Systematic errors by sound signals. What the beeps mean when you turn on your computer
What do they mean sound signals when you turn on your computer?
When you turn on a working PC, after a few seconds, one short beep is heard, which should please the ear of any user ...
Remove dust from it.
Check that the power pad is securely attached to motherboard.
If it does not help, replacement or repair of the power supply unit is required.
2. Continuous signal - power supply is faulty. See item 1.
3. 1 short signal - no errors were found, the PC is working properly.
4. 1 short repetitive signal - problems with the power supply. See item 1.
5.1 long repetitive signal - malfunction random access memory.
6. 2 short beeps - minor errors detected.
Check that the cables and cables are securely fastened to the motherboard connectors. Set the BIOS to default values (Load BIOS Defaults).
7. 3 long signal- keyboard controller malfunction.
Check the integrity of the keyboard cable and the quality of the connections. Test the keyboard on a known good PC. If it does not help, you will need to repair or replace the motherboard.
8. 1 long and 1 short signals - a malfunction of the RAM. See item 5.
9. 1 long and 2 short signals - video card malfunction.
10. 1 long and 3 short beeps - keyboard malfunction. See item 7.
11. 1 long and 9 short beeps - error while reading data from the BIOS chip.
1. There are no signals - the power supply unit (PSU) is faulty or not connected to the motherboard.
Remove dust from it. Check that the power pad is securely attached to the motherboard. If it does not help, replacement or repair of the power supply unit is required.
2. 1 short signal - no errors were found, the PC is working properly.
3. 2 short signals - malfunction of the RAM.
Try removing the RAM module from the slot and reinserting it. If it doesn't help, replace it.
4. 3 short signals - error of the first 64 KB of main memory. See item 3.
5. 4 short signals - malfunction of the system timer.
6. 5 short signals - central processor malfunction.
Reboot your PC. If it does not help, you will need to replace the processor.
7. 6 short signals - keyboard controller malfunction.
Check the integrity of the keyboard cable and the tightness of the connections. Test the keyboard on a known good PC. If it does not help, you will need to repair or replace the motherboard.
8. 7 short signals - motherboard malfunction.
Reboot your PC. If it does not help, you will need to repair or replace the motherboard.
9. 8 short signals - malfunction of the RAM of the video card.
Reboot your PC. If it does not help, replace the video card.
10. 9 short beeps - an error while checking the checksum of the BIOS chip.
Rewriting (flashing) of the microcircuit is required. If it does not help, replace the microcircuit.
11. 10 short beeps - it is impossible to write to CMOS-memory.
Reset the contents of the memory (to do this, turn off the PC, unplug the power cord. Find the switch next to the CMOS-memory battery, set it to the Clear CMOS... Press - with disabled network cable! - PC power button. Set the switch to its original position. If there is no switch on your motherboard, remove the battery for half an hour). Set the BIOS to default values (Load BIOS Defaults). If it does not help, replace the microcircuit.
12. 11 short signals - malfunction of the RAM. See item 3.
13. 1 long and 2 short signals - video card malfunction.
It is recommended to remove the video card and reinsert it. Check the integrity and quality of the monitor cable connection. If it does not help, replace the video card.
14. 1 long and 3 short signals - video card malfunction. See item 13.
15. 1 long and 8 short signals - video card malfunction. See item 13.
Phoenix BIOS signals
1-1-3. Error writing / reading CMOS data.
1-1-4. Checksum error of the contents of the BIOS chip.
1-2-1. The motherboard is defective.
1-2-2. DMA controller initialization error.
1-2-3. An error occurred while trying to read / write to one of the DMA channels.
1-3-1. RAM regeneration error.
1-3-3. An error occurred while testing the first 64 KB of RAM.
1-3-4. Similar to the previous one.
1-4-1. The motherboard is defective.
1-4-2. RAM test error.
1-4-3. System timer error.
1-4-4. I / O port access error.
2-x-x. Problems with the first 64k memory (x - from 1 to 4)
3-1-1. Error initializing the second DMA channel.
3-1-2. Failed to initialize the first DMA channel.
3-1-4. The motherboard is defective.
3-2-4. Keyboard controller error.
3-3-4. Video memory testing error.
4-2-1. System timer error.
4-2-3. Line error A20. Defective keyboard controller.
4-2-4. An error occurred while working in protected mode. The central processor may be defective.
4-3-1. An error occurred while testing the RAM.
4-3-4. Real time clock error.
4-4-1. Serial port test error. May be caused by a device using this port.
4-4-2. An error occurred while testing the parallel port. See above.
4-4-3. An error occurred while testing the math coprocessor.
Attention!!!
1. If you do not feel sufficiently prepared, in case of problems - contact the specialists.
2. Perform all manipulations with the "hardware" with the power off!
3. Before repairing your PC, you must discharge the electrostatic charge (for example, by touching the nickel-plated surface of the faucet with both hands).
4. Even after removing the electrostatic charge, try, if possible, not to touch the pins of the central microprocessor, video adapter processor and other microcircuits.
5. Do not clean the oxidized gold-plated contacts of the video card and RAM modules with abrasive materials! For these purposes, you can use a rubber band like "eraser".
6. Remember that most of the "malfunctions" of the PC are "healed" by a simple reboot!
7. If you do not know which BIOS manufacturer is installed on your PC, look at the top line on the monitor screen during boot, for example, for Award there will be a line like Award Modular BIOS, for AMI - American Megatrends, Inc. The BIOS version must also be indicated in the passport of your PC.
Remove dust from it.
Check that the power pad is securely attached to the motherboard.
If it does not help, replacement or repair of the power supply unit is required.
2. Continuous signal - power supply is faulty. See item 1.
3. 1 short signal - no errors were found, the PC is working properly.
4. 1 short repetitive signal - problems with the power supply. See item 1.
5.1 long repetitive signal - malfunction
random access memory. Try removing the RAM module from the slot and reinserting it. If it doesn't help, replace it.
6. 2 short beeps - minor errors detected.
Check that the cables and cables are securely fastened to the motherboard connectors. Set the BIOS to default values (Load BIOS Defaults).
7. 3 long beeps - keyboard controller malfunction.
Check the integrity of the keyboard cable and the quality of the connections. Test the keyboard on a known good PC. If it does not help, you will need to repair or replace the motherboard.
8. 1 long and 1 short signals - a malfunction of the RAM. See item 5.
9. 1 long and 2 short signals - video card malfunction.
10. 1 long and 3 short beeps - keyboard malfunction. See item 7.
11. 1 long and 9 short beeps - error while reading data from the BIOS chip.
1. There are no signals - the power supply unit (PSU) is faulty or not connected to the motherboard.
Remove dust from it. Check that the power pad is securely attached to the motherboard. If it does not help, replacement or repair of the power supply unit is required.
2. 1 short signal - no errors were found, the PC is working properly.
3. 2 short signals - malfunction of the RAM.
Try removing the RAM module from the slot and reinserting it. If it doesn't help, replace it.
4. 3 short signals - error of the first 64 KB of main memory. See item 3.
5. 4 short signals - malfunction of the system timer.
6. 5 short signals - central processor malfunction.
Reboot your PC. If it does not help, you will need to replace the processor.
7. 6 short signals - keyboard controller malfunction.
Check the integrity of the keyboard cable and the tightness of the connections. Test the keyboard on a known good PC. If it does not help, you will need to repair or replace the motherboard.
8. 7 short signals - motherboard malfunction.
Reboot your PC. If it does not help, you will need to repair or replace the motherboard.
9. 8 short signals - malfunction of the RAM of the video card.
Reboot your PC. If it does not help, replace the video card.
10. 9 short beeps - an error while checking the checksum of the BIOS chip.
Rewriting (flashing) of the microcircuit is required. If it does not help, replace the microcircuit.
11. 10 short beeps - it is impossible to write to CMOS-memory.
Reset the contents of the memory (to do this, turn off the PC, unplug the network cable. Find the switch next to the CMOS-memory battery, set it to the Clear CMOS position. Press - with the network cable disconnected! - the power button of the PC. Set the switch to its original position. there is no switch on your motherboard, remove the battery for half an hour). Set the BIOS to default values (Load BIOS Defaults). If it does not help, replace the microcircuit.
12. 11 short signals - malfunction of the RAM. See item 3.
13. 1 long and 2 short signals - video card malfunction.
It is recommended to remove the video card and reinsert it. Check the integrity and quality of the monitor cable connection. If it does not help, replace the video card.
14. 1 long and 3 short signals - video card malfunction. See item 13.
15. 1 long and 8 short signals - video card malfunction. See item 13.
Phoenix BIOS signals
1-1-3. Error writing / reading CMOS data.
1-1-4. Checksum error of the contents of the BIOS chip.
1-2-1. The motherboard is defective.
1-2-2. DMA controller initialization error.
1-2-3. An error occurred while trying to read / write to one of the DMA channels.
1-3-1. RAM regeneration error.
1-3-3. An error occurred while testing the first 64 KB of RAM.
1-3-4. Similar to the previous one.
1-4-1. The motherboard is defective.
1-4-2. RAM test error.
1-4-3. System timer error.
1-4-4. I / O port access error.
2-x-x. Problems with the first 64k memory (x - from 1 to 4)
3-1-1. Error initializing the second DMA channel.
3-1-2. Failed to initialize the first DMA channel.
3-1-4. The motherboard is defective.
3-2-4. Keyboard controller error.
3-3-4. Video memory testing error.
4-2-1. System timer error.
4-2-3. Line error A20. Defective keyboard controller.
4-2-4. An error occurred while working in protected mode. The central processor may be defective.
4-3-1. An error occurred while testing the RAM.
4-3-4. Real time clock error.
4-4-1. Serial port test error. May be caused by a device using this port.
4-4-2. An error occurred while testing the parallel port. See above.
4-4-3. An error occurred while testing the math coprocessor.
Attention!!!
1. If you do not feel sufficiently prepared, in case of problems - contact the specialists.
2. Perform all manipulations with the "hardware" with the power off!
3. Before repairing your PC, you must discharge the electrostatic charge (for example, by touching the nickel-plated surface of the faucet with both hands).
4. Even after removing the electrostatic charge, try, if possible, not to touch the pins of the central microprocessor, video adapter processor and other microcircuits.
5. Do not clean the oxidized gold-plated contacts of the video card and RAM modules with abrasive materials! For these purposes, you can use a rubber band like "eraser".
6. Remember that most of the "malfunctions" of the PC are "healed" by a simple reboot!
7. If you do not know which BIOS manufacturer is installed on your PC, look at the top line on the monitor screen during boot, for example, for Award there will be a line like Award Modular BIOS, for AMI - American Megatrends, Inc. The BIOS version must also be indicated in the passport of your PC.
Imagine the following situation in your head: you wake up in the morning, go to the shower, make tea, and turn on your computer to check your mail or play your favorite toy.
You turn it on and look forward to how you will win in a virtual shootout of other players on the server, but instead of turning on the monitor and Windows boot from system unit strange squeaks emanate.
No, this is not a mouse that lives there. These are signals from BIOS! Many will ask: “What does this term mean? What do the BIOS beeps mean when you turn on the PC? " Perhaps this will be the topic for our article!
What is BIOS?
BIOS is special program which is built into the main board personal computer... Many people will be surprised, but given word pronounced correctly in English, like "Bayos". By the way, it is the correct pronunciation that eliminates confusion with another concept - BeOS (operating system).
What does this program? First of all, it tests the state of the computer during the startup process. Thanks to sounds, the user can easily find out what is malfunctioning in your computer or not functioning at all.
There are signals that are output to the monitor and by means of low-frequency vibrations using a speaker (small speaker). The second purpose is to load the operating system, without which you would not be able to use your computer.
Its constituent parts are drivers that help link programs, machine language, computer devices and an interface into a single, inextricable system. In addition, the BIOS helps to customize the operation of removable media and attached devices.
Believe it or not, Bayos was outdated back in 2000. It was replaced by EFI, a more modern version that can be called small operating system... A big plus is the built-in browser that allows you to access the Internet without loading the main OS - Windows or Lunix. 
Also, using the EFI, you can interact with connected devices and with Internet networks. But, unfortunately, the version has many flaws and "bugs".
What the BIOS beeps mean
Remember the situation given in the example at the beginning of the article. To troubleshoot, you need to know your BIOS manufacturer: AMI, Award, Phoenix. You can find them out by looking at the motherboard, where there is a ROM circuit with a special code written on it.
You can also see the name when the PC boots up on the splash screen. Second, listen to the signal and notice the sequence.
There are long and short squeaks, which encrypt signals about faults. We believe that this effective method for precise definitions of the problems of the "iron monster".
Previously, the popular BIOS system was AMI, developed by American Megatrends. Soon it was replaced by Award Software, but after some time AMI again took its crown place. Peripheral giants such as Gigabyte, MSI and AsusTeK use it to make their motherboards.
Then a new competitor entered the world market - Intel. The company adopted the AMI platform for its BIOS. This is how a new system appeared - AMI / Intel. Also in the era of "Pentiums" another BIOS came out, from Phoenix, which is still the most popular.

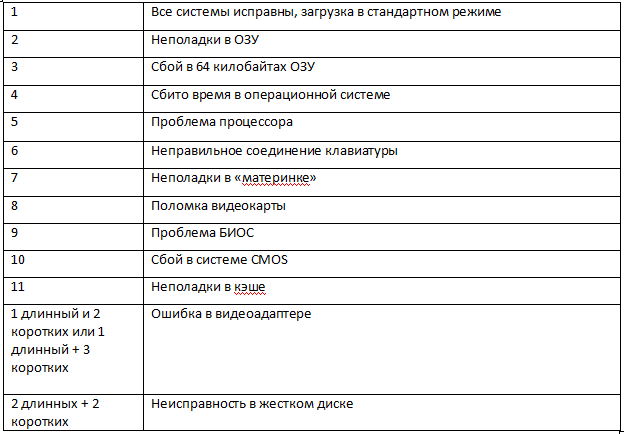
You can decrypt them using the table below.
AMI BIOS
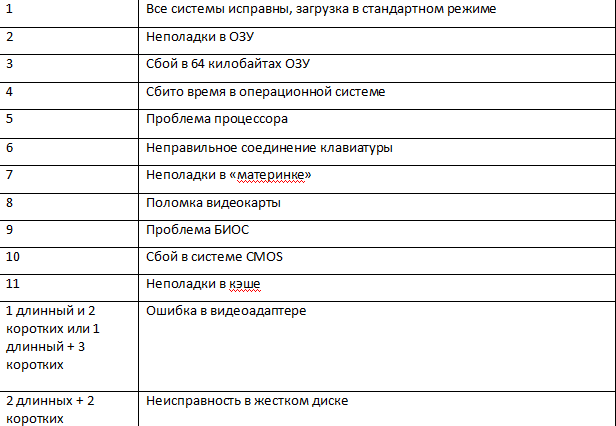
Award BIOS
Below are short beeps.
Award BIOS
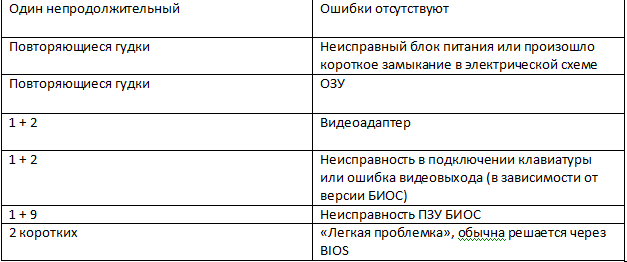
Phoenix
And finally, the most difficult thing that can hardly be identified. Phoenix uses short beeps that sound at intervals. A dash indicates a pause and an asterisk indicates a beep. It's like a real Morse code!
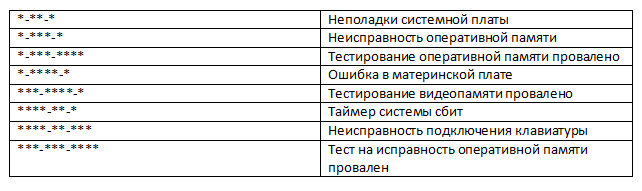
Conclusion
Dear readers of our blog, our article has come to an end. Thanks to her, you learned what the BIOS beeps mean when you turn on the PC and what it is.
We list all the important points that you should definitely know:
- This system monitors the initial technical condition, as well as at startup.
- Crash reporting occurs via speaker and output sounds text message on the computer display. In addition, using the BIOS, the user has the ability to control the devices connected to the computer.
- There are three most popular BIOS ROMs: Award, Phoenix, and AMI. You can find out which one you have using a sticker on the motherboard or by the splash screen that appears when the computer boots.
- You can find out what kind of problem you have, what hardware of your computer is connected with, thanks to the table above.
We also hope that the article was not empty for you and helped you solve the problem! We will be glad if you leave your comment in which to express your opinion.
It is important and helps us to improve our content in order to delight you later. Thank you for your attention and for being with us!
 Bugs in Singularity?
Bugs in Singularity? Just Cause 2 crashes
Just Cause 2 crashes Terraria won't start, what should I do?
Terraria won't start, what should I do?