Photo of a keyboard with Russian layout. Computer keyboard - buttons, layouts, classification
Hello!
Today I decided to introduce you to the computer keyboard. Now everything is easy to find on the Internet, but I decided to make an assembly. I would like all this to be at hand, so you can save yourself a link on your page by clicking on the social media button. Although the article turned out to be very tricky, but
knowing this, you can make your job easier and save time!
So, function keys.
F1- calls "help" Windows or the help window of the active program. V Microsoft Word the key combination Shift + F1 shows text formatting;
F2- renames the selected object on the desktop or in the explorer window;
F3- opens a search box file or folder on the desktop and in File Explorer. The Shift + F3 key combination is often used to search backward;
F4- opens a dropdown list for example, listing the address bar in the 'My Computer' window or in Explorer.
Keyboard shortcuts Alt + F4 on Windows it is used to close applications,
a Ctrl + F4- to close a part of a document or program (for example, tabs);
F5- updates the active window open web page, desktop, explorer, and so on. In Microsoft PowerPoint, F5 starts the slideshow from the beginning, and the Shift + F5− key combination starts from the current slide;
F6-switching between screen elements in a window or on the desktop. In the explorer and Internet Explorer- moving between the main part of the window and the address bar;
F7- checks spelling(in Word, Excel);
F8- when loading the operating system, selects boot mode... In the Word editor, includes enhanced text selection. The selection of a fragment from the initial to the final position of the cursor occurs without holding down the Shift key.
Repeated pressing The F8 key selects the word closest to the cursor. The third is a sentence containing it. Fourth paragraph. Fifth, the document. You can remove the last selection by pressing the Shift + F8 keyboard shortcut. You can disable the mode by pressing Esc;
F9- in some programs updates the selected fields;
F10- activates p full menu, and the key combination Shift + F10 activates the context menu;
F11- moves the window to full screen mode and vice versa, for example, in Internet Explorer;
F12- go to the selection of parameters save file a (File -> Save As).
Ctrl(read "control") - used in combination with other keys, for example: Ctrl + A- in Windows, selects all the text in the window; Ctrl + B- in MS Word editor switches the font to "bold-normal";
Ctrl + C- in programs with WinAPI copies the text to the clipboard, and in console programs - completes the command; Ctrl + F- in many programs calls the search dialog;
Ctrl + I- in the MS Word editor switches the font to "italic-normal";
Ctrl + N- in programs with a multi-window interface, opens a new empty window;
Ctrl + O- in many programs calls the dialog for opening an existing file;
Ctrl + P- in many programs sends text to print or calls the print dialog;
Ctrl + Q- in some programs, exit from it;
Ctrl + R- in browsers, updates the contents of the window;
Ctrl + S- in many programs saves the current file or calls the save dialog;
Ctrl + T- opens a new tab in browsers;
Ctrl + U- in MS Word editor toggles text underlines;
Ctrl + V- in programs with WinAPI, inserts the contents of the clipboard;
Ctrl + W- in some programs, closes the current window;
Ctrl + Z- in many programs cancels the last action;
Ctrl + F5- updates the content in browsers;
Ctrl + Home- in programs with a text field, it moves to the beginning of the edited document; Ctrl + End- in programs with a text field, it jumps to the end of the edited document;
Ctrl +- v Total commander makes a transition to the root directory of the disk.
Alt(read "Alt") - used in conjunction with other keys, modifying their action. For example: Alt + F4- in all programs closes them;
Alt + F7- in some programs calls the search dialog;
Alt + F10- In some file managers calls a directory tree;
Alt + Tab- in Windows, goes to the next running window;
Alt + letter- in some programs calls menu commands or opens menu columns. Also, the keyboard shortcuts Alt + Shift or Ctrl + Shift usually used to switch keyboard layouts NS.
Keyboard buttons to remember
 - if you press this button and, without releasing it, on any key with a letter, the letter will be printed in capital. In the same way, you can print a symbol instead of a digit: No.! () *? "+ Etc.
- if you press this button and, without releasing it, on any key with a letter, the letter will be printed in capital. In the same way, you can print a symbol instead of a digit: No.! () *? "+ Etc.
After pressing this button once, all letters will be printed in large. You do not need to hold it for this. To return to small print, press again Caps lock.
Indents (red line).
![]() is a space. With this button you can make the distance between words.
is a space. With this button you can make the distance between words.
 - drops one line below. To do this, put a blinking stick (blinking cursor) at the beginning of the part of the text that you want to move down, and press the Enter button.
- drops one line below. To do this, put a blinking stick (blinking cursor) at the beginning of the part of the text that you want to move down, and press the Enter button.
 - deletes the character in front of the blinking cursor. Simply put, it erases the text. Also, this button raises the text one line higher. To do this, put a blinking stick (blinking cursor) at the beginning of the part of the text that you want to move up, and press Backspace.
- deletes the character in front of the blinking cursor. Simply put, it erases the text. Also, this button raises the text one line higher. To do this, put a blinking stick (blinking cursor) at the beginning of the part of the text that you want to move up, and press Backspace.
Capslock(read "Capslok") - transition to upper case mode (fixed switching). Pressing the key again cancels this mode. Used when typing in CAPITAL letters.
Control key Esc(read "Escape"), used to undo the current operation or the last change, minimize the application, go to the previous menu or screen, or deselect, located in the left corner of the keyboard next to the block of function keys.
Keyboard shortcut Ctrl + Shift + Esc calls the Task Manager.
Tab(read "Tab") - in text editors introduces tab character and works with indentation, and in GUIs moves focus between elements.
Key action AppsKey tantamount to clicking right click mouse and calls the context menu for the selected object.
Line feed key Enter(Input) - serves to enter a line feed when typing text, select a menu item, submit a command for execution or confirm an action, and so on.
(reads "Backspace") - in text editing mode, deletes the character to the left of the cursor, and outside the typing area - returns to the previous screen of the program or web page in the browser.
Delete(read "Divides") - deletes the selected object, selected text fragment or character to the right of the input cursor.
Key Insert(read "Insert") is used to switch between the modes of insertion (the text is as if moved apart) and replacement (new characters replace the existing text) when editing text.
Keyboard shortcut Ctrl + Insert replaces the "copy" command, and Shift + Insert- "insert". In the file managers Total Commander and FAR Manager, the key is used to select a file or folder.
PrtScn(print screen) (read "Print screen") - takes a screenshot and places it on the clipboard. In combination with the Alt key, a snapshot of the currently active window is copied to the clipboard.
The ScrLk (Scroll Lock) service key (read "Scroll Lock") blocks scrolling and when it is activated with the cursor keys, the contents of the entire screen are shifted, which is very convenient when editing large tables, for example, in Excel.
Pause / Break(read "Pause" or "Break") - suspends the computer. In modern operating systems this key is only relevant when the computer boots up.
The up, down, right and left arrows refer to the cursor control keys and allow you to navigate through the menu items, move the input cursor to the corresponding side by one position. Combined with the Ctrl key, the arrows move to a greater distance. For example, in the Microsoft Word editor Ctrl + ← moves the cursor one word to the left. WITH with the Shift key a block of text is highlighted.
Keys Home and End move the cursor to the beginning and end of the current line in a document or list of files. What hotkeys are useful to know.
Keyboard shortcut Ctrl + Shift + Esc indispensable when the computer freezes, it calls the "Task Manager", with which you can end the process, remove the task or shut down the computer.
Keys Alt + Tab let you switch between open windows... A panel with all open applications appears in the center of the screen, and when you select the active window, you need to press the Tab key several times without releasing the Alt key.
Combination Alt + Space(spacebar) opens the window's system menu, with which you can restore, move, maximize, minimize and close the window without using the mouse.
Alt + Shift or Ctrl + Shift- switching keyboard layouts.
With help Win + D you can minimize all windows and show the desktop, and the Win + M keys minimize all windows except dialog ones.
Win + E opens the My Computer folder.
Win + F- opens a window to search for a file or folder.
Frequently used keyboard shortcuts:
Ctrl + Shift + Esc - Opens the Task Manager.
Ctrl + F - search box in the active program.
Ctrl + A - Selects all content in the open window.
Ctrl + C - copy the selected fragment.
Ctrl + V - paste from clipboard.
Ctrl + P - print the current document.
Ctrl + Z - cancel the current action.
Ctrl + X - cut the selected area of text.
Ctrl + Shift + → selection of text by words (starting from the cursor position).
Ctrl + Esc - Opens / closes the Start menu. Alt + Printscreen - screenshot of the active program window.
Alt + F4 - Closes the active application.
Shift + Delete - irrevocable deletion object (past the basket).
Shift + F10 - Call context menu active object.
Win + Pause - system properties.
Win + E - launches explorer.
Win + D - minimizes all open windows.
Win + F1 - Opens Windows Help. Win + F - brings up the search box.
Win + L - lock your computer. Win + R - open "Run the program".
How to make symbols on the keyboard if there are no such keys?
This can be done using Alt codes, simultaneously pressing Alt and a number.
For example,
Alt + 3 =
Alt + 8734 = ∞
Alt + 0128 = €
Attention! If additional numeric keypad not enabled - Num Lock is not pressed, then the Alt + number key combination may lead to unexpected results. For example, if you press Alt + 4 in the browser, without Num Lock enabled, the previous page will open.
Here are the tables of the symbols of the codes on the keyboard (click on the picture to enlarge).

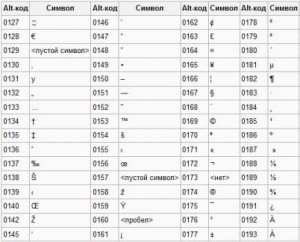
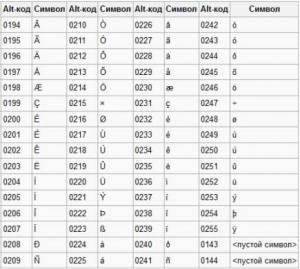
Punctuation marks with Cyrillic
"(Quotes) - Shift + 2
No. (number) - Shift + 3
; (semicolon) - Shift + 4
% (percentage) - Shift + 5
: (colon) - Shift + 6
? (question mark) - Shift + 7
* (multiplication or asterisk) - Shift + 8
((open bracket) - Shift + 9
) (close bracket) - Shift + 0
- (dash) - button with the inscription "-"
, (comma) - Shift + "period" + (plus) - Shift + button with a plus sign "+"
... (dot) - the button to the right of the letter "U" Punctuation marks with Latin letters
~ (tilde) - Shift + Ё
! (exclamation mark) - Shift + 1
@ (dog - used in the address Email) - Shift + 2
# (hash) - Shift + 3
$ (dollar) - Shift + 4% (percentage) - Shift + 5 ^ - Shift + 6
& (ampersand) - Shift + 7 * (multiplication or asterisk) - Shift + 8
((open parenthesis) - Shift + 9) (close parenthesis) - Shift + 0
- (dash) - key on the keyboard with the inscription "-" + (plus) - Shift and +
= (equal) - button equal sign, (comma) - key with the Russian letter "B"
... (dot) - key with the Russian letter "U"
< (левая угловая скобка) - Shift + Б
> (right angle bracket) - Shift + U
? (question mark) - Shift + button with a question mark (to the right of "Yu")
; (semicolon) - letter "Ж"
: (colon) - Shift + "F"
[(left square bracket) - Russian letter "X"
] (right square bracket) - "b"
((left curly brace) - Shift + Russian letter "X"
) (right curly brace) - Shift + "b"
How do I change the keyboard layout?
there are two ways to do this: by pressing Alt + Shift or Ctrl + Shift. Typical keyboard layouts are English and Russian. If necessary, you can change or add the keyboard language in Windows 7 by going to Start - Control Panel - Clock, language and region (sub-item "changing keyboard layout or other input methods"). In the window that opens, select the "Languages and keyboards" tab - "Change keyboard". Then, in a new window, on the General tab, click Add and select the desired input language. Don't forget to save your changes by clicking "OK".
Keyboard - a keyboard device designed to control the operation of a computer and enter information into it. Information is entered in the form of alphanumeric character data.
The standard keyboard has 104 keys and 3 indicator lights in the upper right corner informing about the operating modes.
Many modern computer keyboards, in addition to the standard set of one hundred and four keys, are equipped with additional keys.
Keyboard device
Keyboard- is a matrix of keys combined into a single whole and an electronic unit for converting a keystroke into a binary code.
Typeskeyboards:
membrane (film),
touch (capacitive),
semi-mechanical,
mechanical.
Membrane: when the keys are pressed, two membranes are closed. In places of contact, the membranes have special. coating that provides low contact resistance. The membranes look like discs on printed plastic sheeting. 20-30 million clicks.
Advantages:
1.the membranes are located on the inner side of the film, so the structure is well protected, for example, from spilled coffee;
2. low noise;
3. ease of pressing the keys;
4. protection from small objects and liquids;
5. low price.
Flaw: fragility.
Touch (capacitive) keyboard. Its principle of operation is based on the amplification of the potential difference applied to one element. Inside the button is an electrode attached to the button and two metal protrusions on the printed circuit board that form the fixed electrodes of the variable capacitor. When you press the button - the electrode approaches the protrusions and changes its capacity - the circuit is triggered. 100 million or more clicks.
MeritsO: greater reliability of the keyboard.
Semi-mechanical : more durable and non-rubbing metal contacts are used, in expensive models they can be gold-plated. All this is located on the printed circuit board. The key is returned by a rubber dome. Similar to the previous ones, but more expensive. 50-100 million clicks
Dignity: durability.
Mechanical: the key is returned by a spring.
Advantages:
1. durability;
2. reliability;
3. there is no fatigue, that is, the resistance to pressing does not depend on the number of pressing.
disadvantages:
1. there is no tightness (although there are models with protection);
2.noisiness;
3. high price.
Ergonomicskeyboards
An ergonomic keyboard means the user-friendliness of the keyboard:
The thickness of the keyboard (the thinner the better) and the angle of inclination (optimal 15 degrees);
layout of keys, shape and size;
coefficient of reflection of light from the entire surface of the keyboard;
ease of reading inscriptions;
the required effort to press the key and its free return.
There are two general layout principles for keyboard performance:
monoblock - the keyboard is made as an integral part of the system unit (Notebook);
polyblock - the keyboard is designed as a separate device.
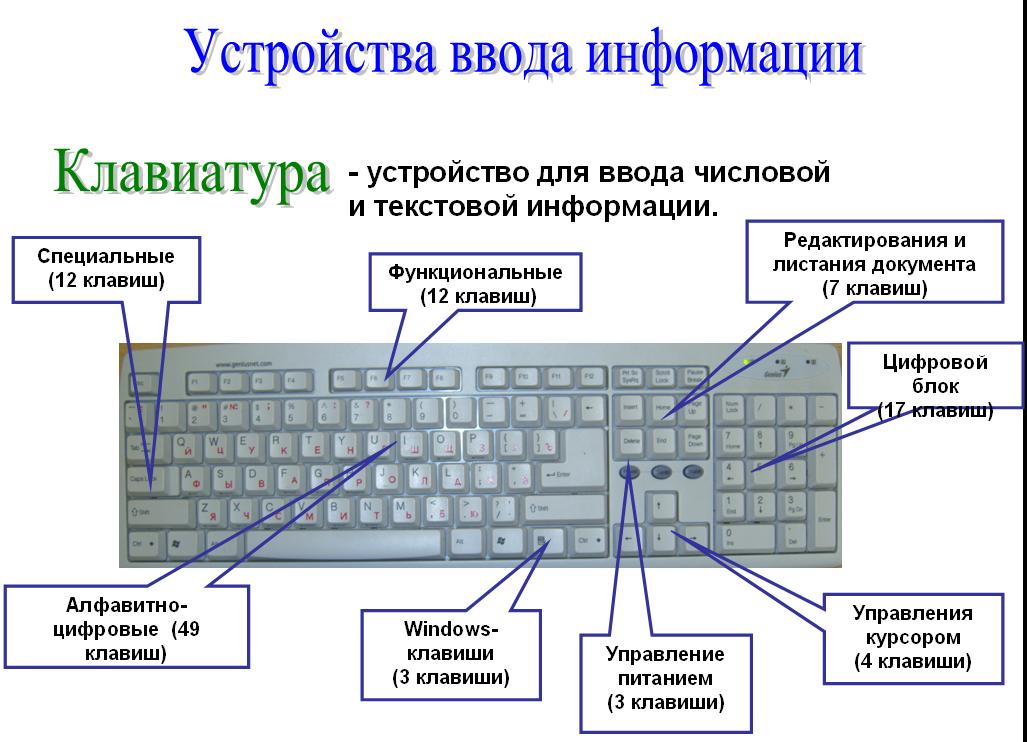
Groupskeyskeyboards
1. Alphanumeric and Signed
Typewriter keys for entering upper and lower case letters, numbers, and special characters;
2. Function keys fromF1beforeF12
a function is associated with each key, different programs have different functions)
3. Cursor keys(8 pcs.): Arrow keys (up, down, right, left), Home (move the cursor to the beginning of the line), End (move the cursor to the end of the line), Page Up (move the cursor one page up), Page Down ( moving the cursor one page down)
4. Register switch keys: Caps Lock, Num Lock.
5. Modification keys(auxiliary keys) Ctrl, Alt, Shift
6. Rest: Esc - exit from the program, cancel any action, Tab - move the cursor a fixed number of positions forward, Space - key for setting a space, moving the cursor one position forward, Enter - key for completing a command, moving the cursor to another line, Bask Space - moving the cursor to the left and erasing characters, Print Screen - printing the image, Scroll Lock - scrolling the screen, Pause - setting a pause, Insert - enabling the insert / replace mode in typing mode, Delete - deleting the character above the cursor

Keyboard connection interface
There are three types of interface:
AT, PS / 2 and USB interface.
AT - is already outdated;
PS / 2 - for motherboards ATX format (purple), round;
USB - slotted rectangular connector.
Computer keyboard- buttons, layouts, classification
Captain Obvious briefly glanced at our light and suggested that the computer keyboard is one of the critical devices data entry. If not the most important thing. Therefore, it is imperative to talk about this thing with buttons. Moreover, in accordance with tradition, to tell not just like that, but from the point of view of a practical person. Therefore, we will focus on what types of keyboards are suitable for solving industrial and professional, social, everyday and creative tasks.
Brief classification
Standard panel with pushbuttons to be connected to system unit is traditionally referred to as "AT" or "PC / AT". According to legend, this designation comes from the old computers "IBM / AT", produced from 1984 to 1990.
In addition, the configuration is marked as "QWERTY-keyboard", since the left half of the top row of alphabetic buttons contains exactly these Latin letters. Thus, the structural and conceptual difference from the keyboards of a mobile phone, calculator, ATM and other electronic digital devices is emphasized.
According to the form of existence of the keyboard there are:
- physical, materialized in a plastic incarnation;
- on-screen, virtual, appearing on displays;
- projection, drawn with a laser beam on the table surface.
By their structure, there are
- full, with a numeric block on the right, where the buttons are arranged approximately like a calculator;
- without the above excess;
- multimedia, hung additional buttons and looking almost like a starship control panel.
Available in small laptops and screens in tablet PCs - usually without a digital block. Such, in general, is not so badly needed.
Projection screens are suitable only for stationary workstations with an available table surface, since they are extremely difficult to use on the street, in the park on a bench, lounging on a sofa among the pillows, in an armchair with a laptop on your lap, and so on.
Keys
Strictly speaking, the computer keyboard is the successor of typewriters. Without further ado, people have kept the time-tested layout of the buttons, if we talk about the alphanumeric part. But they added something. However, we will consider everything in detail.
The topmost row is the so-called function keys F1 ... F12. For what they are needed, this is determined by the software. There are some traditional actions though. For example, F1 calls up the help system, F11 maximizes browser windows to full screen, and F5 refreshes the contents of them. However, it all depends on the software developers.
Below is a series of numbers. Moreover, without pressing Shift, these are just numbers, and with pressing - other symbols. Such as "@", "#", "$" if English keyboard is enabled. If Russian - quotes, "№", ";" ... Exclamation point, snowflake and brackets are common. But we'll get to layouts later.
The same is with the letters arranged in three rows. Large ones are sent to the computer either in combination with the pressed Shift, or with activated mode Caps Lock.
In other words, Shift serves to expand the functionality of the keyboard. Like Alt with Control (Ctrl). For example, F4 does what is assigned by the program (or does nothing at all), but Alt + F4 closes the active window.
The Longest Key, aka Any Key, is a space. Also exactly like a typewriter. In dialog boxes, it often works like Enter, confirming input.
In general, directly with typing and editing text, you can figure it out pretty quickly. The main thing is to remember that Backspace - erasing a character, not moving the cursor to the left. Arrows are intended for translation.
MUNICIPAL EDUCATIONAL BUDGETARY INSTITUTION
SECONDARY EDUCATIONAL SCHOOL NAMED AFTER FATIKH KARIM S. AITOVO
KEYBOARD LOCATION PRINCIPLE
Completed by: Vafina Ilyuza Ildusovna, MOBU Secondary School named after Fatih Karim s. Aitovo, grade 6
Leader: Amineva Salima Gabdrashitovna, teacher of informatics, MOBU secondary school named after Fatih Karim s. Aitovo
Aitovo-2017
Content:
Introduction …………………………………………………………………… ... 3
Chapter 1. From the keyboard …………………………………………… 5
Chapter 2. Research of texts …………………………………………… ..11
Conclusion ……………………………………………………………… ..14
List ..15
Appendices ………………………………………………………………… .16
Introduction
Relevance
Currently Personal Computer more and more enters the life of people.Schoolchildren have to type a lot, preparing various messages, reports, abstracts for lessons or chatting.
When I first sat down at my computer and started typing, I was faced with the fact that it was difficult for me to find the desired letter on the keyboard. However, I noticed that over time, my fingers got a little used to this strange arrangement of letters. But still, I continued to think about why the letters on the keyboard are not arranged alphabetically, but are scattered in a mess.Then everyone would know that the letter "A" is in the left corner of the top row, and the letter "I" is in the opposite right corner of the bottom row, and he would not be looking for anything. It was decided to conduct a study and determine what the order of letters on keyboards depends on.
Purpose of my research: find the answer to the question "Why did you need to arrange the letters so inconveniently?"
Research hypothesis: the arrangement of letters on the keyboard depends on the frequency of their use in different texts.
Purpose and hypothesis of the study identified the followingtasks:
pick up several texts that are different in content and meaning;
analyze the result;
find out how this arrangement of letters appeared on the keyboard;
make a conclusion about whether the arrangement of letters on the keyboard depends on the frequency of their use in the text.
Object of study: keyboard.
Research methods: analytical, comparative.
The practical significance of the study: dIn order to increase the speed of typing, you need to know the layout of the keys on the keyboard, learn the ten-finger blind method of typing text.
From keyboard history
I decided to start my work by searching for information on the Internet and fiction. In Wikipedia, I found the definition of a keyboard.
Keyboard - a set of keys arranged in a certain order for controlling a device or for entering data.
Computer keyboard - a device for entering information into a computer and supplying control signals. Contains alphanumeric, special, function and cursor keys. Then I began to study the history of the keyboard.
The history of the keyboard began with the invention of the typewriter. The first such machine was invented by Henry Meal in 1714, that is, almost three hundred years ago. However, no information about its device has survived, as, indeed, the typewriter itself .. In the next 60 years, several more printing devices were created, but they did not receive much popularity.
But in 1863, the ancestor of all modern printing machines already appeared. Invented it Christopher Sholes and Samuel Soule are both former printers. First, they came up with a device for numbering pages in counting books, and then the idea came up - to build a machine that prints words on the same principle.
In 1869, our compatriot, Mikhail Ivanovich Alisov, developed his own version of a typewriter, which he named "The Fast Printer". "Fast printer" allowed typing text at a speed of up to 120 characters per minute. In 1873, the car was shown at the World Exhibition in Vienna and was awarded a medal. However, it did not go into mass production, since the very first batch he made (in 1877) was equated with printing machines in relation to compliance with censorship regulations. And all because of High Quality the resulting print, indistinguishable from the typographic one. As a result, those wishing to purchase a bunch of additional problems with the machine were not found.
The most common was the American typewriter. The first version of their typewriter had two rows of keys with numbers and an alphabetical arrangement of letters from A to Z (there were no lowercase letters, only capital letters, there were also no numbers 1 and 0 - the letters I and O were used instead), but this option turned out to be inconvenient. Why? There is a legend according to which, when quickly sequentially pressing on the letters located nearby, the hammers with the letters got stuck, forcing them to stop work and rake the jam with their hands. But this is just a legend.
The alphabetical arrangement of letters turned out to be inconvenient, so the inventors made an attempt to improve the arrangement of letters on the keyboard, the result of which is the QWERTY we know.
According to another legend, Scholes's brother analyzed the compatibility of letters in English and proposed an option in which the most common letters are spaced as far as possible, which made it possible to avoid sticking when typing. However, there are other versions as well. According to one of them, it is assumed that they could, in search of the optimal arrangement of letters, consult with typographers (for whom the letters in the typesetting boxes were not at all alphabetical). This keyboard is named "QWERTY", as the letters of the first row are located in this order. A quick glance can be really convinced that this is the case. The QWERTY keyboard is a keyboard that made typists work slower. This means that more and more people were forced to learn this system and more and more companies - to make such keyboards, until it became the only existing standard.

QWERTY keyboard
We must admit that the arrangement of letters on the QWERTY keyboard is far from the most rational. A much more convenient layout was invented by Arthur Dvorak, a professor of statistics at the University of Washington. It contains frequently used letters in the middle and upper rows. Under the left hand in the middle row are all the vowels, and under the right hand are the most frequent consonants.
At the same time, the load on the arms is more balanced. Judge for yourself: in an 8-hour working day, our fingers travel about 2 km on the Dvorak keyboard, while on traditional keyboard QWERTY the same figure is already 7 kilometers. Accordingly, the typing speed on the Dvorak keyboard is 2 times higher than on the QWERTY keyboard.

Dvorak keyboard
Key point The transformation of the typewriter into a computer keyboard was the invention in the late 19th century of the Baudot teleprinter. This method replaced the telegraph. In the Baudot connection, a code was used to encode the letters of the alphabet, with the help of which complex electromechanical devices printed the received text onto paper.Communication was synchronous, and the telegraph operator had to press the button only when he received a special sound signal.
The year 1943 was marked by the advent of the ENIAC computer (an application that made a splash in the world of science. This computer was used by the military for ballistic calculations. It received initial data through punched cards and teleprinter tapes.
In 1948, the development of UNIVAC (Application) and BINAC (Application) computers began, intended not for single, but for relatively more mass production. Special attention in these machines was paid to input-output devices. The means of input-output for them were teletypes or tabulators-punchers. BINAC could write information to magnetic tape.
1960 marks a watershed in the history of computer keyboards - an electric typewriter enters the market. She had a capacitive keyboard.
The capacitive keyboard was produced on printed textolite boards. Such a keyboard allowed you to enter text at a speed of up to 300 characters per second. Its main advantage was the ease of entering text - now, to type, you did not need to put as much effort as, for example, on the classic Scholze typewriter.

A standard computer keyboard has 101 or 104 keys. The arrangement of the keys on the keyboard obeys a single generally accepted scheme, designed based on the English alphabet.
According to their purpose, the keys on the keyboard are divided into four main groups:
functional;
alphanumeric;
cursor control;
digital panel.
In the center are locatedalphanumeric keys... They have numbers on them Special symbols("!", ":", "*", Etc.), letters of the Russian alphabet, Latin letters. With the help of these keys, they type all kinds of texts, arithmetic expressions, write programs. At the bottom of the keyboard is a large key without symbols on it - "Space". Space is used to separate words and expressions from each other.
When working with a keyboard, to enter text, they usually use thiscalled the blind ten-fingermethod, i.e. each key on the keyboard is assigned to a specific finger, thus the user types text without looking at the keyboard.
Unfortunately, the Russian computer keyboard also has drawbacks. For example, for a comma, which is used, you see, very often, they did not bother to select a separate key, but placed it on the same key on which the period is located - in upper case! Therefore, in order to print a comma, you need to press two keys. Maybe that's why modern schoolchildren who like to surf the Internet so often skip commas? ..
Research of texts
I have selected three excerpts from texts that are different in content and meaning:

I counted out exactly 500 characters in each text, and then proceeded to calculate the frequency of using the letters of the alphabet. The counting results were entered into a separate table. (ANNEX 1).

I compared the arrangement of letters on a computer keyboard and on a typewriter keyboard, which until recently was one of the main devices for typing typed text.
Research results
After doing research, I got the following results:
The letters located in the center of the keyboard appeared from 30 to 66 times in the text, while the letters located at the edges - no more than 10 times, i.e. less often 3 times, or even 15-20 times. For example, in 2 text the letter "o" was encountered 66 times, and the letter "f" - 2 times, in 1 text the letter "i" was encountered 42 times, and the letter "z" only 7 times. (ANNEX 1).
The frequency of using letters in different texts is different, but letters located in the center of the keyboard are found in all texts much more often than letters located at the edges (APPENDIX 2).
Having noted on the keyboard the keys with the letters that have the highest frequency of use, I saw that the index finger is mainly responsible for pressing these keys in the ten-finger blind method, and also some keys correspond to the middle fingers of the left and right hands (APPENDIX 2).
In the process of counting, in addition to letters, I counted the frequency of use of other symbols. More often than other characters in all texts there is a "space", the key of which is located at the bottom of the keyboard and is much larger in size than other keys. Consequently, when typing, it is used much more often than other keys (APPENDIX 3).
After comparing the arrangement of keys on a computer keyboard and a typewriter keyboard, I came to the conclusion that the letters on them are located the same.
Having studied the location of the keys on the keyboard and analyzed the calculations of the frequency of using the period and comma, I found that the comma occurs in most texts more often than the period (APPENDIX 4).
For example, in texts 1 and 3, the comma occurs 13, 7 and 4 times, and the period only 4 times. However, on the keyboard, the comma is in upper case, i.e. in order to write a period, you need to press one key, and in order to write a comma, you need to press two keys. Quite a big drawback of the Russian keyboard layout, which slows down the typing speed.
conclusions
Based on the results of the work done, I came to the following conclusions:
The letters that are more common in text are located in the center of the keyboard. This is done to increase the speed of typing using the ten-finger method, as well as to reduce the time it takes to move your fingers from key to key. The center of the keyboard is chosen because the more popular letters have to be pressed with dexterous fingers.
The letters on the computer keyboard are arranged in the same way as on a typewriter.
The QWERTY key layout makes it easier for the computer user to enter text.
Conclusion
My hypothesis was confirmed: the location of the letters on the keyboard depends on the frequency of their use in different texts.
In order to increase the speed of typing, you need to learn the ten-finger method of typing text.At the same time, there will be no need to be distracted by the search for the necessary keys, thereby significant time savings, convenience and freedom when working with text are possible.
In addition, I concluded that the study can be continued further, figuring out how to arrange the frequently occurring letter combinations more profitably in order to further reduce the time for typing.
I think that those who work with texts should definitely know the Russian layout of the QWERTY keyboard and master the ten-finger blind method of typing text. To teach this method, you can use various computer simulators: Baby Type, Stamina, Virtuoso, etc.
About the location of letters on the keyboard
Electronic encyclopedia "Computer". Keyboard.
Today - education, tomorrow - success. Aitovskaya school - 100 years. - Ufa, 2013.-232 p., Editor: R.Z. Sultanov.
Moments of life. The book of memoirs / dedicated to the 50th anniversary of Ildar Gimaev.- Ufa: Mir print.-2012.-112s. + Ill. 32s.
An article in the newspaper "Light Path".
ANNEX 1
SymbolsText 1
Text 2
Text 3
O
49
66
47
NS
15
10
12
R
21
15
27
with
21
22
21
T
22
21
28
at
11
11
7
f
5
2
4
NS
1
2
6
c
3
3
2
h
9
15
3
NS
5
7
3
SCH
1
0
0
b
0
0
0
NS
9
9
5
b
9
5
11
NS
1
1
4
NS
1
0
1
I am
6
5
13
Total
422
418
442
SymbolsText 1
Text 2
Text 3
a
30
40
32
b
4
9
8
v
19
6
11
G
8
10
10
d
9
7
13
e
23
28
41
e
2
3
2
f
5
1
4
s
7
7
10
and
42
21
45
th
4
7
4
To
17
12
10
 Backlash of the volume and power buttons on the iPhone - a marriage or not?
Backlash of the volume and power buttons on the iPhone - a marriage or not? The network card does not see the cable: instructions for solving the problem What to do if the Internet cable does not work
The network card does not see the cable: instructions for solving the problem What to do if the Internet cable does not work StoCard and Wallet: discount cards from the application
StoCard and Wallet: discount cards from the application