Symbolic keys. Flash, Keyboard Keys Designation
Bashkir Economic and Legal College
Specialty 480201 "Law and organization of social security"
FINAL WORK
by discipline: "Informatics"
on the topic: "Keyboard, purpose and use of the main groups of keys»
Completed by: Khismatullina Ilyuza
Checked by: Bikbulatova A.F.
r.p. Chishmy - 2015
Introduction
1. Purpose of the keyboard
2. Types of keyboards
Conclusion
Bibliography
Introduction
The keyboard is one of the main parts of a computer. It is used to enter alphanumeric data and control the operation of the computer.
There are many different keyboard designs available today. Also keyboards differ in functionality.
The keyboard is something that, along with the mouse, is in direct contact with the user, respectively, in many respects determines whether you will feel comfortable or not very comfortable when working with a computer.
Someone will say that the keyboard is a relic, and that now the mouse is needed much more often than the keyboard. This is true and not. On the one hand, we live in an age of total dominance of Windows, but even this operating system, with its graphical interface, cannot completely do without a keyboard. After all, they have not yet invented another text input device. Of course, many attempts are being made to develop speech recognition systems, but they are not that far from perfect, they are just monstrously far from it. There are also attempts to recognize handwriting, but these systems are also imperfect. And if you work in a terminal, some DOS program, or just chat, then you definitely cannot do without a keyboard.
The purpose of the abstract is to consider the keyboard as a modern basic element of the computer.
1. Purpose of the keyboard
The IBM PC keyboard is designed to enter information from the user into the computer. Typing on the keyboard is still the main method of entering alphanumeric information from the user into the computer. Each key on the keyboard is a cover for a miniature switch (mechanical or membrane). The keyboard contains a small microprocessor that monitors the state of these switches, and when each key is pressed or released, it sends a message (interrupt) to the computer, and the computer programs ( operating system) process these messages
Conventionally, four groups of keys can be distinguished on the keyboard:
1. Alphanumeric and sign keys (space, numbers 0-9, Latin letters A-Z, symbol Cyrillic A-Z, punctuation marks, service symbols "+", "-", "/", etc.).
2. Function Keys: F1, F2, F3 ... F12.
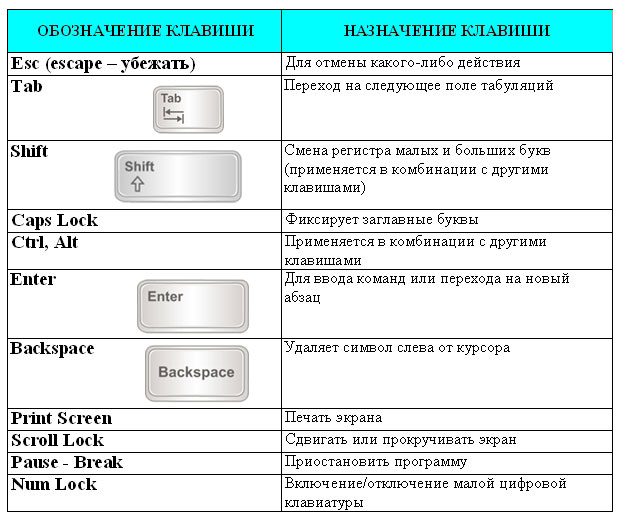
3. Service keys: Enter, Esc, Tab, arrow keys Left, Up, Down and Right, PgUp, PgDn, Home, End and many others.
4. Right (sub) keyboard.
Functions of some keys in most programs.
{Caps lock) - usually serves as a switch between the upper and lower case of the keyboard.
(Shift) - switches the keyboard to the opposite mode set by the Caps Lock key.
(Alt), (Ctrl) - have no independent meaning, they work in conjunction with other keys.
(Enter) - signal about completion of input. Select a menu item. Pressing the OK button.
(Esc) - cancel the last command entered.
(Tab) - Move between screen zones or tab stops.
(Home) - move the cursor to the beginning of the line.
(End) - move the cursor to the end of the line.
(PgUp) - move one page up.
(PgDn) - move down one “page”.
(Ins (Insert)) - switching the mode of insertion and replacement when entering information into the text about output editors and editors without data.
(Del (delete)) - deletes the character under which the cursor is located.
(Backspace (<-)} удаление символа слева от курсора.
(Print Screen) - print a text screen (DOS). Send a graphical screenshot to the clipboard (Windows).
(Print Screen) - generates a copy of the screen on the printer.
(Scroll Lock) - smooth screen scrolling.
(Pause) - temporarily pauses the running program.
When you press a key, a certain number is transmitted to the computer - the number (code) of the pressed key. This code does not depend on the language or the alphabet, but only on the specific key pressed. The system contains special tables, which indicate which key corresponds to which ASCII code, and sends the required ASCII code to the program that is currently waiting for input from the keyboard, for example, to a text editor. Nonam would like to somehow tell the system that pressing the key on which the letter "A" is drawn, in some cases should be perceived as a lowercase "a", and in others - as an uppercase "A". In addition, we would like to enter other necessary characters using the same keyboard, because it is stupid to connect several keyboards to one computer just to enter a few additional characters.
The so-called modifier keys - Command, Control, Option (Alt), Shift, Caps Lock, allow using the same keyboard to specify several options for converting the code of the pressed key to the ASCII code of the entered character. To do this, for each script, the system stores several tables of correspondence between the code of the pressed key and the ASCII code of the character entered with its help. When, together with pressing the main keys, we also hold a certain combination of modifier keys, the system automatically switches to the desired table. Since the keyboards of Macintosh computers have five modifier keys, there are 32 possible keystrokes for each script and, therefore, 32 tables of correspondence between key codes and entered ASCII codes.
The keyboard layout is exactly the collection of all 32 tables of correspondence of key codes and characters entered with their help. When we say: “We must switch to the Russian keyboard, this means that we must activate 32“ Russian ”tables of the Cyrillic script.
The Unicode Hex Input keyboard layout is used to enter Unicode characters using a set of numeric code values. To do this, you must additionally hold down the Option key to "warn" the system that further one Unicode character will be entered in hexadecimal notation, and not four separate alphanumeric characters. Keyboard layouts are associated with a general writing system, with some "base" alphabet defined by a script. Within the framework of the same script, several keyboard layouts can exist, each of which takes into account the specifics of a particular language, that is, it serves to enter not only characters from the general basic alphabet, but also additional characters specific to a particular language. The keyboard layout respects the language-specific arrangement of the keys on the keyboard. For example, for a Roman script, there are American, French, German, Spanish, and other layouts. Similarly, Russian, Ukrainian, Belarusian layouts are created for the Cyrillic script.
In "international" systems, there are tools that allow you to easily switch between different scripts and keyboard layouts, which will make it possible to use the same keyboard to enter different sets of characters in accordance with national standards and peculiarities.
Now a few words about fonts in the context of typing text from the keyboard and displaying characters.
Using the keyboard, we enter the ASCII or Unicode codes of the characters we need, but at the same time we want the images of the characters themselves to appear on the screen or on paper, and the calculated values of their codes. Moreover, we would like to change the style of characters depending on the style of the document or our mood, for example. For these purposes, fonts are used.
In each font, for most of the 256 ASCII codes, a graphical representation is created - an image of a specific character, maintained in a single style of a specific font.
For Unicode fonts, the number of characters can be significantly more than 256, although, probably, one font does not contain the entire set of characters included in the full Unicode table.
There are some service symbols that are not intended for display on the screen or printing on paper. There are no corresponding images for such symbols.
You can create fonts in which, instead of letters, numbers, punctuation marks, there will be images of useful graphic objects: arrows, asterisks, pictograms or even company logos.
The specific form of describing the curves that make up the fragments of the graphical representation of font characters depends on the type of font. Bit map fonts specify each point in the image, while PostScript, TrueType, and Open Type fonts store mathematical descriptions of the portions of the curves that make up the symbol graphics.
2. Types of keyboards
Today you can find a huge variety of keyboards. Keyboards are membrane, semi-mechanical, mechanical and reed switches.
The principle of operation of a membrane keyboard is that when a key is pressed, two membranes are closed, while the return is carried out using a rubber dome. The main advantage of such a keyboard is its protection against the penetration of foreign substances, such as crumbs or coffee, into the interior, the disadvantage is fragility, the contacts applied to the membrane tend to wear off.
The semi-mechanical keyboard is more durable, as it uses non-abrasive metal contacts located on the PCB, although the key is still returned using a rubber dome.
Mechanical keyboards differ from semi-mechanical ones in that instead of a rubber dome, a spring is used to return the key, which significantly extends the life of the keyboard and increases its reliability. The disadvantage of mechanical and semi-mechanical keyboards is that they are not protected from external objects.
Recently, reed switch keyboards have become increasingly common, i.e. keyboards in which reed switches (contacts in a vacuum cylinder that react to a magnetic field) and magnets are installed under the keys. The positive aspects of such keyboards are a rather long service life (reed switches practically do not wear out) and a very soft fit, so it is easy and pleasant to work with them. The main disadvantage is dependence on external magnetic fields. Many electronic devices can generate magnetic fields that affect the keyboard and cause false key operations. If you have a reed switch keyboard, you can do a simple experiment: put a cell phone next to it, connected to a charger, and observe the behavior of the computer. The keyboard behaves in the most unpredictable way, from false triggering of individual keys to complete "fury". A similar experiment can be carried out with other electromagnetic devices, however, not every device and not in every situation will create such significant interference.
Also keyboards differ in stroke length. Naturally, the larger it is, the longer it will take to press the key. But even a short stroke length is not good, as it can lead to frequent accidental clicks. The main thing here is to try different options and choose something that is most convenient for you. By the way, some keyboards tend to knock loudly when you press the keys. This is called a click. Why is clickable keyboard good? Only by the fact that you will always know for sure whether you pressed a key or not, which should save you from accidental key presses.
Another parameter, as mentioned above, is the shape and location of the defining keys. Basically, keyboards differ in the shape and location of the Enter key. It can be straight in the form of a "-" sign or in the form of mirror images of the letters "L" and "G".
"Ergonomic" is a keyboard in which the profile of the alphabetical part of the keyboard is an arc, the field itself is divided into two halves, one for each hand, and endowed with a "rest for the hands". It is, of course, beautiful, but, firstly, this ergonomics with its stand takes up quite a lot of space on the table, and secondly, a person who does not know the method of touch typing has to constantly move his eyes from one half of the field to another, constantly changing the focal point. distance of the lens, which makes the eyes tired.
Many keyboards have additional keys. There are usually three of them: two with the Microsoft "a" icon and one with the image of an arrow that selects something from the list. These are the so-called Windows keys. They are quite convenient when working in the "operating system" of the same name. Combined with other keys, you can quickly perform common operations such as launching the Start menu, launching File Explorer, or minimizing all windows, which are not required in other operating systems.
More and more often we come across keyboards with three additional keys. As a rule, an on / off icon, a month and a sun (or an alarm clock) are drawn on them, respectively. The first button is used to turn off the power of the computer. The second key sends the computer into sleep mode, for example, if you need to move away for a while, which significantly reduces power consumption, and the third key, accordingly, returns the computer to normal operation and wakes it up.
Less common, but nevertheless, there are already keyboards with "Internet keys". These are the keys designed to facilitate navigation on the worldwide computer network Internet. They, as a rule, allow you to connect / disconnect from the network (in case of DialUp connection), receive / send mail, and by pressing one button go to the specified site.
There are also so-called "multimedia keys". They are used to control the multimedia CD player. They can be used to change the volume, jump from song to song, start / stop playback, open / close the CD-ROM, or turn off the sound.
Quite common are keyboards with the Fn or Turbo button, with which you can change the speed of repeating characters on the keyboard and lock it.
An important parameter when choosing a keyboard is its size. Many manufacturing firms, trying to solve this problem, give various options for its solution. The only acceptable method of shrinking the keyboard size without sacrificing its usability is to reduce the bezel, and maybe shrink the keys slightly.
It is also necessary to pay attention to some useful little things that make the work more pleasant and convenient. If you own, or are going to master the method of touch typing, so-called "hooks", which are usually found on keyboards, on the keys "F", "J" and on the gray "5", will be very useful to you. Also, pay attention to the presence of the FCC symbol on the back of the keyboard, which means that the keyboard complies with the FCC standard and has a low radiation level. Also, the metal bottom contributes to the reduction of the radiation level, which, moreover, increases the life of the keyboard. And the last is the color of the Russian layout. If you do not want to constantly get lost and confused, choose the keyboard on which the Russian layout is marked in red.
There are also wireless keyboards. The option is spectacular, although the keyboard (in the context of a desktop computer, and not, say, a web set-top box) seems to be the device that the wire gets in the least.
There are, of course, all sorts of unusual keyboards such as the following: Flexis FX 100.
The Flexis FX 100 is a keyboard that you can fold up and take with you on your travels. Flexis FX100 has solid advantages, as the list of its characteristics eloquently testifies: sealed, silicone, dust-, dirt-, moisture-proof housing; it is easy to clean with soap and water;
- corresponds to the size of airplane tables; low weight ensures ease of transportation; no moving parts reduce the possibility of breakage; tactile feedback similar to a standard keyboard; easy connection; no batteries required.
Conclusion
So, the keyboard is the main element of the computer, traditionally used to enter text into the computer. There are four groups of keys: alphanumeric and sign, functional, service, auxiliary.
Many keyboards have various additional keys, for example, to navigate the Internet or multimedia keys. The presence of such keys facilitates the user's work.
The choice of keyboards is huge today. Keyboards are membrane, semi-mechanical, mechanical and reed switches. There are also wireless keyboards, silicone keyboards, and many more.
When choosing a keyboard, it is necessary to consider for what purpose it is needed, what design and size is more suitable and some other factors that are important for working on the keyboard.
Bibliography:
1. Medvedovsky I. Keyboards. // COMPUTER. - 2002. - No. 1.
2. Semyanov P. Choose the keyboard. /Work with computer. - M .: Olma-press, 2000.
3. Semenov V. Keyboards. 2003.
"Keyboard. Key groups and their purpose "
Lesson summary on the topic
"Keyboard. Key groups and their purpose "
Lesson plan:
Lesson summary:
Modern computers can process numerical, textual, graphic, audio and video information.
Microphones are used to enter sound information into a computer; scanners, digital cameras and camcorders are used to enter complex graphic images, photos and videos; numeric and text information can also be entered into computer memory using a scanner. But in order to work successfully on a computer, you need to know the keyboard - essential device input into the computer memory.
Keyboard - a computer device that is located in front of the display screen and serves to type texts and control the computer using the keys on the keyboard.
Take a close look at your computer keyboard.
All keys can be conditionally divided into several groups:
- alphanumeric keys;
- function keys;
- control keys;
- cursor control keys;
- numeric keys.
In the center there are alphanumeric keys, very similar to the keys of a conventional typewriter. They have numbers on them Special symbols("!", ":", "*", Etc.), letters of the Russian alphabet, Latin letters. With the help of these keys you will type all kinds of texts, arithmetic expressions, write your programs. At the bottom of the keyboard is a large key without symbols on it - "Space". Space is used to separate words and expressions from each other.
Russian keyboards are bilingual, therefore, both Russian and English alphabets are drawn on their keys. In the Russian language mode, texts are typed in Russian, English - in English.
The alphanumeric keyboard is the main body of the keyboard with the alphanumeric keys on which characters are drawn, along with all of the closely adjacent control keys.
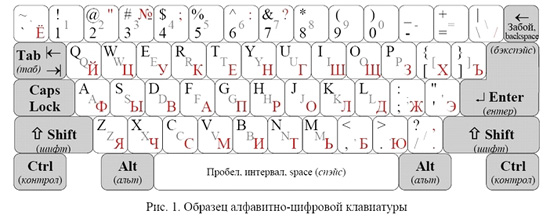
Figure 1 shows one of the types of alphabetical numeric keypad... Keyboard types differ from each other in the shape of some control keys and the location of the backslash key \.
Alphanumeric keys are shown in white, controllers - in gray. On the left side of the keys are drawn characters that are typed in of English language... On the right - the symbols of the Russian language mode, if they differ from English. If the same character is typed in both modes, then this character is not drawn to the right.
The function keys F1 - F12 located at the top of the keyboard are programmed to perform certain actions (functions). So, very often the F1 key is used to call up help.
The place of entry of the next character on the monitor screen is marked by a blinking dash - cursor.
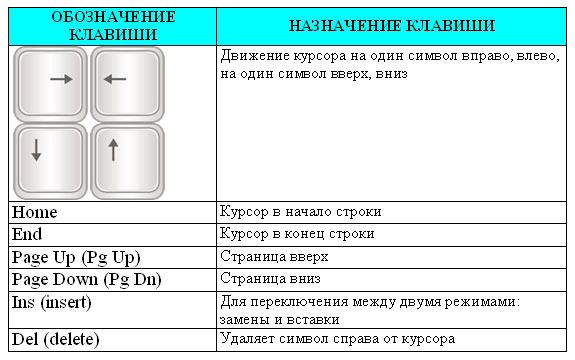
To move the cursor, use the cursor keys, they show arrows pointing up, down, left and right. These keys move the cursor one position in the corresponding direction. The PageUp and PageDown keys allow you to “scroll” the document up and down, and the Home and End keys move the cursor to the beginning and end of the line.
Control keys are used very often. They are not collected in one group, but placed so that it is convenient to press them.
The Enter key (sometimes depicted with an arrow) completes a command and invokes its execution. When typing, it completes the paragraph.
The Esc key is located in the upper corner of the keyboard. Usually serves to cancel the action just performed.
Shift, Ctrl, alt keys adjust the actions of other keys.
Numeric keys - when the Num Lock indicator is on, a convenient keypad with numbers and signs of arithmetic operations. Positioned like a calculator. If the Num Lock indicator is off, then the cursor control mode works.
Comment: the name "Num Lock" literally means "fixing numbers"
Keyboard equivalents
CTRL + Z - Undo
CTRL + A - Select All
BACKSPACE - Go to folder top level
CTRL + TAB - Switch from one tab to another
F4 - Expand address bar
F1 - Help
F10- Go to menu SHIFT + F10 - Call context menu for the selected object
CTRL + ESC - Open the main menu
CTRL + ESC - Click on the Start button
alt + TAB - Switch from one window to another (change window activity) alt + M - Minimize all windows
Win + R - Open the Run Program window
Win + M - Collapse All open windows
Win + F1 - Call Help Windows system
Win + E - Call Windows explorer
Win + F - Find file and folder
CTRL + Win + F - Find Computer
Win + Tab - Navigate between Taskbar applications
Win + Break - Call system properties
Name of some symbols:
/ - forward slash (slash);
‘- apostrophe;
& - ampersand;
$ - dollar;
~ - tilde;
@ - commercial "et" (or frog);
() - "open" "closed" parenthesis;
() - "open" "closed" curly brace;
< >- sign "less" "more";
_ - underline;
\ - backslash (backslash);
# - hash (sharp);
"" - quotes;
^ - cover;
* - asterisk.
A keyboard is an electronic device that contains microcircuits and other parts inside. Therefore, it should be handled carefully and carefully. Do not allow the keyboard to become dirty with dust, small rubbish, metal clips, etc. There is no need to hit the keys hard. Your finger movements should be light, short and jerky.
A keyboard simulator is loaded on each computer.
Homework (children are given cards with assignments).
1. Fill in the table.
| Operation | Key or key combination |
| Switching the keyboard from the mode of entering Latin letters to the mode of entering Russian letters and vice versa | |
| Switch the keyboard from lowercase input mode to input mode uppercase letters and back | |
| Caps mode function / unlock this mode | |
| Retrieving characters alongside the numeric characters in the top row of the keyboard | |
| Delete the character to the right of the cursor | |
| Delete the character to the left of the cursor | |
| Turning on on additional keyboard mode of operation with numbers and signs of arithmetic operations |
2. Solve the Inscriptions on the Keys crossword puzzle.
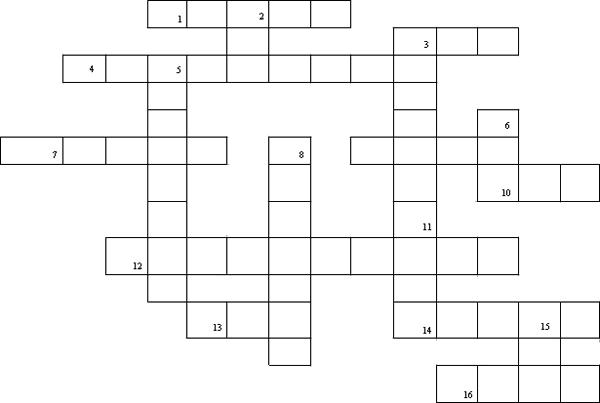
Horizontally:
1. The name of the key for switching keyboard registers (SHIFT).
3. Short name of the key with which you can delete the character located to the right of the cursor (DEL).
4. Key label that deletes the character to the left of the cursor (BACKSPASE).
7. The inscription on the key, translated into Russian as "pause" (PAUSE).
9. Abbreviated name of the Control (CTRL) key.
10. The inscription on the tab key (TAB).
12. The inscription on the key next to the Pause (SCROLLLOCK) key.
13. The inscription on the key, when pressed, the action is canceled or a certain state is exited (ESC).
14. The inscription on the key, which is sometimes called the most important key (ENTER).
16. Brief inscription on the key that moves the cursor one page down (PgDn).
Vertically:
2. Brief inscription on the key for switching between the "insert" / "replace" (INS) modes.
3. The full name of the key used to delete the character located to the right of the cursor (DELETE).
5. The inscription on the key, when pressed, the upper case is fixed (CAPSLOCK).
6. Inscription on the keys located on either side of the space bar (alt).
8. The inscription on the key fixing the numeric mode of the numeric keypad (NUMLOCK).
11. Inscription on the key that moves the cursor to the beginning of the current line (HOME).
15. Inscription on the key that moves the cursor to the end of the current line (END).
Do you think we have completely learned to work on a computer? Of course not. We are waiting for more than one trip to the amazing computer world.
Literature:
- Journal "Informatics and Education". 2005. No. 3.
- Journal "Informatics at school". 2004. No. 6.
- Journal "Informatics and Education". 2004. No. 6.
- http://festival.1september.ru/
15.04.2008
Keyboard presentation
Flash file "Keyboard" in ZIP archive, 69 Kb (keyboard.swf 69 Kb)
Keyboard keys, depending on their purpose and location, can be divided into groups: -Alphanumeric; -Functional; -Block additional keys(numeric keypad); - Cursor keys; - Service (control keys).
Alphanumeric keys.
Purpose: Enter letters, numbers, punctuation marks and other special characters. The SPACE key also falls into this category.
-Function keys
This includes the F1-F12 keys. There are no permanently assigned functions for these keys (the only exception is the F1 key, which is used to get help). These keys, as a rule, are already programmed by the user for each program separately.
-Block of additional keys (numeric panel)
Repeat the action of the numeric and some symbolic keys of the main panel This panel can be used in two modes: * Entering numbers; * Cursor control. Mode switching is carried out with the NUM LOCK key
- Cursor keys
Cursor - An on-screen pointer that indicates where the next character is entered (for text) or the current position (point) to which the mouse action will be applied. The arrow keys move the cursor one position on the monitor screen in accordance with the direction. The PAGEUP and PAGEDOWN move the cursor one page up and down, respectively, and the HOME and END keys move the cursor to the beginning and end of the current line. The INSERT key switches the data entry modes: insert and replace (in insert mode, new characters are entered without replacing existing characters, and in replace - replace) The DELETE key deletes characters to the right of the current cursor position, and the BACKSPACE key deletes characters to the left of the current cursor position.
Service (control keys)
Enter (English Enter - "Enter") - used to move to a new line (when typing), confirm some action or readiness of the user, select a command from the menu. Keys CTRL and ALT - are used in combination with other keys (two directly or separately) to execute a specific command SHIFT is a modifier key. Used to enter uppercase (uppercase) letters (while pressing Shift keys and letter keys), as well as punctuation marks. It is also used in combination with other keys on the keyboard (as well as the mouse) to perform various commands. TAB key. There are two main functions of the TAB key: - enters tabulation characters into the text (inserting blank characters); - allows you to alternately switch between controls within the same window. ESC key - intended to return to the previous state or (not always) to exit the application or program. PRINT SCREEN - printing, the current state of the screen on the printer. It also saves the image of the current state of the screen in the RAM buffer. PAUSE / BREAK key - is intended to pause the current process (program). CAPS LOCK key - fixes the mode of entering uppercase (capital) letters. The keyboard has an indicator that displays the state (on / off) of the key. NUM LOCK key - enables / disables the optional numeric keypad. The mode is indicated by one of the three LEDs on the keyboard: the SCROLL LOCK key. When Scroll Lock is on, the arrow keys move the screen. The keyboard has an indicator that displays the status (on / off) of the key. WIN key - used to launch the Windows START button. In combination with other keys, it can execute other commands. Application key (located between the WIN and CTRL buttons on the right) is equivalent to pressing right button mice.
Lesson summary on the topic
"Keyboard. Key groups and their purpose "
Lesson type:
Lesson in learning new knowledge
Educational purpose of the lesson:
Study and primary consolidation of knowledge;
Updating leading knowledge;
Consider all groups of keys and their purpose.
Lesson plan:
1. Organizational part (greeting, checking the students present, writing the date and topic in a notebook)
3 min.
2. Explanation of the new material
30 minutes.
3. Independent work of students
10 min.
4. Homework
2 minutes.
Lesson summary:
Modern computers can process numerical, textual, graphic, audio and video information.
Microphones are used to enter sound information into a computer; scanners, digital cameras and camcorders are used to capture complex graphics, photographs and video films; numerical and text information can also be entered into the computer memory using a scanner. But in order to work successfully on a computer, you need to know the keyboard - the most important input device into the computer's memory.
A computer device that is located in front of the display screen and serves to type texts and control the computer using the keys on the keyboard.
Take a close look at your computer keyboard.
All keys can be conditionally divided into several groups:
alphanumeric keys;
function keys;
control keys;
cursor control keys;
numeric keys.
In the center are locatedalphanumeric keys , very similar to the keys of a conventional typewriter. They are marked with numbers, special symbols ("!", ":", "*", Etc.), letters of the Russian alphabet, Latin letters. With the help of these keys you will type all kinds of texts, arithmetic expressions, write your programs. At the bottom of the keyboard is a large key without symbols on it - "Space". Space is used to separate words and expressions from each other.
Russian keyboards are bilingual, therefore, both Russian and English alphabets are drawn on their keys. In the Russian language, texts are typed in Russian, English - in English.
Alphanumeric keyboard - the main part of the keyboard with alphanumeric keys on which symbols are drawn, along with all the closely adjacent control keys.

Figure 1 shows one of the types alphanumeric keyboard... Keyboard types differ from each other in the shape of some control keys and the location of the backslash key \.
Alphanumeric keys are shown in white, control keys are shown in gray. On the left side of the keys are drawn characters that are typed in English mode. On the right - the symbols of the Russian language mode, if they differ from English. If the same character is typed in both modes, then this character is not drawn to the right.
Function keys F1 - F12 located at the top of the keyboard are programmed to perform certain actions (functions). So, very often the keyF1 serves to callreference .
The place of entry of the next character on the monitor screen is marked by a blinking dash -cursor .
To move the cursor, usecursor keys , they show arrows pointing up, down, left and right. These keys move the cursor one position in the corresponding direction. The PageUp and PageDown keys allow you to “scroll” the document up and down, and the Home and End keys move the cursor to the beginning and end of the line.
Very often usedcontrol keys ... They are not collected in one group, but placed so that it is convenient to press them.
KeyEnter (sometimes depicted with an arrow) completes the command and causes it to be executed. When typing, it completes the paragraph.
KeyEsc located in the upper corner of the keyboard. Usually serves to cancel the action just performed.
KeysShift, Ctrl, alt adjust the actions of other keys.

Numeric keys - when the Num Lock indicator is on, a convenient keypad with numbers and signs of arithmetic operations. Positioned like a calculator. If the Num Lock indicator is off, then the cursor control mode works.
Comment: the name "Num Lock" literally means "fixing numbers"
Keyboard equivalents
CTRL + Z - Undo
CTRL + A - Select All
BACKSPACE - Go to the top-level folder
CTRL + TAB - Switch from one tab to another
F4 - Expand Address Bar
F1 - Help
F10- Go to the menu SHIFT + F10 - Call the context menu for the selected object
CTRL + ESC - Open the main menu
CTRL + ESC - Click on the Start button
alt + TAB - Switch from one window to another (change window activity) alt + M - Minimize all windows
Win + R - Open the Run Program window
Win + M - Minimize all open windows
Win + F1 - Call the Windows help system
Win + E - Call Windows Explorer
Win + F - Find file and folder
CTRL + Win + F - Find Computer
Win + Tab - Navigate between Taskbar applications
Win + Break - Call system properties
Name of some symbols:
/ - forward slash (slash);
‘- apostrophe;
& - ampersand;
$ - dollar;
~ - tilde;
@ - commercial "et" (or dog);
() - "open" "closed" parenthesis;
- "open" "closed" square bracket;
() - "open" "closed" curly brace;
< >- sign "less" "more";
_ - underline;
\ - backslash (backslash);
# - hash (sharp);
"" - quotes;
^ - cover (degree);
* - asterisk.
A keyboard is an electronic device that contains microcircuits and other parts inside. Therefore, it should be handled carefully and carefully. Do not allow the keyboard to become dirty with dust, small debris, metal clips, etc. There is no need to hit the keys hard. Your finger movements should be light, short and jerky.
A keyboard simulator is loaded on each computer.
Homework (children are given cards with assignments).
1. Fill in the table.
Operation
Key or key combination
Switching the keyboard from the mode of entering Latin letters to the mode of entering Russian letters and vice versa
Switch the keyboard from lowercase to uppercase and vice versa
Caps mode function / unlock this mode
Retrieving characters alongside the numeric characters in the top row of the keyboard
Delete the character to the right of the cursor
Delete the character to the left of the cursor
Enabling on the additional keyboard the mode of operation with numbers and signs of arithmetic operations
2. Solve the Inscriptions on the Keys crossword puzzle.

Horizontally:
1. The name of the key for switching keyboard registers (SHIFT).
3. Short name of the key with which you can delete the character located to the right of the cursor (DEL).
4. Key label that deletes the character to the left of the cursor (BACKSPASE).
7. The inscription on the key, translated into Russian as "pause" (PAUSE).
9. Abbreviated name of the Control (CTRL) key.
10. The inscription on the tab key (TAB).
12. The inscription on the key next to the Pause (SCROLLLOCK) key.
13. The inscription on the key, when pressed, the action is canceled or a certain state is exited (ESC).
14. The inscription on the key, which is sometimes called the most important key (ENTER).
16. Brief inscription on the key that moves the cursor one page down (PgDn).
Vertically:
2. Brief inscription on the key for switching between the "insert" / "replace" (INS) modes.
3. The full name of the key used to delete the character located to the right of the cursor (DELETE).
5. The inscription on the key, when pressed, the upper case is fixed (CAPSLOCK).
6. Inscription on the keys located on either side of the space bar (alt).
8. Inscription on the key fixing the numeric mode of the numeric keypad (NUMLOCK).
11. Inscription on the key that moves the cursor to the beginning of the current line (HOME).
15. Inscription on the key that moves the cursor to the end of the current line (END).
Do you think we have completely learned to work on a computer? Of course not. We are waiting for more than one trip to the amazing computer world.
Literature:
Journal "Informatics and Education". 2005. No. 3.
Journal "Informatics at school". 2004. No. 6.
Journal "Informatics and Education". 2004. No. 6.
 Bugs in Singularity?
Bugs in Singularity? Just Cause 2 crashes
Just Cause 2 crashes Terraria won't start, what should I do?
Terraria won't start, what should I do?