The clear cmos jumper is where it is. Power supply and zeroing of CMOS memory. What is Flash ROM
Hello dear friends, everyone! Users, having set a password for Bios, often forget it. Only now it is impossible to enter the system without typing a password. I decided to write about how the BIOS password is reset in this article.
This is what the monitor looks like when prompted for a password:
Clear CMOS
Turn off the computer, unplug the power cable from the computer. Now find the Clear CMOS jumper on the motherboard (the Clear CMOS label is usually located near the battery, and the inscription can also be written in abbreviation). Now move the jumper to the adjacent place. After it has been moved, click on the "Power" button (turn on the computer). Now put the jumper back and you can turn on the computer.
Motherboard manufacturers have long since straightened their strengths and the time has passed when some of the company's motherboards showed superior superiority over others, even though they were based on the same schematic set. At present, the differences in the performance of different brands and models are within the statistical error of the tests carried out and practically do not have of great importance... Therefore, only comparisons between different chipset models are interesting.
What are POST-Codes?
It is for this reason that motherboard manufacturers focus on other things to differentiate their products. Ecology and the so-called "green" movement did not get through this industry. All manufacturers pay close attention to this, and as a result, we see implementation in motherboards new and emerging technologies to save energy. In the end, the choice of a motherboard is limited by its functionality, cost and technical support... Taking into account the fact that the differences in performance tests different models and motherboard models based on the same chipset are insignificant, we decided to compare only different chipsets.
After these steps, the password and default settings (Default) will be reset.
In the event that you have not found exactly where the Clear CMOS inscription is located, read the instructions for your motherboard, which they give when buying a computer. If it is absent (lost, thrown out), enter the model of your motherboard into the search engine and find the place where Clear CMOS is located.
For this reason, we compared only a few motherboard models that came in for editing tests. We mainly used gaming applications to measure performance. But here we will not go into details, because there is a lot of information on this issue on specialized forums. There is a place here to clarify the situation. It is for this reason that some manufacturers have added another bridge, thus providing the functionality of the top model at a much lower cost.
Some companies, of course, have their own designs. It does not use thermal cooling of the components, but is classic with conventional aluminum heatsinks, which do the same in general, because they are quite massive. In addition, the board is all solid state electrolytic capacitors and 8-phase processor power. Despite the simplified design, the board's overclocking capabilities do not deteriorate and are in no way inferior to the overclocking capabilities of its large counterparts.
How to reset the password on Bios using the battery located on the motherboard, read below.
Battery in motherboard
Reset BIOS Password If Clear CMOS is missing on the motherboard, then you need to remove the battery and wait 30 to 180 minutes... To do this, turn off the computer, pull out the power cable and on the motherboard, take out the battery (where it is located, see the picture above).
The processor power is 8 phases and with improved filtering of the output voltage. This guarantees good overclocking stability even on older quad-core processors. There are two buttons on the board that have become an integral part of the enthusiastic solutions and make them much easier to manipulate when using the stand. Overall, the board performed well in our tests and we didn't have any problems with it.
Do I need to change the battery?
In fact, the design of the board is different from the one described above. Cooling has also been simplified. We were very surprised, since the smaller model did not have such problems. We hope that things will change in a positive direction with the release of the new firmware update. The design of the board is very precise and the location of each component is well thought out. Cooling is based on heat transfer technology, and an additional fan is added to the kit, which is especially useful when overclocking. The PCB has several LEDs that indicate the status of the individual subsystems.
Use a small screwdriver to remove the battery. Just press the latch that is in the battery compartment and it will lift itself up. Remove the battery, press the Power button (the power cable should not be connected while pressing) and leave the computer in this state for 30 - 180 minutes.
From these actions, the password will be reset and the default settings will be restored (Default). When time has passed, you can put the battery back in and turn on the computer. After that, when the computer boots, the message “CMOS checksum error - Defaults loaded. Press "F1": to continue, "DEL": BIOS Setup "or" CMOS checksum Failure ".
There is also an extended set of parameters and monitoring parameters, as well as an external indicator of what happens during the procedure after the procedure. The board was very stable and showed excellent overclocking capabilities. The only drawback is its higher price.
Cooling is carried out using heat transfer technology, and the south bridge is independently cooled by a classic aluminum radiator. The kit includes an additional heatsink with a blade, which is mounted on another, which improves cooling, which is especially necessary when overclocking. The motherboard performed well in tests. It has become fashionable for companies to create special series for the enthusiast. The components are optimally positioned and the slots are different colors. Cooling is classic, and separate aluminum radiators are used for the north and south bridge of the chipset.
The inscription may be different, but the meaning remains the same . In the figure below, you can see an example of such a message:
If you want to boot the computer with the default parameters (Defaults), then press the "F1" key. More experienced users can enter BIOS Setup by pressing the "Delete" key, where you can configure the BIOS. After setting, press "F10" and confirm the changes made with the "Enter" key.
This is not a problem at factory frequencies, but when overclocking requires replacement with a more adequate one. The power is four-phase, and this makes the motherboard not particularly suitable for the more extreme overclocking of 65nm quad-core processors. The board performed well in tests, but when overclocked it did not show a particularly satisfactory result. The motherboard has a high contour. It was also equipped with the best cooling of all the proposals tested. Superior hybrid cooling is used, in which the overclocking components are further cooled by both water and conventional airflow.
Together with this article read: ""
Good luck! Try not to forget your BIOS passwords!
The section is still in work ...
The basics
What is a CPU?
CPU (from the English "Central Processing Unit") - a central processing unit - a central processor, the main part of the architecture of a personal computer. Designed for computing general purpose(performs logical and arithmetic operations), input / output operations, as well as to control all other components of the computer. Physically it is realized, as a rule, in the form of a discrete microcircuit. This microcircuit is either installed in a special connector on the motherboard (socket), or soldered directly on it.Motherboard form factor
Form factor of the motherboard (from the English "Form Factor") - the form factor - an industry standard that determines the overall dimensions of the motherboard, the number and location of its attachment points to the case, location on it various devices and connectors (CPU socket, slots for random access memory, bus interfaces, input / output ports, etc.), as well as the location and type of connector (or connectors) for connecting the power supply to it.With regard to ordinary (office or home) computers, the main modern form factors of the motherboard are: ATX, Micro ATX, Flex ATX and Mini-ITX.
This ensures that all components are sufficiently cooled under all conditions to satisfy even the most discerning consumer. The menus and settings are pretty detailed and intuitive. The card was great in benchmarks and showed tremendous overclocking capabilities. The aim was to reduce the cost without affecting its other qualities. The bottom is well balanced in both price and opportunity. Cooling is classic with ordinary aluminum radiators, which are sufficient to operate at factory frequencies or even slightly overflow.

Main modern motherboard form factors (dimensions in inches)
The retail market is mainly represented by ATX, Micro ATX and Mini-ITX boards.
Rarely, but there are other options. So, AMD, specifically for small-sized home computers, proposed the DTX / Mini-DTX form factor, which, unfortunately, has not received mass distribution. And EVGA has released several HPTX form factor boards aimed at wealthy enthusiast maniacs.
But if you plan to use it for more serious overclocking, you will need to replace it with a more appropriate way for this purpose. This, however, can hardly be considered a disadvantage. In tests, the motherboard performed well without any anomalies in its behavior. This motherboard immediately catches its black color and strange form of coolant cooling. The design of the board is very well thought out and every component is in the best possible position. Of course, this is only an approximate value as it only takes into account the motherboard, processor, memory and expansion board, but cannot read the consumption of other expansion cards or more powerful video accelerators that require additional external power.
Professional form-factor E-ATX (Extended ATX) cards are practically not found on the non-professional computer market, but sometimes the compatibility with them is indicated by the manufacturers of computer cases.
The table below shows the characteristics of modern motherboard form factors in descending order of their overall dimensions.
The motherboard is distinctive black and painted in different slots. In fact, the chipset and this additional bridge are not the coolest, and even with light overclocking they bake a lot, so the board must be sucked in by an additional fan. In tests, the motherboard was excellent and showed some of the better opportunities overclocking. The board is equipped with a massive cooling system and a fan is added to it. The chipset is pretty hot, so even if you don't expect more stable overclocking, it's a good idea to add an extra heatsink in place.
| Form Factor (standard) |
Dimensions, mm | Number of slots for cards enlargement |
|
| width | height | ||
| HPTX | 381 | 345 | up to 9 |
| E-ATX | 330 | 305 | 7 |
| ATX | 244 | 305 | 7 |
| Micro ATX | 244 | 244 | 4 |
| Flex ATX | 191 | 229 | 3 |
| DTX | 244 | 203 | 2 |
| Mini-DTX | 170 | 203 | 2 |
| Mini-ITX | 170 | 170 | 1 |
A few comments on the table.
In bold the main modern form factors of the motherboard are highlighted.
If a computer case is designed for a board of one form factor, then all the downstream ones will also fit into it.
It should also be noted that the form factor is of a recommendation nature, so manufacturers can change the size of motherboards (usually in the direction of decreasing width), while declaring compatibility with the standard.
What is Flash ROM?
The board performed very well in the tests and showed excellent overclocking capabilities. Thanks for the kindness of the companies. We start with design and equipment. To improve cooling, the engineers also provided 4 fan headers. The abbreviation in parentheses in the nomenclature indicates that the bottom is made entirely of polymer capacitors. The field-effect transistors in the four-channel voltage regulator are passively cooled by a finned heat sink.
Another bizarre design idea is to fill in the gaps on the sparsely populated rear panel at the bottom, combining a modern chipset with nautical memories of peripheral ports like a pair of serial and parallel ports. The processor voltage regulator is 4-channel, without additional cooling of the components.
BIOS
What is BIOS?
BIOS (from the English "Basic Input / Output System") - the basic input / output system - software providing interaction operating system and hardware resources of the computer.The physical implementation of the BIOS is a set of microcircuits on the motherboard, plus a battery that powers the CMOS.
The BIOS program itself is stored in the Flash ROM chip (for older computers in EPROM or EEPROM). V modern computers this microcircuit, as a rule, is removable and lies in a special "crib".
To "translate" into real game language, see the results in the large comparison table. The color combination is rigid - black and blue, the design is unusual: the processor socket is rotated 90 degrees from the standard orientation, and the memory slots move along it and are parallel to the "northern" edge of the board.
General specifications tested motherboard models. Comparison of processor and memory performance for different chipsets. Comparison of the performance of different chipsets in video applications. In this situation, it is recommended to decrease them by one degree.
What is EPROM?
EPROM (from the English "Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory") - read-only memory, erasable, programmable - a chip of permanent (non-volatile) memory, the contents of which are erased using an ultraviolet lamp. To write information into such a microcircuit, you need a special device - a programmer.What is ЕЕPROM?
EEPROM (from English "Electrically Eraseble Programmable Read Only Memory") - read-only memory, electrically erasable, programmable - a permanent (non-volatile) memory chip whose contents are erased using an electrical signal. For recording, you also need a programmer.EPROM and ЕЕPROM are outdated types of microcircuits, and they are no longer used in modern computers for storing the BIOS program.
High load alarms. When alarm messages start to appear when the computer is overloaded, such as during video playback or transcoding, hardware components overheat. Provide better cooling inside the PC case, improve air circulation and install an additional fan. You can cool down your computer temporarily by opening the lid.
To do this, turn off your computer and unplug the power cord. If these problems are caused by overclocking, do not set such high values next time. Motherboard manufacturers use different codes. Their meaning is given in the instruction manual of the disc.
What is Flash ROM?
Flash ROM (from English "Flash Read Only Memory") - read-only memory, on flash chips - "flashable" permanent (non-volatile) memory. You can update information in such a microcircuit and by software(usually from DOS).What is CMOS?
CMOS (from the English "Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor") - memory for storing information about the current configuration (settings) of the computer hardware. The name comes from the technology for the production of transistors - the complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) structure. It is to save this information when the power is off that the same battery is used.What is CMOS Battery?
CMOS Battery (from the English "CMOS Battery") - CMOS battery - a power source needed to store information in CMOS when the computer's power is off.Some people mistakenly think that there is a battery on the board - no, there is an ordinary 3V lithium battery. Why does it last so long? Because the current required to power the CMOS chip is very small, and the battery itself is very high quality :)
Equipment damage. If your computer fails despite the aforementioned resuscitation attempts, you are most likely dealing with hardware damage. Motherboard errors are rare. Most of the subnets that have been overclocked are eligible. To get them, enter diagnostics in the Start search box and click on the found entry.
This can help when alarms are shown with a blue background and when the system freezes frequently. This should also be done if components such as working memory or HDD, unstable or too slow. However, on the other hand, this operation carries a certain risk.
Do I need to change the battery?
If the computer is already old (well, over eight years, for example), then the battery may be discharged. The first sign of this approaching is the lag of the system clock. This is not good, because if the battery is completely discharged CMOS data will be erased, and the computer will either turn on with CMOS settings reset to default values, or not turn on at all. Therefore, it is better to change the battery. Any type of CR2030 or CR2032 lithium power supply (this is preferred) will do.
Otherwise, the computer may not detect new components or select incorrect settings for their job, so they won't work as expected or with poor performance. For example, in laptops, manufacturers tune in newer versions of software. fan speed and temperature. Then it turns on less often and works for more low speeds and even quieter. In addition, the manufacturer can change the default brightness on the screen.
When to stop updating. This should not be done if there are no prerequisites for this. Therefore, if your computer is performing as expected, it is best not to update. In fact, these are two completely independent creations. It contained 64 bytes for data storage, of which 10 bytes are reserved for the clock function. Although the layout is called non-volatile memory, it really isn't. Most lithium batteries can last 5 years or more.
Here it should be borne in mind that without a battery, the CMOS data is erased (after a couple of seconds). Therefore, before replacing it is useful to remember or write down all the settings by going to BIOS Setup. Well, after replacement, respectively, restore them there.
The process of removing and reinstalling (after a couple of seconds) the battery can also be useful if you need to clear the CMOS (and most importantly, erase the password for entering BIOS Setup :), and no other means were found for this :)
For simpler and safer manipulations with CMOS data, it is recommended to use the CMOS De-Animator program - a utility that allows you to erase the CMOS checksum, reset all BIOS settings to default values and also erase all BIOS passwords(If there are any). In addition, the program can save the current CMOS settings to a file, as well as restore them from a saved file. You can download this program from here.
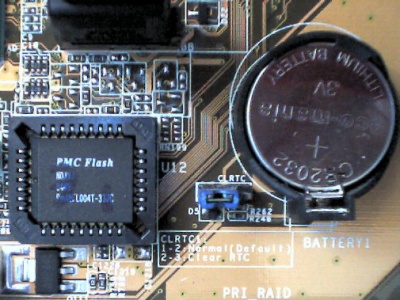
What is Clear CMOS?
Clear CMOS (from the English "Clear CMOS") - clear CMOS- erasing all information stored in the CMOS. All settings are then reset to some basic values (default values). A jumper (jumper) on the motherboard, located somewhere near the battery, is usually responsible for the implementation of this function. How to use this jumper should be indicated either in the description of the board, or directly on its PCB.
As a rule, to erase CMOS data, you need to move the jumper to the adjacent position, turn on the computer, wait a couple of seconds, turn off the computer and rearrange the jumper.
What is RTC?
RTC (from the English "Real Time Clock") - real time clock - an electronic circuit designed to record chronometric data ( current time, date, day of the week, etc.). It is a system consisting of an autonomous power source and a metering device.What is Clear RTC?
Clear RTC ("Clear Real Time Clock") - clear (reset) the real time clock. As applied to computers, it is generally the same as Clear CMOS.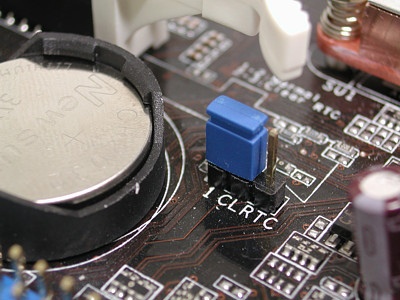
What is POST?
POST (from English "Power On Self Test") - self-test at power-on - check of functioning hardware computer before loading the operating system. Performed by programs included in the motherboard BIOS.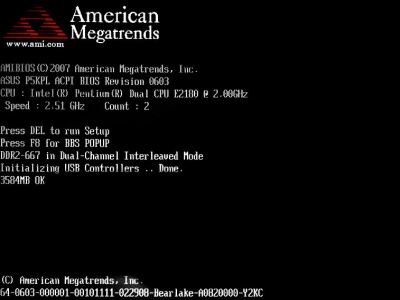
What are POST-Codes?
POST-Codes (from the English "Power On Self Test Codes") - self-test error codes (digital, in hexadecimal format). The meaning of these digital codes should be listed in the BIOS description of the motherboard.What is BIOS Setup?
BIOS Setup (from English "Basic Input / Output System Setup") - a program for setting the current configuration of the computer. The phrase "enter BIOS" implies launching this particular program :)
In general, it is more correct to say not BIOS Setup, but CMOS Setup, since it is not the BIOS program that is configured, but the CMOS data. Nevertheless, the phrase BIOS Setup is more common.
What is ESCD?
ESCD (Extended System Configuration Data) - extended system configuration data - are responsible for configuring Plug & Play devices. When changing the hardware configuration of the computer, for example, when replacing a video or sound card, they are subject to updating. For this, there is a corresponding item in the BIOS Setup.What is ACPI?
ACPI ("Advanced Configuration and Power Interface") is an advanced configuration and power management interface. ACPI replaces APM (Advanced Power Management) and defines a common interface for hardware discovery, power management, and configuration of the motherboard and other devices. ACPI's job is to provide interoperability between the operating system, hardware, and motherboard BIOS.BIOS Software Companies
BIOS software manufacturers:- Award Software, owned by Phoenix Technologies Ltd. (Award BIOS)
- American Megatrends Inc.(AMI BIOS)
- Phoenix Technologies Ltd.(Phoenix BIOS)
Download all required programs to work with BIOS, you can from the corresponding section of our file archive.
UEFI
What is EFI?
EFI (from the English "Extensible Firmware Interface") - an extensible firmware interface (firmware) - software that provides interaction between the operating system and firmware that directly control the hardware of the computer. The main purpose of EFI is to correctly initialize the existing hardware and transfer control to the operating system loader.The EFI specification was originally created for Intel's first systems, HP Itanium, in the mid-1990s. The EFI 1.02 specification was released by Intel on December 12, 2000.
What is UEFI?
UEFI (from the English "Unified Extensible Firmware Interface") - unified extensible firmware interface (firmware) - EFI version for Intel x86, Intel x64 and ARM architectures. Positioned as a replacement for BIOS in personal computers.The Unified EFI Forum is currently developing UEFI. The last one, on this moment, UEFI 2.5 was adopted in April 2015.

In fact, EFI / UEFI is a kind of operating system, with its own services, drivers, support for drives and file systems (including FAT32) and with its own graphical shell (EFI shell). The shell can be used to run various EFI applications such as system setup, OS installation, diagnostics, firmware updates. EFI shell commands allow you to copy and / or move files and directories in supported file systems, load and unload drivers. The shell can also be used for, for example, CD / DVD playback or Internet access (without booting the "main" OS), provided that the EFI applications support these capabilities.

In other words, the EFI shell is a functional replacement for the textual BIOS interface and interpreter command line DOS.
You can download all the necessary programs for working with UEFI from the corresponding section of our file archive.
The material is still in work ...
 Bugs in Singularity?
Bugs in Singularity? Just Cause 2 crashes
Just Cause 2 crashes Terraria won't start, what should I do?
Terraria won't start, what should I do?