What does the correct lmhosts file look like. Windows hosts file. Using hosts for your own purposes
Today, users of social networks like VKontakte or Odnoklassniki are often faced with the problem of logging into the site. The system controls this through the HOSTS file, which is located in the C: \ Windows \ System32 \ drivers \ etc tree. Unfortunately, this is the service most commonly affected by viruses. Let's try to figure out how to fix the situation.
What files are in the C: \ Windows \ System32 \ drivers \ etc directory, and what are they responsible for?
Most people are familiar with these files, but they often get frustrated when they don't work as expected. This is usually due to the fact that they have very simple but specific requirements for them to work at all. The catch is there are several mistakes you need to be aware of.
- Always use capital letters to be safe.
- It is also helpful to add Domain name.
- This takes two lines and uses extremely critical formatting.
What files are in the C: \ Windows \ System32 \ drivers \ etc directory, and what are they responsible for?
First, let's pay attention to the files in this folder. In addition to the file you are looking for, there should be only four more objects here. If there is something else, you can safely say that or something like that.
As far as file functions are concerned, for example, the C: \ Windows \ System32 \ drivers \ etc \ services object and other files, including HOSTS, protocol, lmhosts, and networks, are responsible for some of the functions of a user accessing certain resources on the Net.
How do I find and edit this file?
Keep in mind that when editing these files, you may run into conflicts or ineffective changes if you don't reload or clear the local name caches. This documentation is archived and not supported. If the name is marked between double quotes, it is used exactly as specified. By default, the 16th character is set to identify the network client service that registered this name. As you can see, the only difference between these two names is the 16th character. The 16th character uniquely identifies each of the network client services running on the computer.
- Each entry should be on a separate line.
- The final write to the file must be terminated with a carriage return.
The considered one determines the correspondence of the database of domain names to IP addresses. In addition, its use involves accelerating the user's access to the most frequently visited pages on the Internet bypassing DNS servers, as well as blocking some unwanted resources or banner links. By default, in addition to the descriptive text part, it contains a single entry of interest to us at the end of the text, namely: 127.0.0.1 localhost. Everything! There should be no more additional entries in it.
Note the following characteristics of the previous example. Since his name includes spaces, the name and special character are enclosed in double quotes. This entry should be added to the following registry subkey. Don't use Registry Editor to edit the registry directly unless you have an alternative. Registry editors bypass the standard precautions provided by administrative tools. These precautions prevent you from entering conflicting settings or settings that could degrade performance or damage your system.
Checking the IP address of sites
If we talk about an example of matching a domain name real IP address resource, you can check it in a completely elementary way, using in command line the standard input of the ping command, followed by the URL of the checked resource, separated by a space.

Fixing the hosts file
When domain controller activity occurs, such as a logon request, the computer sends requests for the domain group name. On the local subnet, the computer broadcasts the request, and it is picked up by any local domain controllers. This ensures that login authentication, password changes, browsing, etc. will work correctly for the local domain. This ensures that promoting a standby domain controller to the primary domain controller does not affect the promoted domain controller's ability to offer all services to domain members. Again, standby domain controllers in remote domains must also be enabled so that promotion to the primary domain controller does not interfere with the ability to view remote domains. Special groups are limited to a total of 25 members.
To get the IP of any resource, you must use the following combination: ping www. (Site name). (Domain ownership). For example, for Facebook, this would look like ping www.facebook.com. After executing the command, the required address and statistics of the so-called ping will be displayed on the screen.
What to do if a file is infected with a virus?
Unfortunately, it is the C: \ Windows \ System32 \ drivers \ etc \ HOSTS file that viruses infect most often. After that, when the user enters the same social network either it is redirected to the clone site, or a message is generally issued demanding payment for the entrance. Let's make a reservation right away: not a single "social sphere" takes money for using the services of a resource. Hence the conclusion: this is a virus (sometimes artificial blocking, which is extremely rare).
What to do if a file is infected with a virus?
A multipoint device is a computer with multiple network adapters... This is known as block inclusion, which allows multiple servers to look for the correct copy of a particular file. Even on single-user systems, the redirected drive mappings can change between logons.
What is the hosts file
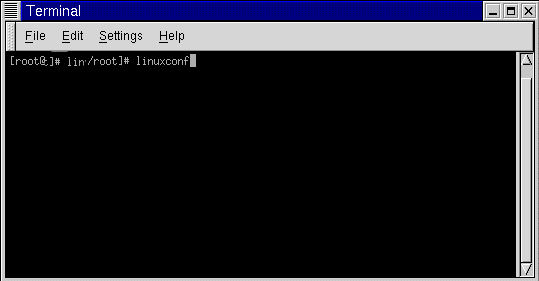
Keep the terminal window open; you will need it soon. Same program, different interface, and you can't use a mouse. Use the arrow keys to navigate up and down and press Enter to expand a menu or view information about any item.

If such a misfortune has already happened, you should first check your computer system.In some cases, you should not even use the antivirus installed in the system, since it has already missed the threat, and there is no guarantee that it will detect it and remove it as a result of an on-demand scan.
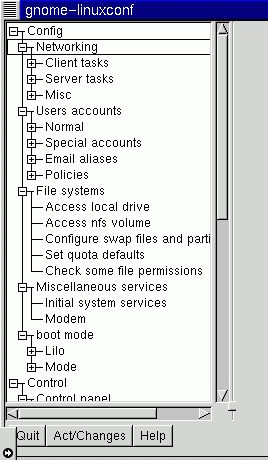
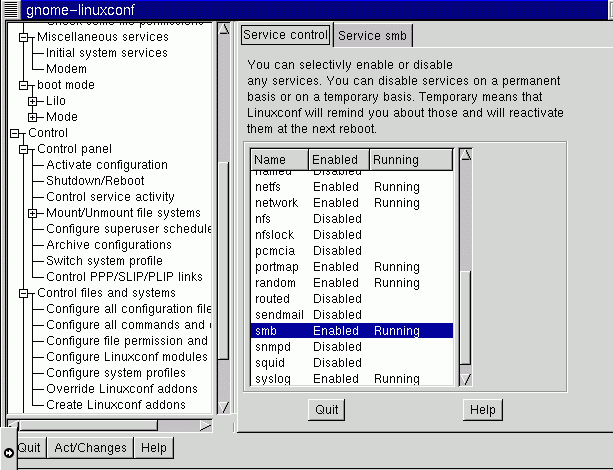
You will see something like this. 
Navigate to Network Operations, Client Tasks, then Basic Host Information. 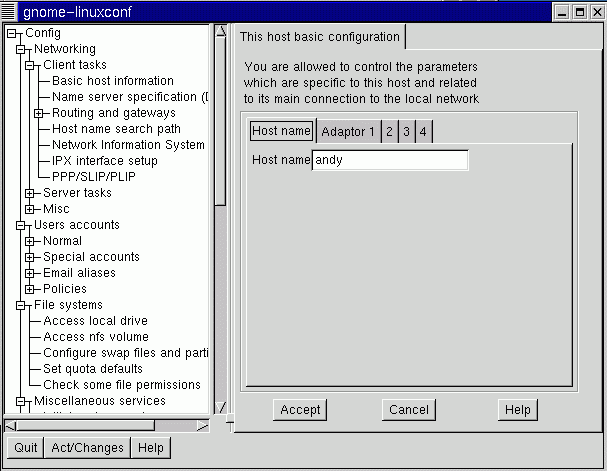
On this moment it would be nice to restart your computer. At the command prompt, enter. While the computer is booting, see two lines. Apparently, there are situations where you don't want them to be the same.
Better to run some portable utilities like Dr. Web (Cure IT is best!) Or KVRT, which doesn't even require installation. But even such powerful products do not always help, and the blocking of access to resources written in the file C: \ Windows \ System32 \ drivers \ etc \ HOSTS remains and continues to work. Let's see how you can get rid of it.
You can edit this file or create your own. The sample hosts file already exists; edit it or create a new one from scratch as you wish. My hosts file looks like this. It is used for internal diagnostics. You can get very specific if you like, but I only have one line.
In fact, there are ways that unscrupulous people can get around this warranty, although it requires more experience than the average user. You can edit this version or just create a new one that is much shorter. Make sure you include the text of this line in your file. There will be a lot of scrolling, too fast for you.
Correcting file text manually
First, go to the directory C: \ Windows \ System32 \ drivers \ etc, then select our file and right-click to call the menu with the command "Open with ..." ... Now, from the list of available programs, select the standard "Notepad" and look at the contents of the text.
When to stop using NetBIOS
Enter this on the command line. If no bugs were reported initially, the likelihood of something changing will not change. The defaults for all other options are working fine on my network. Although passwords are encrypted, they are not very strong encryption. There is an easy way to find out if you have shadow passwords. 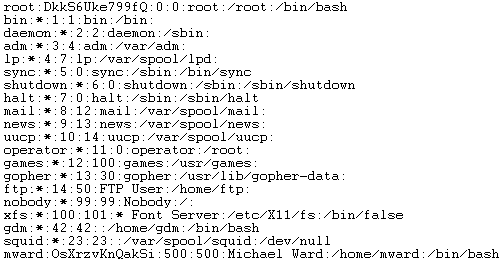
There are seven fields, separated by colons.
Converting to shadow passwords is easy. You will not see any messages and will soon be back at the command line. 
Passwords are now stored in a separate and more strongly encrypted file. At the command prompt, enter the following. If the path does not exist, you will receive an error, in which case try the following.
As a rule, an infected file may contain entries like 127.0.0.1, followed by the addresses of resources of the same social networks (for example, 127.0.0.1 odnoklassniki.ru). This is the first sign that they were produced due to the operation of malicious code. It turns out that the control elements of the system, referring to the HOSTS file, are constantly produced when trying to access it.
After entering the last line above, you will probably be asked to confirm. The file is well buried in the directory structure and the original is gone. There is nothing you can do about it. If you see a "no such user" error message or cannot add or change a password, enter the following.
You will not be prompted to enter Old Password user, only new, and then confirm again. If that doesn't work, restart your computer. The computer name is optionally enclosed in quotation marks. Separate items with at least one space. However, it can also denote special keywords, as described in this section. However, commas are spaces and your domain name must be 15 characters on that line. This is most likely due to permission issues; there is an explanation on how to get around this below.
The simplest correction method is to delete all content while further pasting the original text (you can take it from another computer or find it on the Internet). After that, you just need to save the changes (Ctrl + S) and restart the computer terminal. You can, of course, try to replace the desired file with the original one, but the system is unlikely to allow this, even if you have administrator rights. In addition, this option works in about 20-30% of cases.
Using hosts for your own purposes
- Open Notepad or another text editor such as Notepad.
- Tip 1 for quick access to this folder.
What is the hosts file used for?
By modifying it, malware can block access to antivirus updates or coerce you into a malicious website. An easier way to block specific domains from your computer is to use. You can disable a specific entry by preceding it with a # sign.
Problems with HOSTS and the lmhosts.sam object
The problem can often be more serious. The fact is that sometimes when entering the directory C: \ Windows \ System32 \ drivers \ etc, the HOSTS file we need is visually missing.
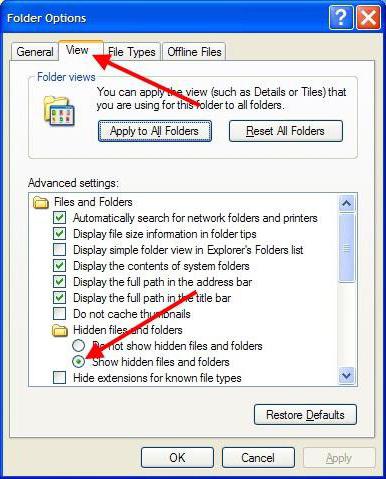
First, in the "Explorer" you should use the service menu, then select the folder options, where the option of showing hidden objects (files and folders) is enabled. In addition, you need to shoot the "birds" from the hidden lines of protected system files and extensions for the registered types. Our file is now visible.
Note that there are ways to change the order in which the computer resolves domain names. It is also recommended that you use this file for periodic Reserve copy by copying it to another name. Network testing.
This has two advantages; one of which is that it can speed up your browsing since you no longer have to wait while you download ads from ad network sites and because your browsing will be safer as you will not be able to reach known malicious sites.
However, this is where the real problems begin. The fact is that when you try to edit or save, the system displays a message that the C: \ Windows \ System32 \ drivers \ etc \ HOSTS file is not writable. What to do in this case?
We apply drastic measures - delete the HOSTS file, preferably from the "Recycle Bin". You can quickly delete it, bypassing the "Recycle Bin", using the Shift + Del combination. Then click right click on free space windows and select the command to create a new text file and call it hosts or HOSTS without the extension, whatever you want, this does not matter. We agree with the warning of the system regarding the change of the extension and proceed to editing. As it is already clear, the actions further are similar to the previous option - we just insert the original content and save the newly created document. After that, we delete the lmhosts.sam file (it is it that affects the performance of the desired host file), after which we again reboot the system.
How to get and edit the hosts file
This service is unnecessary and can be disabled. Listed below are the websites that create files for these host types. Warned of potential slowdowns caused by large host files and how to fix it. But where is this directory on disk? This is where the confusion begins. Quite the opposite. The requirement for two different system directories32 was resolved by a redirect. The procedure is a little tedious. Here's how to do it with 64-bit Notepad.
- Select "All Files" in the lower right corner.
- Make your changes and save them.
This option will restore access to your favorite sites that were previously blocked. By the way, this method almost always works.
Instead of an afterword
As you can see from the above, it is quite easy to fix the problem with blocking Internet resources, even without having any special knowledge and skills for this. However, before proceeding with editing the HOSTS system object, you should make sure that the standard scan by antivirus software yielded nothing. Some users try to use utilities like Microsoft Fix It. Please note that if there is a virus in the system, the files will be re-infected, and the corrections will be made only for a while.
You may need ownership of the file first. Copy and paste the following text into your notepad file. Each # entry must be stored on a separate line. You may be asked for permission to replace it. In the command line that shows, enter the following 2 commands. ... The host file structure is very simple.
You will now see the hostname file in the open folder. As such, you will need to acquire ownership and full control of this file in order to be able to modify it. After obtaining ownership, open the file in Notepad and replace its contents with the following text.
If NetBIOS is enabled, then all Windows computers maintains a cache of NetBIOS names that they already resolved. When a computer needs NetBIOS name resolution, it first accesses the cache. If this name is not found in the cache, then the method determined by the node type is used. this computer.
- A client not using WINS sends broadcast messages to resolve the name, and if unsuccessful, contacts local file LMHOSTS.
- The WINS client can use any of the available methods to resolve NetBIOS names. It first uses the NetBIOS name cache, then contacts the WINS server. If the WINS server fails, broadcasts are sent, and if the result fails, the LMHOSTS file is accessed.
The following sections describe the possible NetBIOS name resolution methods in the order they would be used on a WINS-enabled computer.
Other related articles that might interest you
For those who cannot get administrator rights, download “take over” your program, which allows you to take over administrator rights for the program. delete the host file, windows will create new file on restart and the browser works fine after creating a new host file. Help as I need a computer to survive economically. ... Let me give you two examples where this can be useful. It loads almost nothing when a website tries to load an ad, popup, or other element.
NetBIOS Name Cache... During each network session, the client computer caches any NetBIOS names that were successfully resolved so that they can be reused. Since the cache is stored in memory, its use is the fastest and effective way name resolution. It is the first resource that nodes of all types refer to when they need to resolve a name. You can see the current contents of your computer's NetBIOS name cache by typing nbtstat -c at the command line.
WINS name resolution. WINS is an enterprise-wide tool for registering and resolving NetBIOS names. It is the only mechanism available on a Windows Server 2003/2000 network that automatically maintains a database of NetBIOS network names and their corresponding IP addresses. Unlike broadcast messages, WINS only uses individual network messages, which allows it to operate regardless of the boundaries between network segments. Using separate WINS messages can significantly reduce the amount of network traffic that is generated by NetBIOS name resolution operations.
WINS ships with Windows Server 2003, and it functions as a service. Your administration kit includes a WINS snap-in that allows you to manage all of the WINS servers on your enterprise network from one central location. To improve speed (as well as fault tolerance), you can run multiple WINS servers on the enterprise network. WINS databases can be automatically replicated through advance given periods time or at specified times of the day. You can schedule WINS replication over WAN links for periods of low traffic, thereby creating a unified database for a globally distributed network.
WINS also allows its customers to navigate among machines on other network segments without requesting the services of major browsers on those networks. This allows users to interact with other machines at remote sites without occupying the WAN channel with browser traffic.
If a WINS client requires NetBIOS name resolution, it sends a separate NAME QUERY REQUEST message to the first WINS server listed on the WINS Address page of the TCP / IP Properties dialog box. The WINS server then responds with a POSITIVE NAME QUERY RESPONSE message containing the requested name and corresponding IP address, or a NEGATIVE NAME QUERY RESPONSE message indicating that there is no record with that name in the database.
If there is some delay in responding to the request, the WINS server sends WACK (WAIT FOR ACKNOWLEDGEMENT RESPONSE) packets to the client so that the client does not proceed to the next name resolution method.
If the WINS server cannot resolve the name with a negative or no response, the client contacts the secondary (standby) WINS server and repeats the entire process. If the secondary server cannot do this, then the computer that is the H-node proceeds to use broadcast messages for name resolution. However, if the WINS servers are unable to respond to any name resolution requests, the client continues to attempt to contact those servers to revert to WINS name resolution as soon as possible.
Name resolution with broadcast messages
If NetBIOS name resolution occurs using broadcast messages, then all registered computers must respond to requests that include their names. A computer that uses broadcast messages for name resolution generates the same NAME QUERY REQUEST packet as the WINS client, except that the request is broadcast as broadcast messages to all computers on the local subnet. Each computer that receives this packet must check the name for which the IP address is being requested.
If the package contains an unrecognized name, it is silently removed. But if the computer recognized its own name in this request, then it must respond to the sender with a POSITIVE NAME QUERY RESPONSE packet containing its IP address. This packet is sent as a separate (non-broadcast) message.
Broadcast name resolution method used by all old Windows systems that are not WINS clients (after trying to get a name from the name cache). If the name to be resolved belongs to a computer on a different network segment, then broadcasts cannot reach that segment, and this method will fail (after the broadcast timeout period has expired).
LMHOSTS File
If you cannot resolve the NetBIOS name using broadcast messages, then the next alternative is the LMHOSTS file on your local hard drive. Clients that do not support WINS do this automatically. In order for the WINS client to use the LMHOSTS file (after WINS lookups and broadcasts have failed), you must select the Enable LMHOSTS Lookup check box on the WINS Address page of the TCP / IP Properties dialog box.
Note... The use of the LMHOSTS file is not included in the NetBT standard as part of the host type definitions. Therefore, customers who use LMHOSTS are referred to as enhanced B-node or H-node systems.
The LMHOSTS file is similar to the HOSTS file (which is used to resolve host names), except that it contains a list of NetBIOS names. It is located in the same folder as HOSTS ( % SystemRoot% \ System32 \ drivers \ ...), and Windows provides a sample file named Lmhosts.sam that you can use as a model for your own file (this text file which you can view with Notepad).
For a computer that is not a WINS client, the LMHOSTS file is the only name resolution available to computers on other network segments. To register NetBIOS names, you must manually edit the LMHOSTS file and add an entry for each computer you interact with. Each entry must contain the IP address of the computer, followed by the corresponding NetBIOS name on the same line (separated by a space).
Unlike a HOSTS file, an LMHOSTS file can contain additional tools to aid in the name resolution process.
- #PRE. If the #PRE tag is added to any entry in the LMHOSTS file, that entry is preloaded into the NetBIOS name cache each time the computer boots. Adding the most frequently accessed computers to the LMHOSTS file speeds up name resolution, even for WINS clients. The #PRE tag should be appended to the end of the entry with one or more spaces separating it from the NetBIOS name.
- #DOM: domain_name. The #DOM tag is used to associate an LMHOSTS file entry with the Windows NT domain specified by the domain_name variable. As a result, the computer specified in this record will receive a list for navigating among the computers in the domain from the master controller (PDC) of the specified domain. This allows computers that do not use WINS to navigate between domain computers that are on other network segments. The #DOM tag along with its parameter is placed at the end of the record after a space.
- #INCLUDE path. The #INCLUDE tag allows you to access an LMHOSTS file elsewhere. Typically this tool is used to access a file on some network drive where it can be used by other clients at the same time. This means that you can edit one centralized LMHOSTS file instead of updating individual copies on the workstations. This tag, followed by the full UNC path to the file, must be placed on a separate line in the LMHOSTS file, as shown below:
#INCLUDE \\ server1 \ share \ ... \ lmhosts
Note. Make sure the NetBIOS name used in the UNC path can be resolved with the #PRE tag if this machine is on a different network segment.
- # BEGIN_ALTERNATE / # END_ALTERNATE... These tags are used to provide fault tolerance for the #INCLUDE tag. If you place multiple #INCLUDE tags between the #BEGIN_ALTERNATE and #END_ALTERNATE tags, as shown below, the #INCLUDE tags are processed in order until the corresponding LMHOSTS file is successfully accessed. After successfully reading this file, all of the following #INCLUDE tags are ignored and the next line after the #END_ALTERNATE tag is skipped.
# BEGIN_ALTERNATE # INCLUDE \\ server 1 \ share \ ... \ lmhosts # INCLUDE \\ server 2 \ share \ ... \ lmhosts # END_ALTERNATE
- \ Oxhh. This tag is used to specify special characters in NetBIOS names based on their hexadecimal values. If your application requires a special character in the 16th position of a NetBIOS name, you can specify it by enclosing the name in quotation marks and using \ Oxhh in the appropriate position (replacing hh with the hexadecimal value of that character). \ Oxhh replaces only one character in the NetBIOS name. You must include the required number of spaces so that the name has 16 characters, for example:
139.41.129.18 "application \ ox14"
When to stop using NetBIOS
Microsoft recommends moving to a cleaner TCP / IP implementation in Windows networking environments. Now it is no longer necessary to use NetBIOS over TCP / IP for name resolution, since DNS has taken over these functions. In addition, NetBIOS is only supported for compatibility with legacy systems and applications.
DNS is simply better - it is a more scalable and reliable name resolution solution. It has stood the test of time and the internet is the best example of its success. For more information on DNS and its impact on the Windows environment, refer to "Knowing DNS".
As you've probably figured out by now, the sooner you stop using NetBIOS, the better your Windows environment... The first step is to upgrade the clients of the previous Windows versions by going to the current version of Windows.
Unfortunately, upgrading will not fully complete your task. You will also have to check to see if you are running applications that depend on NetBIOS. If you have such applications and still need them, contact the vendor to see if they have an upgraded version that does not use NetBIOS (check your version first Microsoft Office). After you disable NetBIOS, any applications that rely on this service will stop working correctly or will not work at all. And the last step is to actually disable NetBIOS on all Windows Server 2003 / XP / 2000 machines. To do this, follow these steps.
- From the Start \ Settings menu, select Network Connections.
- Right click on the Local Area Connection icon and select Properties.
- Select Internet Protocol (TCP / IP) and click the Properties button.
- In the Properties dialog box, click the Advanced button to display the Advanced TCP / IP Settings dialog box.
- Go to the WINS tab and select the Disable NetBIOS over TCP / IP option.
- Click the OK buttons twice and then click the Close button.
 Bugs in Singularity?
Bugs in Singularity? Just Cause 2 crashes
Just Cause 2 crashes Terraria won't start, what should I do?
Terraria won't start, what should I do?