Windows 7 with uefi support. UEFI - what is it? Download, installation, benefits, configuration features. Computers with old BIOS
Windows 7 has been very popular since its release. Subsequent versions of the operating system from Microsoft were greeted by users ambiguously, and this is especially true of the eighth edition. Although the “ten” still has a fairly large number of fans, many people want to know how to install Windows 7. This is not such a complicated process as it might seem, and most users will be able to install this OS on their computer or laptop on their own.
Preparatory stage
Every PC owner should remember that the OS can be completely reinstalled or an existing one can be updated. If the computer is unstable, then you should choose the first option. Since this process involves formatting the system disk, it is necessary to transfer all important files from it to another partition. Otherwise, they will be destroyed.
To install Windows, you must have a boot disk or flash drive. Also, the user must understand what kind of operating system to install. Determining this is quite simple - if the PC has at least 4 GB of RAM installed, then Windows 7 64-bit is selected. When there is less RAM, then it is worth stopping the choice on the 32-bit edition.
In addition, you should make sure that all the necessary drivers are available. If the OS will be installed on a laptop, then they must first be downloaded from the manufacturer's website. At the time of purchase of a desktop PC, disks are included with the motherboard and video adapter. It is on them that all the drivers necessary for the normal operation of the computer are contained.
It remains to decide which version of the operating system will be installed. Total company Microsoft offers six editions of this OS:
 After carrying out the preparatory activities, you can answer the question of how to install Windows 7 yourself from the Internet. It should be warned right away that this OS lacks support for USB 3.0 ports. To be able to distinguish the standard from earlier ones, they are colored blue. If the installation will be carried out from a USB flash drive, then it must be inserted into USB 2.0. It is also worth remembering that new PCs are equipped with UEFI BIOS and the process of installing the operating system on them has some features.
After carrying out the preparatory activities, you can answer the question of how to install Windows 7 yourself from the Internet. It should be warned right away that this OS lacks support for USB 3.0 ports. To be able to distinguish the standard from earlier ones, they are colored blue. If the installation will be carried out from a USB flash drive, then it must be inserted into USB 2.0. It is also worth remembering that new PCs are equipped with UEFI BIOS and the process of installing the operating system on them has some features.
Computers with old BIOS
If the BIOS supports the Boot Menu, then after rebooting the PC, you need to call it. For this, one of the keys is most often used - F8, F2, Esc, F11. In the window that appears, select the desired device.
However, this method is not suitable for all computers, and in such a situation it is necessary to change the boot priority in BIOS manually. To do this, you need to reboot the PC and at the moment the logo appears, press the Del key. Some motherboards and laptops use different buttons.
Actions after entering the BIOS depend on its version:
- Phoenix-Award - the "Advanced BIOS Features" section is selected, and it contains the line "Hard Disk Boot Priority" or "First Boot Device". Then, using the arrows, the desired device will be selected, for example, a USB-HDD for a flash drive.
- AMI - on the top panel, you need to find the "Boot" tab and go to the "Boot Device Priority" section. Having inserted on the line "1st boot", you should press "Enter", and then select the desired device with the arrows.
After completing these steps, you will need to save the settings and restart the PC. If everything was done correctly, the OS installer will start loading. The further sequence of actions looks like this:

After that, a window for selecting HDD partitions appears, and the user is faced with the question of which disk to install Windows 7 on. The first one is designed to store system backups and has a size of about 100 MB. You should choose the second one and it must be formatted before installing win 7. For this, the following steps are performed:
- Click on the line "Disk Setup".
- After selecting the desired partition, the "Format" button is pressed, and then "OK" to confirm the operation.
When the formatting process is completed, you need to select the partition again and click on the "Next" button. After that, you can wait 20 minutes for the installation process to complete and the PC will automatically reboot several times. After installing the operating system, you must select the operating parameters of the system and install the drivers.
Machines with UEFI BIOS
And now about how to install Windows 7 on new PCs on your own. Logging into UEFI is done with the F2 or Del keys. Then you need to get to the "Boot" section and change the value of "Secure Boot" to "Disable" in it. As a result, a new item should appear - "OS Mode Selection". In it, select "UEFI and Legacy OST" and save the changes made by pressing the F10 key.
 The PC will start to reboot, and at this point you need to go back to UEFI. Then, in the "Boot Device Priority" menu, the desired boot device is selected. If the computer was previously installed "eight" or "ten", then some problems may arise. This is because the latest versions of Windows format the hard drive according to the GPT partition table layout standard, not MBR. For the work of the "seven" a second format is required. To solve the problem, you will have to use the step-by-step guide.
The PC will start to reboot, and at this point you need to go back to UEFI. Then, in the "Boot Device Priority" menu, the desired boot device is selected. If the computer was previously installed "eight" or "ten", then some problems may arise. This is because the latest versions of Windows format the hard drive according to the GPT partition table layout standard, not MBR. For the work of the "seven" a second format is required. To solve the problem, you will have to use the step-by-step guide.
In this case, you should select the disk where the user wants to place the OS, then set the operating system language and click on "Full system installation". The next step is to call the command line using the keyboard shortcut "Shift + F10". After her appearance the desired order of entering commands is as follows:
- diskpart;
- sel dis 0;
- clean;
- convert gpt;
- exit;
- exit.
After clicking the Update button, the installation can continue. Upon completion of the process, it is necessary to set the system operation parameters, as well as install the drivers.
Do not be afraid to install the OS yourself, because this is not the most difficult process and it is absolutely not necessary to pay money to a specialist for its implementation.
The UEFI BIOS has made a lot of noise in the digital world, and since this interface is already installed on all new computers and laptops, we received a whole bag of letters regarding this topic by mail. Questions are primarily of this nature.
What is UEFI BIOS and why did it replace the regular BIOS? Why can only Windows 8 be installed on a laptop with UEFI BIOS, but you can install no other operating system or still another OS, then how to do it?
Why on a laptop with BIOS UEFI Can't install Windows 8 other edition?
BIOS UEFI
After reading all the letters, I decided to answer them with one article and so that everything was clear even to a novice user.
An important incentive for writing this article was the fact that, according to my observations, a lot of people who buy new computers with an SSD drive and a motherboard that supports the new UEFI interface immediately disable this interface and install Windows 8 on their hard drive with an outdated master boot record MBR.
What then was the point of buying a new expensive computer for 30-40 thousand rubles with an SSD drive and a UEFI BIOS that undoubtedly gives advantages over a simple BIOS. What are the benefits, you ask? This is what I want to talk to you about.
BIOS UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is an interface between the operating system and firmware that controls low-level hardware functions. Developed by Intel. The history of the creation of the UEFI interface goes back to the first half of the 90s and at first it was called the Intel Boot Initiative (Intel Boot Initiative), later it was given a different name EFI. The first EFI 1.02 specification was released by Intel in 2000.We all know what a BIOS is, yes, that's right, it is a "basic input / output system", but humanly it is a firmware built into a simple microcircuit, which in turn is located on the motherboard. So, this firmware (BIOS) is an intermediary between the installed operating system and the components installed on the computer. That is, the BIOS explains to the operating system how to functionally use all the components of the computer: motherboard, processor, video card, RAM, and so on. BIOS starts before the operating system and immediately checks (POST procedure) all the computer hardware listed above: processor, motherboard and everything else, setting the necessary parameters for their operation. In the event of a malfunction of any component, the BIOS issues a signal through the built-in speaker, by the nature of which you can understand which device is faulty.
In short, BIOS turns out to be a rather important thing on a computer, but ... today, friends, BIOS has been replaced by a much more advanced tool called UEFI.
What did not suit the usual BIOS?
Here are the most important reasons.
1) When you turn on the computer, the BIOS, in addition to checking the components for serviceability, checks all hard drives for the master boot record MBR (master boot record), which is located in the zero sector and has a size of 512 bytes, when the boot record is found, the BIOS starts the boot record for execution code in the MBR, then the operating system is loaded. On a computer with a regular BIOS and a hard disk (having an MBR (Master Boot Record)), volume addressing is done in such a way that the maximum addressable space on the hard disk can be a maximum of 2TB, that is, the operating system will NOT see more than 2TB of disk space on 3TB hard drive, which you will agree with the current volume of hard drives is not very convenient.
2) On computers with a regular BIOS, hard drives (having an MBR master boot record) have a limitation on creating primary partitions, that is, you can create only 4 primary partitions on an MBR disk - three main and one additional partition in which you can create logical disks, you can install an operating system on a logical one, but it will not start without a boot manager on the main partition). And the UEFI BIOS works with hard drives that have a GUID partition table (GPT), such hard drives can be divided into 128 primary partitions.
3) And most importantly, UEFI BIOS is much safer. It's no secret that a rootkit has existed for a long time, capable of injecting its own code into the BIOS chip and loading itself earlier than the operating system, thereby gaining unlimited control over the system itself. This is not possible in UEFI BIOS, it has a secure boot procedure "Secure Boot",

Based on special certified keys from Microsoft. Looking ahead, I’ll say that because of this very secure boot, ordinary users cannot install anything other than Windows 8 on computers with UEFI BIOS, since only Windows 8 today has these very certified keys (more information about this later in the article ).
Benefits of UEFI BIOS

So, let's take a look at the new UEFI BIOS in order and find out its main advantages over the usual BIOS. The UEFI interface is a mini operating system, or in other words, an improved and completely redesigned mechanism that will soon completely replace the BIOS. Firstly, UEFI took a lot from its predecessor and is intended primarily for the interconnection of the operating system and the hardware installed on the computer, that is, all computer components. The UEFI interface should test all the hardware for serviceability when the computer is turned on and then pass the baton to the operating system loader.
1) BIOS UEFI has its own very convenient and intuitive graphical control interface with mouse support. There is support for the Russian language.
2) BIOS UEFI works with hard drives that have a GUID partition table (GPT), such hard drives can be divided into 128 primary partitions (by the way, only 4 primary partitions can be created on an MBR disk - three main and one additional partition in which you can create logical disks , you can install an operating system on a logical one, but it will not start without a boot manager on the main partition).
3) BIOS UEFI makes it possible to use hard drives with a capacity of more than 2 TB, the maximum partition size can reach 18 exabytes (18,000,000 terabytes). On a computer with a regular BIOS, the installed operating system will NOT see more than 2.2TB of disk space, which is of course inconvenient.
4) Hard drives with a GUID partition table (GPT) work only with LBA addressing, unlike MBR hard drives that work with outdated CHS addressing.
6) It is easier to recover lost data on GUID (GPT) hard drives.
7) UEFI BIOS has its own boot manager, which is very convenient to use if there are many operating systems on the computer, there is no need to use special bootloaders, like EasyBCD.
8) UEFI BIOS is much easier to update than a simple BIOS.
9) GPT is more secure than MBR because the partition table is written at the beginning and at the end of the disk, providing duplication.
Secure Boot Protocol
But the most important feature of the UEFI mechanism, which causes trouble for users, happens when you reinstall Windows 8 on a new computer or laptop. The UEFI BIOS has such a secure boot protocol "Secure Boot", based on special certified keys that only Windows 8 from Microsoft has and Microsoft requires all manufacturers of PCs and laptops preinstalled with Windows 8 to be enabled by default secure boot protocol "Secure Boot".
Having such Windows 8 keys in its distribution, when installed on a computer of any manufacturer, it successfully passes the UEFI “Secure Boot” secure boot protocol, but none of the old Windows operating systems, as well as Ubuntu or Linux distributions, have such keys. That's why, if your laptop has a UEFI BIOS, then you won't be able to install any other operating system on such a laptop, there is only one way out,

but then you will install the operating system you need on an MBR disk and lose all the advantages of working with a hard disk that has a GUID (GPT) style.
Of course, many users will have thoughts that this is how Microsoft gets rid of competitors, but Microsoft successfully fends off such attacks by explaining that the UEFI interface with all its protocols and secure boot"Secure Boot" it was developed primarily for our security and it is difficult to disagree with it (I already spoke about the rootkit, which is able to write its code into a regular BIOS, at the beginning of the article).
Attentive readers may ask why, all the same, Linux does not agree with Microsoft and computer manufacturers and get these same keys. I found the answer in the blog of one of the developers of the Linux kernel - Matthew Garrett (Matthew Garrett),
Matthew Garrett

it turns out to be difficult both physically (it will take a lot of time, since you need to agree first with Microsoft, then you have to negotiate with each computer manufacturer separately) and legally (the problems are related to the GRUB 2 bootloader licensed under the terms of the GPLv3 license).
Many readers are wondering if it is possible to make a bootable UEFI flash drive with the Windows 7 operating system?
You can make a bootable flash drive (we have an article about this), but you won’t be able to install Windows 7 on a laptop where Windows 8 was previously installed, it just won’t pass one of the Secure Boot verification protocols.
I will say more, even if you want to reinstall Windows 8 on a laptop, you will only succeed with the edition of Windows 8 that was previously installed on your laptop. Typically, laptop manufacturers install Windows 8 for one language (Windows 8 Single Language), so you can only reinstall Windows 8 if you get a Windows 8 Single Language installation disk.
And you just won’t be able to install on your laptop, for example, Windows 8.1 Professional on many laptops, during installation you will get the error “The product key you entered does not match any of the Windows images.”
Note: If you want to change the version of Windows 8, that is, reinstall Windows 8 Single Language (for one language) installed on your laptop, for example, to Windows 8 Professional, this can also be done, but with laptops from some manufacturers this just won’t work and you need will modify additional configuration files that can be used during the Windows setup process to specify the Windows product key and edition, details in our article ""
At the end of the article, I want to say that it is possible to install another operating system instead of Windows 8, for example Windows 7, on a new laptop, but as I already said, in the UEFI BIOS we will have to disable the secure boot protocol "Secure Boot", how to do this, you can read our article "How to install Windows 7 instead of Windows 8 on a new laptop."
If you have a simple desktop computer, then you can install Windows 7 without disabling the "Secure Boot" option in the UEFI BIOS, we also read the detailed article "How to install Windows 7 on a GPT disk."
Read the following article How to disable Secure Boot.
Articles on this topic.
With the release of Windows 8, manufacturers began to actively implement the successor to the BIOS - the UEFI interface, which has already managed to deliver a lot of trouble during its existence. We will tell you how, despite this, to take advantage of its benefits.
The mass transition to UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) has already begun. Microsoft requires this interface to be used on all computers that will ship with Windows 8. More specifically, we are talking about UEFI with Secure Boot. At the same time, only G8 can work on such PCs without problems: neither Windows XP nor G7 can be installed on a UEFI machine without additional manipulations.
You won't be able to boot from a Linux Live or Windows flash drive either. What exactly can happen if you try to start from an installation flash drive on a Sony VAIO laptop is shown in the picture above. And the problems with UEFI do not end there. Each hardware manufacturer configures UEFI at its own discretion, thereby creating unnecessary difficulties for the user. Lenovo's IdeaPad laptop couldn't recognize the same flash drive as bootable media at all. At the same time, there is nothing to blame Lenovo for: the fact is that the bootable flash drive is formatted in the NTFS file system, and UEFI does not support booting from such media. If you connect the same drive to an HP EliteBook laptop, it will boot without problems and allow you to install Windows. The problem is that all the data that was on the EliteBook disk would be deleted after installation.
Everyone configures in their own way
Are you confused? No wonder: UEFI with the Secure Boot function sets new rules for installing and loading operating systems, and hardware manufacturers interpret these rules in their own way, which creates additional difficulties for the user. Therefore, within the framework of this article, we set ourselves the goal of eliminating the confusion around UEFI. Using laptops from major manufacturers as an example, we will explain how UEFI works, what role the Secure Boot function plays, how to get around the “traps” placed by the new interface, and what is needed in order to use bootable flash drives without fear of any devastating consequences.
How UEFI Works
UEFI boots strictly in accordance with the established rules. If the OS does not support UEFI, BIOS emulation mode is activated. The process of booting a BIOS-based PC is quite simple: after pressing the power button, the BIOS starts, which checks the status of the hardware and loads the firmware - simple drivers for individual hardware components. After that, the BIOS searches for the OS bootloader and activates it. That, in turn, loads the operating system or displays a list of available operating systems.
UEFI-based computers boot in the same way, only until the boot options are searched. After that, everything is different. UEFI has its own OS bootloader with integrated startup managers for installed systems. For it, a small partition (100–250 MB) is created on the disk, formatted in the FAT32 file system, called the Extensible Firmware Interface System Partition (ESP). It contains drivers for hardware components that can be accessed by the running operating system. The general rule is that, with the exception of DVD, UEFI can only boot from media formatted with the FAT32 file system.
UEFI is a complex mechanism
ESP has its advantages: thanks to UEFI drivers and an OS loader, Windows starts up faster and more adequately responds to critical driver errors. But the UEFI interface also imposes restrictions: it allows you to install the OS only on hard drives that are marked according to the GPT standard. The latter is not supported by any BIOS version, since, unlike the traditional markup scheme (MBR), it uses 64-bit sector addresses. In addition to Windows 8, only 64-bit versions of Windows Vista and 7, as well as Linux with kernel 3.2 and higher, support the UEFI interface. Moreover, for PCs certified to work with the G8, Microsoft prescribes the use of the Secure Boot option. In this mode, UEFI only runs validated OS loaders that contain Microsoft digitally signed drivers.
Along with Windows 8, only the Shim bootloader (Linux) has drivers with the necessary signatures for Secure Boot. Other OSes don't have them. Therefore, if you want to install Windows 7 or Vista on such a computer, in addition to the G8, you need to open the UEFI menu and disable Secure Boot. If you select a non-UEFI-compatible second OS, you will need to use the Compatibility Support Module (CSM), which can be enabled in UEFI. Unfortunately, manufacturers use different versions of UEFI and it's sometimes difficult to figure out how to disable Secure Boot and enter BIOS emulation mode. We will consider these questions further.
UEFI Based PC Boot Process
Depending on the configuration, UEFI either boots the computer on its own or enters a standard BIOS emulation mode. Only then does the Windows boot manager start.
Installing Windows on a PC with UEFI and Secure Boot On a PC with Windows 8 based on UEFI Secure Boot, other OS versions can only be installed under certain conditions. The user must select the correct boot mode in advance and prepare the installation flash drive accordingly.
 Enabling BIOS emulation mode A complete mess: the way you enter BIOS emulation mode depends on the UEFI version. On Sony VAIO (1) you need to activate the "Legacy" option, on ASUS Zenbook (2) - "Launch CSM".
Enabling BIOS emulation mode A complete mess: the way you enter BIOS emulation mode depends on the UEFI version. On Sony VAIO (1) you need to activate the "Legacy" option, on ASUS Zenbook (2) - "Launch CSM".
 UEFI setup
UEFI setup
Each manufacturer uses its own version of UEFI in laptops and ultrabooks. However, it does not provide access to all the necessary functions. Often, when booting a PC or laptop, the name of the button is not displayed on the display, with which you can call up the UEFI settings menu. We suggest doing the following: in the Metro interface, go to the menu "Options | Change PC settings" on the sidebar and activate the item "General | Special download options. After restarting, the OS boot manager will appear, which will allow you to open the UEFI menu. The exception is HP's UEFI, where this option is not available. The following will help here: during boot, hold down the "Esc" key. In any case, you must first find out which button allows you to enter the UEFI menu. If you change the boot mode to CSM or Legacy BIOS to boot from a rescue flash drive, you must switch from CSM to UEFI again after the restore operation, otherwise Windows 8 will not start. But there are exceptions here too: Aptio Setup Utility on ASUS computers activates UEFI automatically in the absence of a BIOS-compatible bootable media, so simply disconnecting the USB flash drive is enough.
Disabling Secure Boot will be required if, in addition to the G8, you want to install a 64-bit version of Windows Vista or 7. Sometimes the so-called hybrid mode is supported, as in HP devices, in which UEFI can boot from all bootable media and, if necessary, switch to BIOS mode. In the widespread version of UEFI InsydeH2O, this depends on whether the laptop manufacturer has provided the ability to disable Secure Boot or not. This feature is not available on the Acer Aspire S7 and requires switching from UEFI to BIOS mode and back to disable it.
Some new motherboards for laptops and desktops use modern UEFI instead of the usual BIOS for all users. When installing the windows 7 operating system on such equipment, a number of features should be considered.
Unfortunately, this factory software is being implemented very slowly on modern systems. Thus, today it is not ready to replace the BIOS. As a result, you may experience problems when loading in the new mode. Questions most often arise from those users who want to install Windows 7 instead of the eighth version of the system that comes with the laptop.
Why you should switch to UEFI
The main reason why you should switch from BIOS to UEFI is the lack of functionality. It is no longer enough for professional work computers that process large documents. They need to ensure maximum performance of all components. It should be noted right away that when booting in UEFI mode, installing Windows 7 on old partitions marked under MBR will not be possible. There are two methods that can be used to solve this problem.
The first option is to copy all important information to additional or external media. The second option will be more labor intensive. To implement it, you will need to convert all partitions using disks or bootable flash drives with special utilities like Paragon. This will allow you to save all the information available on the computer, except for the disk on which the system is installed. To conclude that you need to install a system under UEFI on your computer, you need to figure out what advantages this type of pre-installed software provides compared to BIOS.
BIOS: old but effective
It's best to start the review process with the BIOS or basic input/output system. From the name it is quite possible to understand what functions this system is responsible for. This software did not appear immediately. The BIOS has gradually evolved and progressed along with the development of computer technology. Thanks to this, many users can today use a fairly wide functionality of this system. By itself, this software has not been able to remove all the needs of modern hardware.
Therefore, in parallel, the development of programs and drivers configured directly in the operating system itself was carried out. But it is the BIOS that is responsible for such operations as the initial recognition of the hardware and determining the devices from which you want to boot. UEFI performs similar functions. For its correct operation, the options described above are required without fail.
Extensive UEFI functionality
UEFI - what is it? The abbreviation UEFI in translation into Russian is deciphered as follows: Extensible Firmware Interface. Intel started developing this system back in 2001. At first it was intended for server hardware.
UEFI was created for the reason that Itanium processors could not support old software, because the core of the server computer needed significantly expanded functionality. Users were able to try out the novelty only in 2006 on Apple computers. Then the novelty began to appear in the products of other companies. This is exactly what the word Unifed in the abbreviation says. UEFI was also used in Microsoft products to optimize the installation of Windows 7. It was also used by other software developers.
Benefits of UEFI
Thanks to the novelty, it is now possible to install Windows 7 on large hard drives. UEFI supports GPT by default. It is under this partition table that the system will be placed. Large hard drives refer to hard drives larger than 2 TB. The old system only supported hard drives, the volume of which did not exceed 2 TB.
This feature is explained by the fact that the BIOS system used partitioning of the MBR type to work with the drive. The size of each record with such a breakdown was 32 bits. Thus, 4 billion sectors were obtained, which amounted to 2 TB. Such a volume to someone today will surely seem redundant. However, this capacity is quite often required by 3d designers and employees who use server hardware.
Thanks to the use of UEFI, the installation of the Windows 7.8, 10 operating system can be carried out on a hard drive with a capacity of up to 8 billion TB.
Equipment Compatibility
On modern motherboards, support is provided for both old hardware with MBR partitioning and new hardware with GPT partitioning. The user can now choose the option that is more suitable for his computer. This is possible thanks to UEFI dualbios. This provides the ability to install the Windows 7, 8, 10 operating system on such equipment simultaneously in two modes. The choice of the mode is carried out by the user at loading.
System Interface
The developers not only made some changes to the code. They also completely redesigned the interface. Thus, user interaction has been accelerated. The ability to control UEFI elements with a computer mouse has also become an advantage. This makes installing Windows 7 easier and more convenient.
It is enough just to get used to the new style and you will forever lose the desire to return to using BIOS-based computers. The developers promise to create additional utilities for UEFI in the future. Special applications are also being created that, as planned, will provide access to the Internet without installing an OS. This task has already been partially completed, since a network protocol is used to update the preinstalled software.
Additional Windows protection
Another important advantage is the secure installation of the Windows 7 operating system. GPT UEFO uses new standards that allow you to strengthen the protection of the OS from Microsoft. Thus, the chances of leakage and loss of information are several times reduced. This option is included in the software by default, but it can be disabled in the settings if the user wishes.
Orientation and speed
The redesigned basis gives UEFI the ability to speed up the loading of the operating system several times. Navigating the new interface is much easier thanks to the use of bright and visually understandable content. The appearance of each icon began to resemble those used in the operating system. There is also a utility section that has not been used to date. It contains applications that allow you to view additional computer properties, such as the temperature of various elements, installed hardware, and more. The specific set of utilities depends on the type of motherboard you are using and its manufacturer.
Moving from MBR to GPT
The first thing to think about when moving to UEFI is saving important information. If this is not required, you can proceed with the installation. If there is important information on the computer, you must first backup or repartition the disk using specialized software.
Preparing a flash drive with Windows 7 for installation on UEFI
After you learn all the principles of working with the new software and decide how appropriate it will be to use it on your current equipment, you should proceed to the preparatory stage. To install Windows 7 through UEFI, you will need to have certain skills regarding writing the system distribution.
Users who are accustomed to using flash drives will need to stock up on the latest version of Windows and one of the programs for burning a bootable flash drive. For example, consider the Rufus program. Download the latest version of the program. You will also need a 4 GB flash drive. Rufus must be run as an administrator.
You will also need to confirm UAC permissions. After that, go to the "Device" section and click on the flash drive of your choice. If you want to install a system with a GPT or MBR disk partition, you must check the corresponding box. By default, it is recommended to install the FAT 32 file system. After that, you need to select the ISO image itself and click on the "Start" button. After the process is completed, the UEFI bootable flash drive will be ready.
To start working, you need to boot correctly. Gigabyte is developing motherboards with Dual UEFI BIOS. Using such equipment, you will simply need to go to the settings by pressing the F9 key and select the desired operating mode. These steps can also be performed on motherboards from other development companies.
Also, fast boot in UEFI mode is often used. To enter this mode, you must select the Boot-devices menu and select a flash drive with a prescribed tag of the mode you need. In the event that the user does not work with the new BIOS, you can deactivate it. In the settings, it will not be possible to disable Lagacy boot even if a UEFI installation of Windows 7 is in progress. Acer was one of the first manufacturers to remove the ability to deactivate modes on their laptops.
You can only use fastboot for selection. At first, GPT partitioning and new built-in protection tools, when installed in this mode, blocked pirated cracks in the Windows operating system. But the hackers still managed to quickly fix the Windows 7 activator. In it, the UEFI mode was fully taken into account. After the user loads the desired method, it will be necessary to perform all other steps when installing the system, which do not undergo any special changes. It is worth noting only the moment that when partitioning a hard disk, the Windows operating system will now create more additional partitions.
Recently, many motherboards have an improved version called uefi instead of the usual bios firmware. The program interface supports language selection, allows you to use new types of hard drives with a capacity of more than 2 TB, and contains other improvements. If you have the latest uefi bios firmware installed on your computer, then we will tell you how to install windows 7 in a few steps.
Benefits of uefi firmware over bios
The advantage of uefi firmware is that it can speed up the loading of your operating system in an extremely effective way. In addition, uefi bios makes it easier to restore information, install updates, and there are other advantages. Experienced users understand the difference between MBR and GPT disks, but don't worry. Just remember that uefi is the real near future and bios is obsolete.
Unpleasant feature of uefi firmware
The saddest feature of this program is the inability to migrate from the installed Windows 8 operating system to a new computer. So if you have 8 preinstalled, then 7 is not so easy for you to install. This is due to the presence of a mandatory protocol that Microsoft now requires from all licensed versions of Windows - downloading Secure Boot, which is not in Windows 7 and is not provided in previously released versions of the OS. You can solve this by disabling this option in the program menu. Go to the Security section, disable Secure Boot.

Don't forget to turn on compatibility mode! The route is as follows: tab Advanced - System configuration - Boot Mod (maybe OS Mode Selection).

We set the found option in this way: change UEFI OS (or UEFI BOOT) to "CSM Boot" or "UEFI and Legacy OS", "CMS OS".

Before proceeding, you either need to create a bootable USB flash drive yourself or have a licensed installation disk with this system. Distribution owners are advised to immediately start reinstalling, because the method of how to work with a bootable USB flash drive is described below in the instructions. The installation disk will not cause any problems.
Now let's configure uefi to install from a USB flash drive.

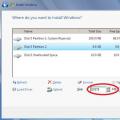 Preparing Your Computer Hard Drive for Windows XP Installation
Preparing Your Computer Hard Drive for Windows XP Installation How to restore the system using the Acronis image?
How to restore the system using the Acronis image?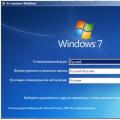 Windows 7 with uefi support
Windows 7 with uefi support