How do I set the BIOS to boot from a disk or USB flash drive?
Or, the boot parameters are collected in a special, which, in turn, may consist of several submenus.
The need to change the boot order of your computer is one of the most common tasks that you have to resort to.
By correctly setting these parameters, and insure yourself against problems that sometimes arise at this stage.
Several devices can be used as boot devices.
C, A, SCSI. In this case, the computer will first try to boot from the hard disk, then from the floppy disk, and lastly from the SCSI device. Installing Boot Priority from hard disk allows the system under normal booting Windows do not waste extra time accessing the drive.
1.With only. Boot from hard drive only. This value, combined with BIOS password protection, complicates unauthorized access to the system.
2.C, CDROM, A. The search sequence will be as follows: HDD, CD drive, floppy drive.
3. CDROM, C, A. The first priority will be booting from the CD drive, which is necessary to start installing the operating system from the CD.
4. D, A, SCSI. This option should only be used if the system has two hard disk and you need to boot from the second.
5. SCSI, A, C. This option is used if operating system was installed on a SCSI hard drive.
2. Names of actually detected drives;
3. The names of the categories of devices.
Let's consider these options in more detail.
Some BIOS versions use a list of devices that can be connected to motherboard... In this list, you can find the following devices:
- Floppy - floppy drive;
- HDD-0 (IDE-0) - hard disk connected to the Primary Master channel;
- HDD-1 (IDE-1) - hard disk connected to the Primary Slave channel;
- HDD-2 (IDE-2) - hard disk connected to the Secondary Master channel;
- HDD-3 (IDE-3) - hard disk connected to the Secondary Slave channel;
- CDROM (CD / DVD) - a CD-ROM drive connected to one of the IDE channels;
- - SuperDisk device (LS-120);
- - ZIP drive;
- LS / ZIP - SuperDisk device (LS-120) or ZIP drive;
- - floppy drive with USB interface;
- USB CDROM - CD-ROM drive with USB interface;
- USB HDD - hard disk with USB interface;
- USB-ZIP - ZIP-drive with USB interface;
- SCSI - SCSI device;
- ATA100RAID - IDE RAID array;
- Disabled (None) - there is no device to boot.
In some newer BIOS versions, the First Boot Device only those drives that were actually detected will be present. If the device you want is not listed, you should check that it is correctly connected to the computer, as well as the device settings in the section and other related sections.
In some BIOS versions, all boot devices are divided into several groups. In this case, the values of the First / Second / Third Boot Device parameters can be as follows:
CDROM Boot Priority, CDROM Drives
To boot the computer, the parameter sets the CD drive; used in the same way as parameters Removable Device Priority and Hard Disk Boot Priority.
Boot Other Device, Try Other Boot Device
The parameter allows booting from other devices that are not explicitly specified in the parameters First / Second / Third Boot Device... Possible values:
1. - only those devices that are explicitly selected in the First / Second / Third Boot Device parameters can be used for booting.
Here came ... BIOS ... For some users, this abbreviation may be unfamiliar. And then they talk about activating the boot from a USB flash drive. The devil is not so terrible as he is painted. So, first things first.
What is BIOS
On the motherboard of any personal computer or a laptop has a special memory chip that stores the BIOS. BIOS (Basic Input / Output System) stands for Basic Input / Output System. BIOS must include a program initial setup computer ( SETUP), with which you can control various system parameters of your computer, for example, date, time, fan speed, device boot priorities ...
Here are the device boot priorities and let's talk in more detail.
From which device the BIOS tries to boot the computer by default
Typically, the first boot device in a computer is the hard drive. But if we need to install an operating system on a computer, then we need to set a CD-ROM or Flash disk in the BIOS settings as the first bootable device, depending on which media we plan to install the operating system from.
The trouble is, to install the first boot device, you need to enter the SETUP program. To do this, after turning on the computer, you must press a certain key combination. Which one?
How to enter BIOS to configure boot from a USB flash drive
BIOSes of different motherboard manufacturers have different key combinations for entering SETUP. As a rule, this is either the " DEL"(most often on desktops) or" F2"(most often happens with laptops). When turned on computer BIOS usually displays a hint about the need to press a particular key, for example, Press DEL to enter SETUP(Press the DEL key to enter the installer).
Well, if a hint on how to enter the installation program does not appear or appears only for a moment, then you need to refer to the documentation for the motherboard. But do not rush to do this. It is usually enough to try keystrokes " F10"(manufacturer HP)," F1"(manufactured by IBM and Phoenix) or" Esc"(Toshiba manufacturer). Well, if these keys did not help, then use the official manufacturer's documentation.
How to activate booting from a USB flash drive in BIOS
We figured out how to enter the installer. Now you need to activate booting from USB Flash. And here again the same parsley awaits us: each motherboard manufacturer has a different installer menu. Therefore, further you will have to describe your actions for different manufacturers.
I note that over time, you will learn to intuitively activate boot priorities regardless of the manufacturer, since in the BIOS of any manufacturer you will find the same familiar device names: Hard drive- HDD, CD-ROM- compact disc, Floppy or FDD- a device for reading floppy disks, Removable Devices- removable devices (removable disks and flash drives).
In the BIOS of some manufacturers, you will see priorities in the form of phrases First Boot Device(First boot device), Second Boot Device(Second boot device) Third Boot Device(Third boot device), Boot Other Divice(Other boot devices), Hard Disk Boot Priority(Boot priority hard drives), and in the BIOS of other manufacturers it will be necessary to move the device names from top to bottom, thereby increasing their boot priority.
Navigation through the menu items in the BIOS is done using the cursor keys, the menu item is selected by pressing the key Enter... To move one level up (or back) use the key Esc... The changes made to the settings are saved by the command SAVE and Exit SETUP(Save changes and exit the installer) in the menu Exit or by pressing the " F10".
Attention! Before activating in BIOS boot from a USB flash drive, insert this same USB flash drive into the USB port of your computer. The fact is that in the BIOS of some manufacturers, the flash drive is displayed in the menu item Hard Disk Priority as a separate hard drive only when it is physically connected to the computer.
Enabling booting from a USB flash drive in BIOS of different manufacturers
Phoenix BIOS Boot then choose USB HDD and press the " F6"or move the device USB HDD up with keys -/+ ... At the end we press " F10
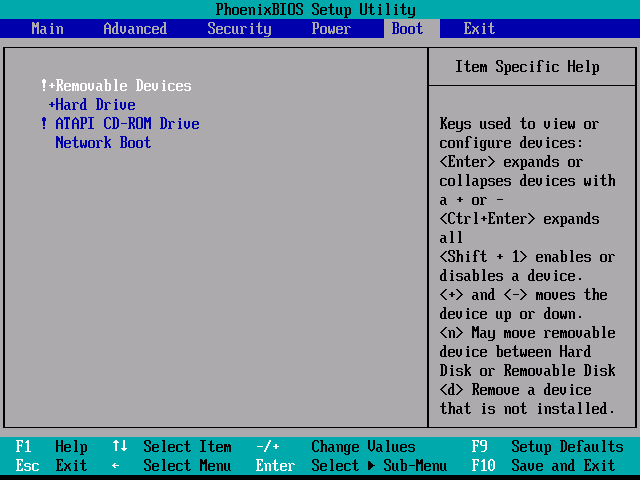
Award BIOS- in the menu you need to find the item Advanced BIOS Features, then go to the submenu Boot Sequence(Boot Seq & Floppy Setup) and choose as First Boot Device device USB HDD... At the end we press " F10"to exit the installer and save your changes.
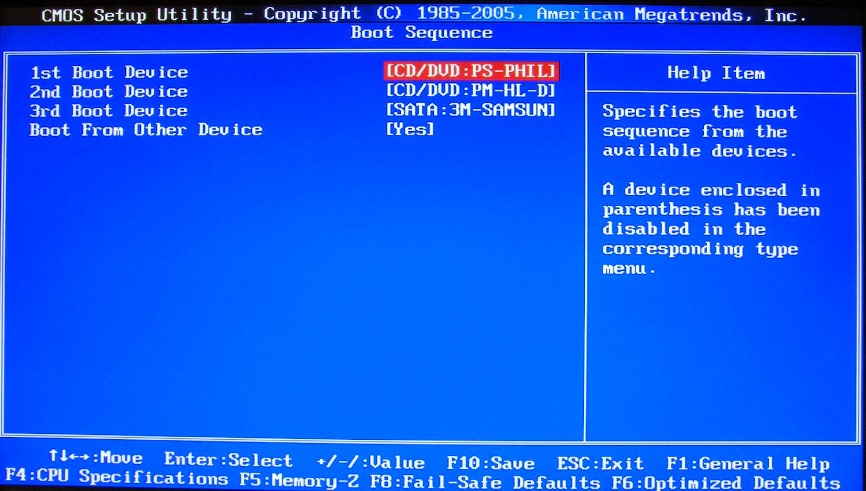
Lenovo BIOS- in the menu you need to find the item Boot then find the parameter Boot Priority Order and select a device USB HDD, then click " F6"to make it first. At the end we press" F10"to exit the installer and save your changes.
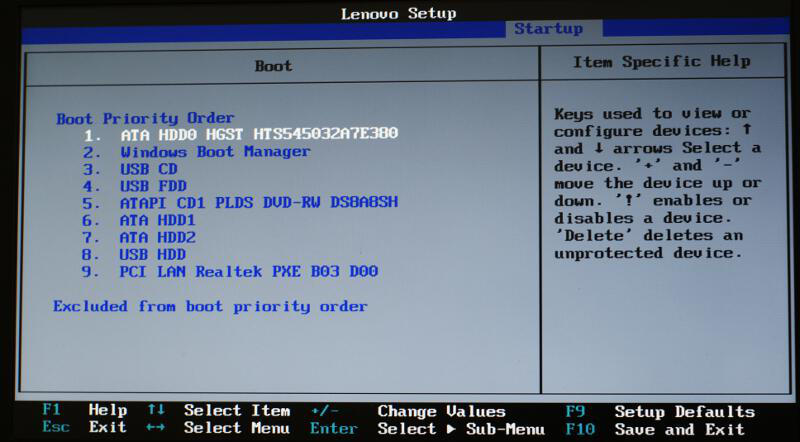
HP BIOS- in the menu you need to find the item Advanced, then go to item Boot options, select device USB Hard Drive... At the end we press " F10"to exit the installer and save your changes.
DELL BIOS- in the menu you need to find the item System, then go to item Boot Sequence and press Enter, then select the device USB Storage Device, press the " U"to make the USB flash drive the first bootable device. In the end, you need to exit the installer and save the changes.
Well, in conclusion, I would like to inform you that it may turn out that the BIOS does not support booting from a USB flash drive (you simply cannot find the USB HDD item). This can happen if the computer was purchased five years ago. The solution in this case is likely to be updating the BIOS version. BIOS update on modern motherboards is a simple process. So go to the manufacturer's website and look for an update to your BIOS version.
Read the article and still don't understand anything? The article 05. Installing Ubuntu: BIOS setup, disk partitioning, installation I described in detail in the pictures the BIOS setting for booting from a USB flash drive using my computer as an example.
That's all. Questions - in the comments.
6.4. Configuring Boot Parameters and General BIOS Configuration
WITH using parameters discussed here, the initial boot of the computer is configured and they do not affect the normal operation of the system. In most BIOS versions, these parameters are located in the Advanced BIOS Features section (Fig. 6.4); there are other options in this section that will be discussed later.
Figure 6.4 - Parameters of the Advanced BIOS Features section
In BIOS versions with a horizontal menu bar, such as modern ASUS boards or ASRock, boot parameters are collected in the Boot section (Fig. 6.5).
System boot order.
The need to change the boot order of your computer is one of the most common problems that you have to resort to BIOS settings... By correctly setting these parameters, you can speed up the download and insure against problems that sometimes arise at this stage.
Once upon a time, computers could only boot from floppy or hard drive, and the order was determined only by the choice of one of these media. Gradually, there were more and more devices available for boot, and the number of corresponding parameters in the BIOS also increased. They will be discussed further.
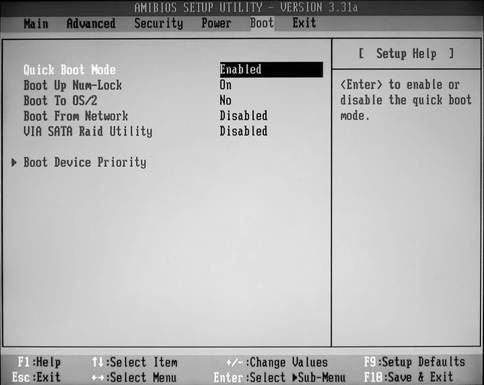
Figure 6.5 - Parameters of the Boot section (screenshot)
Boot Sequence.
The parameter determines the order of searching for the operating system on all storage devices. The value of this parameter is the sequence of devices on which the computer will look for the operating system, or rather the boot sector.
Several devices can be used as boot devices:
1. Disk drive. It is designated by the letter A :.
2. Hard drives... If the system has one hard disk, it will be designated by the letter C :, and when connecting additional ones, the letters D :, E :, F: are used.
3. Drives for CD or DVD. CDROMs are indicated, and if there are two devices in the system, the computer will boot from the one that is installed as Master.
4. SCSI drives and other devices, the list of which depends on the specific motherboard model and BIOS version.
ATTENTION! BIOS letters correspond to attached physical disks, not individual partitions into which a disk is partitioned in MS-DOS or Windows operating systems. For example, if there are two drives in the system, an HDD connected to the Primary Master channel will always be designated as C: in the BIOS, and a disk connected to any other channel as D :, despite the fact that in Windows it may have absolutely other designation.
One more example. When installing the operating system into a logical partition D: or E: of the first (or only) hard disk, to boot from it, specify the value C: in the BIOS, since letters in the BIOS represent physical disks, that is, the first (or only) drive is always will be C: even if it has multiple partitions (logical drives). In this case, the BIOS will transfer control of the Master Boot Record (MBR), and that, in turn, will transfer control to the boot sector of the active partition.
The system can support several types of drives. Therefore, the Boot Sequence parameter can have different sets of values.
1. A, C, SCSI. With this value, the loading order will be as follows:
The system will first look for a floppy disk in the floppy drive and, if successful, will boot from it. If the computer does not find the operating system on the floppy disk, the process will stop with a corresponding message, for example: Non-system disk or disk error. Insert system disk and press any key when ready. In this case, you need to replace the diskette with the system one or remove it to boot from the hard disk;
When no floppy disk is found, the computer will try to boot from the first hard drive. If there is no boot sector on it or there is no disk itself, the system will go to search for SCSI devices;
With a SCSI controller attached, the system will attempt to boot using the SCSI device. If the device is not found, the installation will terminate with the corresponding output.
2. C, A, SCSI. In this case, the computer will first try to boot from the hard disk, then from the floppy disk, and lastly from the SCSI device. Setting it to Boot Priority from the hard drive prevents the system from wasting time using the drive during a normal Windows boot.
4. C, CDROM, A. The search order will be as follows: hard drive, CD-ROM drive, floppy drive. This option is suitable for normal booting of the system from the hard drive.
5. CDROM, C, A. Boot first from the CD drive. This option is used to install the operating system from the installation CD. Then you can return to the primary boot from the hard drive, so as not to waste time polling the drive every time the computer boots.
6. D, A, SCSI. Use this option only if your system has two hard drives and you want to boot from the second drive.
7. SCSI, A, C. This option is used if the operating system was installed on a hard disk with SCSI interface. If it is not possible to boot from the SCSI device, the system will turn to a floppy disk or a regular IDE disk.
8. LS / ZIP, C. System will boot from SuperDisk (LS-120) or ZIP drive first. If no such media is available, the computer will try to boot from the hard drive. This option should be used only if you have one of the specified devices and need to boot from it.
In specific BIOS versions, other combinations are possible, for example A, C; A, SCSI, C; SCSI, C, A. In newer BIOS versions, the Boot Sequence parameter is practically not found, and to set the boot order, several separate parameters are used, which will be discussed below.
First Boot Device (1st Boot Device).
This parameter specifies the primary boot media for the system. If it is not possible to boot from this device, the computer will refer to those specified in the Second Boot Device and Third Boot Device parameters. First / Second / Third Boot Device options are widely used instead of Boot Sequence because they provide more flexibility in choosing the boot order.
The names of individual devices are used as the values for the First Boot Device parameter:
Floppy - floppy drive;
HDD-0 (IDE-0) - hard disk connected to the Primary Master channel;
HDD-1 (IDE-1) - hard disk connected to the Primary Slave channel;
HDD-2 (IDE-2) - hard disk connected to the Secondary Master channel;
HDD-3 (IDE-3) - hard disk connected to the Secondary Slave channel;
CDROM (CD / DVD) - CD drive connected to one of the IDE channels;
LS-120 - SuperDisk device (LS-120);
ZIP-100 - ZIP drive;
LS / ZIP - SuperDisk device (LS-120) or ZIP drive;
USB FDD - floppy drive with USB interface;
USB CDROM - CD-ROM drive with USB interface;
USB HDD - hard disk with USB interface;
USB-ZIP - ZIP-drive with USB interface;
SCSI - SCSI device;
ATA100RAID - IDE RAID array;
Disabled (None) - there is no device to boot.
By choosing specific values for the First / Second / Third Boot Device parameters, you can configure any desired boot sequence.
Recently, there are more and more BIOS versions, where all boot devices are divided into several groups. In this case, the values of the First / Second / Third Boot Device parameters can be as follows:
Disabled - no boot device has been selected.
In some BIOS versions, only certain categories of devices, such as hard drives, are grouped into groups. In this case, in the list of values of the First Boot Device parameter, both individual devices (from the above list) and their groups can be used.
Recently, there are also BIOS versions where only those drives that were actually detected are present as the values of the First Boot Device parameter. If the device connected to your computer is not listed in the boot options, you should check its settings in the Integrated Peripherals section and other related topics.
Second Boot Device (2nd Boot Device), Third Boot Device (3rd Boot Device).
These parameters define the second and third devices to boot the system; the values will be the same as for the First Boot Device parameter. Sometimes you can find a fourth boot device (although it is rarely needed), indicated by the 4th Boot Device parameter.
Hard Disk Boot Priority, Hard Disk Drives.
The parameter Hard Disk Boot Priority, Hard Disk Drives (Fig. 6.6) determines the order of booting from hard disks, if there are several of them. The values can be a list of disks that are connected to this motherboard, and in some newer versions, a list of actually detected disks.
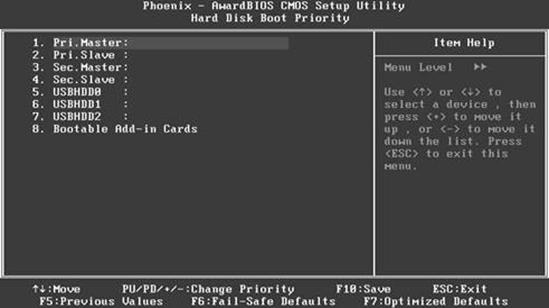
Figure 6.6 - Window for setting the priority of hard drives
To select a priority device, set it first in the list as follows.
1. Highlight the desired drive in the list using the cursor keys.
2. Press the "+" key on the additional numeric keypad to move the device up the list (using the key - down respectively).
Installing the device first in the list does not guarantee that it will boot from it first, since the order is determined by the First / Second / Third Boot Device parameters. So, to boot the system from the hard disk, you need to specify the Hard Disk value for the First Boot Device parameter.
Removable Device Priority, Removable Drives.
To boot the computer, this option selects a device with removable media... The list of such devices supported by the system is used as possible values: Floppy, LS-120, ZIP-100, USB FDD, USB-ZIP, etc. In new BIOS versions, only those devices that actually exist in the computer are available for selection.
The procedure for using this parameter is the same as for the Hard Disk Boot Priority parameter.
CDROM Boot Priority, CDROM Drives.
To boot the computer, the parameter sets the CD drive; used in the same way as Removable Device Priority and Hard Disk Boot Priority.
Boot Other Device, Try Other Boot Device.
The parameter allows booting from other devices that are not explicitly specified in the First / Second / Third Boot Device parameters. Possible values:
Enabled (Yes, On) - booting from explicitly not specified devices is allowed;
Disabled (No, Off) - only those devices that are explicitly selected in the First / Second / Third Boot Device parameters can be used for booting.
Boot From Network, Boot From LAN.
The parameter allows you to boot the computer using local network, for which it must have a server that provides remote loading. This method has already lost its former popularity, and for conventional computers the function must be disabled so as not to slow down the process.
Possible values:
Enabled (On) - priority boot from a network device is set;
 Bugs in Singularity?
Bugs in Singularity? Just Cause 2 crashes
Just Cause 2 crashes Terraria won't start, what should I do?
Terraria won't start, what should I do?