sql update. Upgrading Microsoft SQL Server databases. Update Preparation Program
Microsoft is constantly releasing updates and new versions of its products and SQL Server Express is no exception, so it is useful for novice administrators to know how this SQL server is updated, and today we will deal with update SQL Server 2008 Express to SQL Server 2014 Express.
A little about Microsoft SQL Server 2014 Express
SQL Server 2014 Express is a free data management system that is great for novice programmers and administrators.
This version of SQL Server Express is the latest version at the time of this writing, and it was published on 06/25/2014, you can download it from the Microsoft Download Center - http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=42299
We have already touched on the topic of SQL Server Express, namely, they installed SQL Server 2008 Express and Management studio, and even updated it to SP3 in the material Installing Service Pack 3 (SP3) for MS SQL Server 2008 Express, now it's time to switch to new ones, current versions SQL Server Express, namely the 2014 version.
Note! In past SQL Server Express articles, as a test operating system we used Windows Server 2008 R2, today for a change we will update the SQL server already on the client 32-bit Windows 7 OS.
I also want to note that upgrading SQL Server 2008 Express to 2014 version requires that 2008 version be upgraded to SP3. If you do not know if your SQL server is up to date or not, then this is not a problem, you can find out the current version by using a simple select SQL query, which is listed just below, to do this, open Management studio, then open the query editor and write the following:
Select @@version
In response you will receive detailed information about the version, for example, I have a version before the update:
Microsoft SQL Server 2008 (SP3) - 10.0.5500.0 (Intel X86) Sep 22 2011 00:28:06 Copyright (c) 1988-2008 Microsoft Corporation Express Edition on Windows NT 6.1 (Build 7601: Service Pack 1)
Which tells me that I can safely start the upgrade, and after that we will check to which version we have upgraded using the same query.
Note! Before starting the upgrade process, it is recommended to install all Latest updates operating system, including Microsoft . NET Framework, or provide Internet access to the computer on which you are going to upgrade SQL Server. I also recommend making an archive of the SQL server database, in case you store important data that you do not want to lose in case of critical error in the process of updating.
Upgrading SQL Server 2008 Express to 2014
Since I already said that I have a 32 bit OS, I follow the link above, click download and select the distribution kit for 32 bit systems, namely ExpressAndTools 32BIT\SQLEXPRWT_x86_RUS.exe since this distribution has both the SQL server itself and Management studio, then I click NEXT. Then the download will start, eventually the file will be uploaded SQLEXPRWT_x86_RUS.exe size 888.3MB.
Step 1
We run the file SQLEXPRWT_x86_RUS.exe and you will see a window for selecting a directory in which you need to unpack all the installation files from this distribution, you choose the place that is convenient for you, yes, by the way, so that this place has at least a couple of gigabytes free space. And since we are talking about free space, then on the disk on which SQL Server 2008 Express is installed, you need approximately 2.2 gigabytes additionally free space for 2014 version of SQL server. I selected the test directory on drive C and clicked "OK"
Step 2
After unpacking, you will immediately run " SQL Server Installation Center', where we choose ' Upgrading from SQL Server 2005, SQL Server 2008, SQL Server 2008 R2, or SQL Server 2012 to SQL Server 2014»

During the installation process, the following window will constantly appear, this is normal

Step 3
At this step, you will be asked to agree to the terms of the license for this software, You naturally agree, check the appropriate box, and click " Further»

Step 4
And here I want to note that the entire renewal process takes place almost in automatic mode, the only exceptions are those steps in which you need to participate (choose something) or there were some warnings during the update process, for example, this step will slip for you if everything is fine, but everything was fine with me, it slipped, but for clarity, I went back and took a screenshot of the actions that the installer performed at this step, namely, it checked the global installation rules, i.e. Search possible problems that may occur during the upgrade.

Step 5
In the next step, you will be prompted to use the update center to search important updates, I did not select this item, but you can put it, then click " Further»

Step 6
This step will also slip if you have the Internet turned on, and if not, then a window will appear (the picture below I specifically tried on another computer), in which you will be prompted to “Repeat the check” or skip this step, in principle, there is nothing to worry about if You have this window, taking into account the fact that you have an updated OS.

Step 7
Installation of installation files also skips if everything is fine.
Step 8
At this step, the installation program will check the update rules and if there are any warnings, the program will tell you about it, everything is fine with me.

Step 9
At this stage, you need to select the instance of the SQL server to be updated, if you have several of them, you select the one you need, and since I have only one, I don’t change anything, I press “ Further»

Step 10
This step involves selecting the components that need to be updated, but since our distribution package includes updating all components at once, this window will slip if some conditions are met, for example, if you do not have enough disk space to install the update , then the installation program at this step will tell you about it and will not let you go further, for example, you will receive this window

Step 11
This stage is devoted to another check in which the installer tries to determine whether the update process will be blocked, and for this it checks especially important conditions, and if everything is fine, then this window will be skipped, and if not, the program will issue appropriate warnings . I have passed all the checks successfully and the update started immediately


Step 12
If no errors popped up during the update process, then everything is fine at the end you will receive a message that you need to reboot, and that all components have been successfully updated or, accordingly, not updated.


That's all left to reboot, and then check the operation of the updated DBMS and its controls, for this, we launch a new one Management studio 2014, check the data, if it was there. And of course, we will check the version of both SQL server and Management studio, for this you can click Help->About where you can see what it is a new version management studio

And to check the version of the SQL server, just like before, let's run a query select @@version and in response we get:
Microsoft SQL Server 2014 - 12.0.2000.8 (Intel X86) Feb 20 2014 19:20:46 Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation Express Edition on Windows NT 6.1 (Build 7601: Service Pack 1)
On this I propose to end, if you have any questions, then ask them in the comments or on our forum. Good luck!
The SQL Server Setup Wizard provides an in-place upgrade of all SQL Server components to SQL Server 2016 using a single component tree.
You must run the installer with administrator rights. When installing SQL Server from a remote shared folder, you must use a domain account that has Read and Execute permissions on the remote shared folder and is a local administrator.
If you are upgrading the Database Engine, please review the article and complete the following tasks as appropriate for your environment.
Create backups all database files SQL data Server upgradable instances so that you can restore them if necessary.
Run the appropriate DBCC commands on the databases being upgraded to make sure they are in a consistent state.
Estimate how much disk space, in addition to the user databases, will be required to upgrade SQL Server components. For more information about how much disk space SQL Server components take up, see .
Ensure that the existing SQL Server system databases (master, model, msdb, and tempdb) are configured for auto-growth and that they have sufficient disk space.
Ensure that all database servers have login credentials for the master database. This is important for database recovery because system login credentials are stored in the master database.
Disable all stored procedures that run at system startup. This is necessary because the upgrade process will stop and start services on the SQL Server instance that is being upgraded. Stored procedures that run at system startup can block the update process.
When upgrading instances of SQL Server for which SQL Server Agent has detected MSX/TSX associations, upgrade the target servers before upgrading the core servers. If you upgrade the master servers before the target servers, SQL Server Agent will not be able to connect to the master instances of SQL Server.
Close all applications and services that have dependencies on SQL Server. If there are local applications connected to the instance being upgraded, the upgrade process may fail.
Make sure replication is up to date and stop replication.
For a detailed description of the rolling upgrade procedure in a replicated environment, see .
Upgrading to SQL Server 2016
Insert the SQL Server installation media, navigate to root folder and double-click Setup.exe. To install from a shared network resource, navigate to its root directory, and double-click Setup.exe.
The installation wizard starts the SQL Server Installation Center. To upgrade an existing instance of SQL Server, click Installation in the navigation pane on the left, then select Upgrading from SQL Server 2008, SQL Server 2008 R2, SQL Server 2012, or SQL Server 2014.
On the Product Key page, select an option to indicate whether you are upgrading to a free edition of SQL Server or if you have a PID key for a production version of this product. See articles and for more information.
On the License Terms page, review the license agreement. If you agree with it, check the box I accept the terms of the license agreement and press the button Further. To help improve SQL Server, you can also enable the feature usage monitoring option and send reports to Microsoft.
In the Global Rules window, the installation procedure will automatically proceed to the Product Updates window if there are no rule errors.
Then the page will appear Microsoft updates, unless the Microsoft Update check box is selected in Control Panel\All Control Panel Items\Windows Update\Changes. Selecting the checkbox on the Microsoft Update page will change your computer settings to apply the latest updates when viewed on Windows Update.
The Product Update page lists the latest SQL Server product updates. If you do not want to install updates, clear the checkbox Enable SQL Server Product Updates. If no product updates are found, SQL Server Setup does not display this page and jumps directly to the page Installing files .
On the Installation page installation files» The installer displays progress bars for downloading, extracting, and installing installation files. If a SQL Server Setup update is found, it will also be installed if it is specified to be used.
In the Update Rules window, the installation procedure will automatically proceed to the Select Instance window if there are no rule errors.
On the Select Instance page, select the instance of SQL Server that you want to upgrade. To update common components and controls, select Update only shared components.
The Feature Selection page automatically highlights upgradeable features. After selecting a component, the description of its group is displayed in the right pane of the window.
The requirements for the selected components are shown in the right pane. SQL Server will install a required component that has not yet been installed in the installation step later in this procedure.
On the Instance Configuration page, enter the SQL Server Instance ID.
Instance ID- By default, the instance name is used as the instance identifier. Used to identify installation directories and registry keys for a given instance of SQL Server. Valid for both default instances and named instances. For the default instance, the instance name and ID is "MSSQLSERVER". To set an instance ID other than the default, enter a value in the field Instance ID.
All SQL Server updates (including service packs) apply to each of the components of an instance of SQL Server.
Installed Instances- This grid lists all instances of SQL Server installed on the computer that is running Setup. Because the computer already has a default instance, you must install a named instance of SQL Server 2016.
The set of operations remaining in this section depends on which components were selected for installation. Depending on the selection made, not all pages may be displayed.
The Server Configuration: Service Accounts page for SQL Server services displays the default accounts. The services that you can configure on this page depend on the components you select to update.
Authentication information and logins will be carried over from the previous instance of SQL Server. You can assign a single login account to all SQL Server services, or you can configure service accounts individually. You can also specify whether services will start automatically, manually, or be disabled. Microsoft recommends configuring service accounts individually, giving each of the SQL Server services the minimum permissions required to perform its tasks. See the section for more information.
To specify one login account for all service accounts for this instance of SQL Server, enter the credentials in the fields at the bottom of the page.
Safety note. Don't use blank passwords. Choose strong passwords.
After entering the login details for SQL Server services, click the button Further.
On the Full-Text Search Refresh Options page, specify the refresh options for the databases to be upgraded. See the section for more information.
If all rules are satisfied, the Component Rules window will automatically change to the next one.
The Ready to Upgrade page displays a tree view of the installation options set in the installer. To continue, click the button Install. SQL Server first installs the required components for the selected tools, then installs the tools themselves.
During installation, the installation progress page displays the status of the installation so that you can monitor its progress.
After installation, the Completion page will provide a link to the installation summary log file and other important notes. To complete the SQL Server installation process, click the button Ready.
If you are prompted to restart your computer, restart. After the installation is complete, it is important to read the installation wizard message. For more information about installation log files, see .
After upgrading to SQL Server, complete the following tasks.
Server Registration: the upgrade process removes the registry settings for the previous instance of SQL Server. After the upgrade, you must re-register the servers.
Statistics update- To optimize query performance, it is recommended to update statistics for all updated databases. Call a stored procedure sp_updatestats to update statistics in user tables in SQL Server databases.
Setting new installation SQL Server- To reduce the vulnerable surface area of the system, SQL Server selectively installs and activates key services and functions. See the Readme file for this release for more information about customizing the surface area.
Updating data in the database means changing the values in existing table records. In this case, it is possible both to change the values of fields in a group of rows (even all rows of a table), and to edit the value of a field in a separate row.
In SQL, you can change a record in a database table using the UPDATE command. In its most minimal form, the data update command looks like this:
UPDATE table SET field = value
Here, UPDATE– a command indicating that a request is made to update the data;
table– the name of the table in which the changes will be made;
SET– a command followed by comma-separated fields with assigned values;
field– the field of the table in which the change will be made;
meaning– the new value to be entered into the field.
For example, if you want to set a field in all rows of a table to zero, you can run the following query:
UPDATE goods SET price = 0
In this case, the price field in absolutely all available rows of the table will take the value 0.
Single value change
Changing the value of all fields in a table is extremely rare. Most often, you need to change the value of a particular entry. To do this, at the end of the line with the UPDATE command, a WHERE directive will be added, which specifies a condition that determines which line the update operation should be performed on.
There is a table:
For example, we need to update the cost of a product with its num value known to us. To do this, run the following query:
UPDATE goods SET price = 150 WHERE num = 2
Now, before the operation of changing fields, a row will be selected that satisfies the condition num = 2. There is only one such row in the table. In this stock, the price will be changed to the value 150. As a result, we will get a table with the changed price of the goods.
Making changes to multiple rows with a selection condition
If you remember all the variety of conditions in the query, you can imagine how diverse the selections can be. Therefore, update queries can be executed either with one row, or with a group of rows, or with all rows of the table. It all depends on the task before you, as well as with which rows of the table you need to perform update operations.
For example, we want to halve the price of all items that currently cost 100 or more. Inquiry:
UPDATE goods SET price = price / 2 WHERE price >= 100
Condition WHERE here contains a rule that only products with a price equal to or greater than 100 will be selected, and those products with a price below 100 will not be affected by the query.
price = price / 2- the formula by which the new price of goods will be calculated. The new price will be written equal to the old price divided by two.
As a result of executing such a query, we get a table with changed records:
Update values in multiple fields of a row
If it is necessary to update several fields at once, all fields with their values are specified after the SET directive separated by commas. For example, you need to change the name and price of a product with code 2 to "iron", with a cost of 300:
UPDATE goods SET title = "(!LANG:iron" , price = 300 WHERE num = 2 !}
Such a query will assign each corresponding field in the row to its value. And the condition will indicate in which line the changes will be made.
The above are the main types of update operations. Based on them, queries are formed to solve most of the problems of changing data in development using SQL.
In this article, we will show how upgrade the Evaluation Edition or Express version of SQL Server 2008 R2 to a full working version of SQL Standard or Enterprise. A similar problem can be encountered when there is no one to test / develop software product a trial version of SQL Server is installed. It often happens that after the end of such testing / the end of the trial version period, a decision is made to transfer the system to commercial operation, for which it is necessary to switch to a full-featured edition of SQL Server, but you do not want to reinstall the DBMS.
Note. The instructions also apply to Microsoft SQL Server 2012 and R2.
SQL Server SQL 2008 R2 Evaluation (and newer versions) runtime - 180 days. After the trial period ends, the SQL Server service stops starting. In the case of SQL Server Express, there is a limit on the size of the database.
Upgrading a license license without the need to reinstall SQL Server is possible only from a minor edition to an older one, for example: Evaluation Edition / Express Edition with Advanced Services -> Standard or immediately in Enterprise.
After the end of the testing period, when trying to open SQL Server Management Studio, an error window appears:
Evaluation period has expired. For information on how to upgrade your evaluation software please go to http://www.microsoft.com/sql/howtobuy
MS SQL Server 2008 R2 Edition Update
In the first part, we will understand how to upgrade the version of SQL Server using a license key purchased from Microsoft or partners.
Run the SQL Installation Center (Start -> All Programs -> Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 -> Configuration Tools -> SQL Server Installation Center (64-bit)).

Advice. The same window can be opened by running setup.exe with installation disk SQL Server
Let's go to the maintenance section ( Maintenance) and select the item EditionUpgrade(Editor's update). The Edition Upgrade Wizard will start.

And, following the prompts of the wizard, enter license key SQL Server in the appropriate field.

Then you need to choose which copy (instance) of SQL Server you want to upgrade.
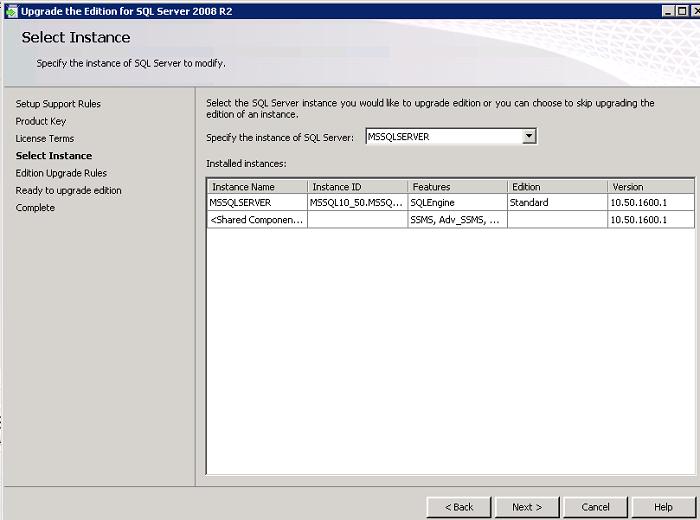
The final report will indicate the status of the version upgrade and a link to a detailed text log.

You can check which edition of SQL Server you are using SQL Server Management Studio by right-clicking on the instance name. In our example, this is SQL Server Enterprise.

The same operation can be performed from command line by running the setup.exe file from the disk with the SQL Server distribution with the specified parameters.
Setup.exe /Q /ACTION=editionupgrade /INSTANCENAME=
Advice. When upgrading from SQL Server Express, you must additionally enable the SQL Server Agent service and use the SQL Server Configuration Manager to set service options. account for the SQL Server Agent service.
Upgrading to a corporate Enterprise version of SQL Server (Volume License)
In the event that you want to upgrade your version of SQL Server through the Microsoft Volume Licensing program, you will be surprised that there are no keys for SQL Server in the Microsoft Volume Licensing Service Center (MS VLSC).

The fact is that the key is integrated directly into the distribution kit. The most interesting thing is that VLSC support recommends uninstalling the installed SQL Server and reinstalling it using the SQL distribution iso file downloaded from VLSC.
Fortunately, it is still possible to get the correct key directly from the distribution

 How to connect telephone sockets to the cable correctly?
How to connect telephone sockets to the cable correctly? How to copy contacts to your phone in Samsung: several ways
How to copy contacts to your phone in Samsung: several ways Rolsen is the largest electronics manufacturer in Russia Rolsen whose company is which country
Rolsen is the largest electronics manufacturer in Russia Rolsen whose company is which country