. Click the More button in the dialog box to display a list of File type to match. If a favorite extension is already registered, the existing item is automatically selected in this list. Otherwise, the item is displayed.<Новый>... The type name in this case is generated automatically; if you, say, choose the extension AAA, the new file type will be registered as File “AAA”.
How do I choose the program to use to open a file with a non-standard type?
If a file with an unusual extension already exists on your computer, the easiest way is to simply double-click its icon. The operating system will display a dialog box informing about the impossibility to open the file. Select the check box Manually select a program from the list and click the OK button. The Select Program dialog box opens. The program used to open such files can be selected from the Programs list or searched using the Browse button. If you select the Use it for all files of this type check box, the operating system will create a registration for the corresponding file type or modify an existing one. In the future, double-clicking on the icon of such a file will automatically launch the selected program. The second way to select a program to open a file is to change the registration of that file type. With My Computer or any folder window open, go to Tools> Folder Options and select the File Types tab. On this tab, register a new file type or find an existing one in the Registered file types list. Click on the Change button and proceed in the same way as described above.
How can I change the characteristics of a registered file type?
Opening the My Computer window or any folder window, give the Tools> Folder Properties command and select the File Types tab.On this tab, select an existing file type in the Registered file types list. Click the Advanced button. In the Changing properties of a file type window that opens, you can enter a description of this file type (the field at the top of the window) or change the icon assigned to this type (the Change icon button). The rest of the controls are used to customize the context menu for this file type!
How can I change the context menu for files of a certain type?
The file icon context menu is composed of two main parts. The permanent part of the menu contains commands for copying, moving, deleting and renaming a file ;;, as well as for creating a shortcut. The variable part contains commands that are specified when registering a file. In the absence of such directives in I or in the absence of registration at all), the Open with command is included in the context menu, which allows you to select a program to open the file. To change the set of commands or the action performed when a command is selected, open a window of any folder or the Explorer program and give the command Tools> Folder Options. On the File Types tab, select the file type whose registration data needs to be changed and click the Advanced button - the Change File Type Properties dialog box will open. The commands assigned to this file type are listed in the Actions list. To add new team, click the Create button. To change already and m< ющуюся команду, следует выбрать ее в этом списке и щелкнуть на кнопке Изменить. В открывшемся диалоговом окне можно изменить имя операции, а также сформировать команду, соответствующую данному пункту контекстного меню. Команда обычно включает в себя имя запускаемой программы (ее можно выбрать кнопкой Обзор), дополнительные параметры и имя используемого значка, для задания которого указывается специальный параметр в виде «%1».
How do I select a double-click command?
Command that is executed in two;>] i
Clicking the icon is also included in the list of possible actions and is considered the default action. When you open the context menu, this command is highlighted in bold. To find the appropriate action, you need to open the dialog box And: change the properties of the file type corresponding to the desired file type (example, My Computer> Tools> Folder Options> File Types> Change e). After selecting the operation to be performed by double-clicking from the Actions list, click the Default button.
How do I unregister a file?
If the file type has been registered and hey installing a program, then the deregistration is usually done automatically when the program is uninstalled. Refusal to use files of a certain type usually also completely replaces the removal of their registration. Thus, this operation is interesting, as a rule, only in case of "accidental" registration of a file type and assignment of an inappropriate program to it. To unregister a file type, open the Folder Options dialog box (for example, My Computer> Tools> Folder Options t File Types), select the desired file type, and click the Delete button.
What information does the file properties dialog box contain?
The context menu of any file icon contains the Properties item. When you select this command, the properties dialog box for this file opens, containing one tab - General. An additional tab Shortcut appears if you used not an icon, but a shortcut / The General tab contains the same data that can be seen in the folder window in Table mode, but presented in more detail. The top bar indicates the file type and application that is typically used to open such files. Below is the folder where the file is located and details the size of the file (including the disk space it occupies). The bottom panel shows the dates of creation, modification and opening of the file. At the very bottom of the dialog box, the file attributes are listed, and these are the only options that can be changed in this case. The Shortcut tab is used to change the parameters used when opening a file (or starting a program) using a shortcut. Here you can view or change the "command line" (the Object field), which is usually the search path for the object, specify which folder should be current when working, and select the initial window size. For especially frequently used documents and programs, you can select a keyboard combination that allows you to use this shortcut at any time and even without using the mouse (Shortcut field). The Change Icon button allows you to change the image used by this shortcut. The Find Object button allows you to quickly open a folder window containing the file associated with this shortcut. Icons and shortcuts for programs also display a Compatibility tab to make it easier to run applications on older operating systems in Windows XP.
What are file attributes?
File attributes are Additional Information associated with this file and stored in the folder. Historically, attributes were introduced in the earliest versions of the MS-DOS operating system. There are four attributes: Read Only (R), Archive (A), Hidden (H), and System (S), the state of which (on / off) can be changed in the properties dialog box of this file.
How to enable display of file attributes in table mode?
To constantly monitor the attributes of files, you can enable them to be displayed in table mode in Windows>, Folders and in the Explorer program. To do this, open the required folder, set its view mode as a table (View v Table), right-click on the bar of the column headings and select the Attributes item in the context menu that opens. This menu flag usually affects only those windows whose setting has been explicitly changed. In the additional column of the table, included attributes are marked with capital letters A, S, H, R.
What does the read-only attribute mean?
The Read-only attribute indicates that this file cannot be changed. If this attribute is included, then “hundred! Standard attempts by the operating system to change, delete or rename the file will fail. This attribute, in particular, is enabled for her ki automata for all files recorded on the CD.
What does the Hidden attribute mean?
The Hidden attribute specifies that the file should not be displayed in the normal folder window. This attribute is intended to protect important files from unintentional or malicious destruction or damage. However, the operating room Windows system XP allows you to enable the mode of displaying such files, if no, .it: the publisher considers it necessary (My Computer> Tools> Folder Options »View> Show hidden files and folders).
What does the Archive attribute mean?
The Archive attribute can be USED by backup programs as a sign that the file has changed. "Regular" programs that modify the contents of a file enable this attribute, while backup programs themselves turn it off. Therefore, if this attribute is enabled, then the file was recently modified and needs to be backed up. Currently, such a system is rarely used, so the Archive attribute does not make much sense. For the reasons stated above, it is enabled for almost all files, but it makes no sense to disable it.
What does the System attribute mean?
The System attribute, as it were, combines the properties of the Read Only and Hidden attributes, at the same time indicating the special importance of the file provided with this attribute. The Windows XP operating system does not allow you to enable or disable this attribute yourself. However, if the display of system files is enabled (on the View tab of the Folder Options window, the Show hidden files and folders check box is selected, and the Hide protected system files check box is cleared), an attempt to perform a delete or rename operation system file or folders will only lead to a confirmation request to perform this operation.
 Bugs in Singularity?
Bugs in Singularity? Just Cause 2 crashes
Just Cause 2 crashes Terraria won't start, what should I do?
Terraria won't start, what should I do?