The format of the picture is what is. Which aspect ratio is better
Storage graphic images
When images are saved to disk, graphic files are created. Graphic information in files is encoded differently from computer memory.
Ø Format is a way of encoding graphic images .
V computer graphics use at least three dozen file formats for storing images. But only some of them have become the de facto standard and are used in the overwhelming majority of programs. As a rule, files of raster, vector, three-dimensional images have incompatible formats, although there are formats that allow storing data of different classes. Many applications focus on their own “specific” formats, transferring their files to other programs forces you to use special filters or export images to a “standard” format.
The variety of graphic formats is explained by the fact that there are a large number of applications for images with different requirements for the files in which they are saved.
When choosing a file format, you must remember that this format must be supported by a given scope. For example, the BMP format does not support images in the CMYK model used in printing, and therefore cannot be used in this area. You should also consider the possibility of subsequent conversion of types and color models that are required in the selected application.
In the process of editing an image, you often have to use masks. Therefore, if you have yet to return to editing, then you must use a format in which, in addition to the image, masks will also be saved.
To mask portions of an image, illustration and publishing programs use clipping paths that are created by the programs themselves. If the image is being prepared for layout, then it is better to choose formats that support clipping paths. You also need to make sure that importing clipping paths into the publishing system from the selected format will work correctly or will be possible at all.
To reduce the size of graphic files, many formats use data compression algorithms. Choosing a similar format can save space on your hard disk or storage media for transferring the file to another computer.
It is impossible to choose the best among the numerous existing formats for storing graphic images, which is explained by significant differences in their purpose. Thus, when choosing a particular format, it is necessary to focus only on its compliance with the work being performed. In particular, formats designed for preparing images for printing are not suitable for posting on the Internet, and vice versa. Below is the short info some of the graphic formats that you have to work with most often. This information can be useful when choosing a format based on its capabilities and the range of tasks to be solved.
Bitmap storage formats
Some common formats for storing bitmap graphics are discussed below.
BMP (Bitmap)- The storage format of raster images in operating system Windows (BMP filename extension). Accordingly, it is supported by all applications running in this environment. This format, created by Microsoft Corporation, is targeted at the operating room. Windows system... This format is used to represent bitmaps in program resources. It only supports RGB images up to 24-bit and does not support additional color and alpha channels, clipping paths, or color management. The format assumes the use of the simplest compression algorithm (RLE - Run Length Encoding) without loss of quality, but this option is rarely used due to incompatibility problems. BMP format exists in two versions - for Microsoft Windows and IBM OS / 2
RSX - one of the first raster formats created by Zsoft for the PC Paintbrush program (filename extension .PCX). Supports monochrome, indexed, and full-color RGB images, and does not support additional color and alpha channels, clipping paths, or color management. The format assumes the use of the simplest RLE lossless compression algorithm. The inability to store color-separated images, the lack of color models and other restrictions have led to the loss of popularity of the format. Currently in modern programs practically not used.
PhotoCD - Format developed by Kodak for storing digital raster images High Quality(filename extension is .pcd). The format of storing data in the file itself is called Image Ras. The file has an internal structure that provides storage of images with fixed resolutions, and therefore the sizes of any files only slightly differ from each other and are in the range of 4-5 MB. Each permission is assigned its own level, measured from the so-called baseline. (Base), constituting 512х768 points. There are five levels in the file - from Base / 16 (128x 192 points) to Basexl6 (2048x3072 points). During the primary compression of the original image, the downsampling method is used, with practically no loss of quality. Then the differences Base - Basex4 and Basex4 - Basexl6 are calculated. The final result is written to a file. To reproduce the information in high resolution, the inverse transformation is performed. The color model is used to store information about the color. YCC.
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) - created by Aldus specifically for storing scanned images. The format is intended for storing high quality raster images (filename extension is .TIF). Widespread and portable across platforms (IBM PC and Apple Macintosh), supported by most graphics, layout and design programs. Due to its flexibility, this format is truly versatile. Despite the fact that quite a long time has passed since the format was created, TIFF is still the main format for storing scanned images and placing them in illustration programs and publishing systems. Versions of it exist on all computer platforms, making this format very convenient for transferring bitmaps between platforms. TIFF supports monochrome, indexed, grayscale, RGB and CMYK images with 8 and 16-bit channels. The format can store clipping paths, calibration information, and print settings. Any number of additional alpha channels is also allowed, but additional color channels are not supported. A great advantage of the format is support for almost any compression algorithm. The most common LZW (Lempel-Ziv-Welch) algorithm - lossless compression of information - provides a very high compression ratio. Numerous compression programs use the same algorithm. general purpose that support ZIP format. The TIFF format comes in two flavors: for Macintosh and PC.
PSD (PhotoShopDocument) - proprietary format Adobe programs Photoshop (filename extension .PSD) is one of the most powerful storage options for raster graphic information. Allows you to remember the parameters of layers, channels, transparency, many masks. Supports 48-bit color coding, color separation, and various color models. Preferred for storing intermediate results of image editing, because preserves their multilayer structure in a form accessible for further editing. The main disadvantage is expressed in the fact that the absence of an effective information compression algorithm leads to a large volume of files.
FPX (FlaxPix)- created for the Internet and has an interesting property. Since images posted on Web pages have a low screen resolution (72 dpi), they cannot be used in printing or printed. The FPX format contains an image at the same time in several resolutions and provides the user with the ability to choose the required image resolution himself, so you can use this image for your own purposes. For application this format requires the installation of a special freeware module in the user's browser. The format supports RGB grayscale and full color images, but does not support additional color and alpha channels, clipping paths, and color profiles.
PNG (Portable Network Graphics) A relatively new (1995) image storage format for publishing them on the Internet (filename extension .PNG). Three types of images are supported - color with a depth of 8 or 24 bits and black and white with 256 shades of gray. Compression of information is practically lossless, there are 254 levels of alpha-channel, interlaced scanning.
JPEG (Join Photographic Expert Group) - this format was the first to implement a new principle of lossy image compression. It is based on removing from the image that part of it that is not perceived (or poorly perceived) by the human eye. As a result, the image, devoid of redundant information, takes up much less space than the original. The compression ratio in this format is set by the user; accordingly, the lower the compression ratio, the higher the image quality. On the other hand, a high compression ratio can significantly degrade the image quality. The most widespread use of JPEG is found on the Internet and in the creation of electronic presentations. In addition, the small size of the files allows them to be transmitted over communication channels, which makes this format indispensable in this area. It is undesirable to use this format in printing, although it can save clipping paths and color profiles. JPEG supports grayscale and full color images in RGB and CMYK, but it does not support additional color and alpha channels. The disadvantage of the channel is that compression defects are strongly manifested in drawings with clear boundaries and large fill areas. Dark lines on a light background are distorted due to the peculiarities of the compression algorithm, which processes the image in square blocks with a side of 8 pixels.
GIF (Graphic Interchange Format) - created by CompuServe (the current division of America Online) specifically for the transmission of raster images on global networks. Standardized in 1987 as a storage medium for compressed images with a fixed (256) number of colors (filename extension .GIF). The format is focused on compactness and uses the LZW compression algorithm, which does not result in loss of quality. It is used only on the Internet due to its high compression ratio. Supports only indexed images and does not support additional channels, clipping paths, or color profiles. In one version of the GIF format, it is possible to save several indexed images in one file at once in a position similar to layers - one below the other. Browsers are capable of accepting this layout and displaying images from the file in turn, thus implementing simple animations. There are two main versions of the GIF format: GIF87 and GIF89a- they are named after the year of standardization. Both versions support the presentation method graphic file with alternating lines. The later version of GIF89a allows one color to be set as transparent. Transparency means that one color in an image (usually the background color) can be declared transparent. This leads to the fact that instead of the background of the image, the background of the Web page itself is visible through it. This makes the image on the page look more natural. Line interlacing means that as the image is received from the Internet, its details are drawn gradually. The effect is similar to what happens when a blurry picture is gradually brought into focus. Due to the alternation of lines, users with slow modems can usually assess the content of the picture and the time required for a complete transmission at the very beginning of receiving a picture, and thereby decide whether to continue receiving or to refuse it. The limited possibilities for the number of colors make it exclusively used in electronic publications.
Greetings to the blog everyone on the blog site. Today I want to tell you about the three most popular image formats that are used on the Internet, on various sites, blogs and more.
This topic is very important because different formats are meant for different purposes. If you know all the nuances, you can easily reduce the load on your hosting because the loading (weight) of various formats is different.
Picture formats png, gif and jpeg
On the Internet today there are practically no sites left on the pages of which there would be no graphic elements. Today the most popular image formats are JPEG, PNG, GIF... They all differ in purpose. It's no secret that the page should "weigh" as little as possible. The size ("weight") of the graphics on the site depends on both picture formats, and on their size. Of course, different compression methods are used to reduce images, which can work with or without reducing image quality.
To get the most optimal image size for the web, you should use oriented ones, which will not create unnecessary load in users' browsers. You can use all known Photoshop, but I've seen recommendations for Adobe's Fireworks program. Next, let's look at three popular image extensions.

PNG (Portable Network Graphics)- originally developed as an alternative GIF extension... PNG was originally intended for use on the web. To date, PNG images have not gained much popularity. To be honest, I started using PNG images on my blog when I switched to transparent background Pictures. When compressing this format, we will not get any loss in color quality. and it has the advantage of saving unfinished images as PNG. With PNG variations, you can easily replace JPEG and GIF:
- PNG 8- the figure eight means that no more than 256 colors will be used when saving (by analogy, as in GIF). In general, PNG 8 was designed to replace GIF images, but at the same time it differs in that it cannot display animation in any form. Low-level transparency can be used.
- PNG 24- 24 means a 24-bit color gamut is being used. This variation was intended to replace JPEG format... As with the JPEG format, PNG 24 preserves the brightness and tints of colors in photographs. This image format uses about 16.7 million colors, which is why it replaced full-color images, like in JPEG. Has support for multi-level transparency, which allows you to make a smooth transition from transparent area to colored.
- PNG 32- similar to variation 24, but different in that you can specify a change in the degree of transparency, and this gives a clearly visible image on any web pages with any background.
If we take into account the load on the web page, the size of PNG 8 is almost half the size of PNG 24, but this is not surprising, because they were intended to replace the GIF and JPEG formats (quality matches the size).

GIF (Graphics Interchange Format) Is the first historical format used in. Even today, this extension is very popular. GIF images are small, so the server load is minimal. Feature of GIF is the presence of animation .
The small size of pictures is explained by the fact that GIFs can have no more than 256 colors. It is because of this that GIFs are not used for displaying full-color images and photographs.
The principle of GIF animation lies in the fact that GIF has a container where not one image is located, but several, and the time for showing the change of the image to each other is spelled out. After the last picture, the first one will start. Thus, GIF animation is created.
Another advantage of using GIFs is the primitive transparency of images. For any pixel, you can set only two values - transparent and opaque.

JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)- This extension is the property of the American Photographers Associations (can be understood by the acronym). It was created for storing full color images, transferring good image quality.
Using JPEG may result in heavy loads... If on a website it is necessary to convey the quality (in detail) of a photograph, then of course you cannot do without a JPEG. If you are blogging, then there is no urgent need to use JPEG, because the size of JPEG images is very large in weight, which puts a load on the hosting.
Greetings friends! In our life, we are constantly faced with images, when photographing, creating a website, scanning, printing. Which image format is better you ask.
The quality of the image and the convenience of its further editing depend on the format in which the file is saved.
With the development of computers and the Internet, new formats have emerged for writing images to files. Each format has its own advantages and disadvantages.
In this article, I decided to try to figure out which image format is better and talk about the most common graphic formats - JPEG, TIFF, PNG, and GIF.
What is the best image format?
JPEG format
Digital cameras and web pages usually use JPEG files - its algorithm compresses data very well and the resulting file is small. However, JPEG uses a lossy compression algorithm, which can be a severe disadvantage.

Small JPEG file size compromises image quality. The compression ratio can be set in the settings graphics programs- the lower the quality, the smaller the image file, and vice versa, the higher the quality, the larger the file is.
JPEG is almost the only format that uses lossy compression to make small files larger Low quality... There is a lossless compression mode - lossless JPEG.
This format is used in cases where small file size is more important than maximum image quality (, Email, transfer to memory cards, etc.). The JPEG format is good enough for most cases, the main thing is not to overdo it in compression.
Always remember that re-editing a JPEG file degrades the quality of the picture, artifacts appear, therefore I recommend that you always save the originals of the images, which can be compressed in the future.
TIFF format
The lossless format used for bitmaps is considered the best format for commercial work. It is used for scanning, in printing for high-quality printing, text recognition, sending faxes. TIFF files are significantly larger than their JPEG counterparts and can be recorded uncompressed or losslessly compressed.
The TIFF format allows you to save several layers, which is very convenient for further editing, and unlike JPEG, it can have 8 or 16 bits per channel. TIFF is the most versatile and is usually used to store original images that can be edited later. But keep in mind that browsers do not render TIFF files.
GIF format
This format was developed by CompuServe in 1987 for the first 8-bit computer video cards and was intended for transmission over a dial up (modem) connection. At one time, it was the most widespread format on the Internet. GIF uses lossless compression LZW, and compresses images very well with many uniform fills (banners, tables, logos, schemes).
This format does not please us with the color depth, only 8 bits (256 colors maximum) and it is not recommended to use it for storing photos (photos have 24 bit color depth).
This format supports image animation, which is expressed in the change of static images after a certain period of time, which can be set. Animation can be made cyclical, which is successfully used in the manufacture of banners and avatars.
PNG format
Was created relatively recently to replace the obsolete GIF (browsers show both formats), and to some extent the more complex TIFF format. PNG is a bitmap format using lossless compression, does not support animation, and can be 48-bit.
One of the advantages of this format is that you can specify the level of transparency for each point, which allows you to make smooth transitions from a clear image to the background. The main application is internet use and graphics editing.
File types depending on the purpose of use:
| Photographic images | Graphics, logos | |
| Properties | Photos 24-bit color and 8-bit b / w | Graphics with many solid colors, few colors (up to 256 colors), text or lines |
| Best quality | TIFF or PNG (lossless compression) | PNG or TIFF (lossless compression) |
| Smallest file size | JPEG with high quality ratio | TIFF or GIF or PNG (graphics / logos without gradients) |
| Compatibility (PC, Mac, Unix) |
TIFF or JPEG | TIFF or GIF |
| Worst choice | GIF 256 colors (very limited color, and file size larger than 24-bit JPEG) | JPEG compression adds artifacts, smudges text and line edges |
Any digital photograph is essentially a program file that stores information about the image obtained by digitizing each of its points and how and when it was taken. The data structure of this information is called photo file format or another file photo format.
There are many such formats, and all of them are of the graphic type. They differ in the information compression algorithm, specification and purpose. Each photo file format has been designed for a different purpose and suits them better than others. For example, for storing images, processing or posting them on the Internet.
There is one way to get your original digital photograph. It is necessary to project a frame of a future photograph onto a matrix consisting of many light-sensitive photocells, measure the signal level of each of them and write all these values into the photo file. This division of the photo into separate points - pixels is called a raster, and the format of its file is raster (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 Any digital photograph consists of individual pixels, information about which is stored in a raster file.
There are two main devices that can make a raster-format photo file - a digital camera or. But at the same time, the number of formats in which you can save photo files is limited. To obtain photo files of a different format, they must be converted in a special program (Fig. 2).
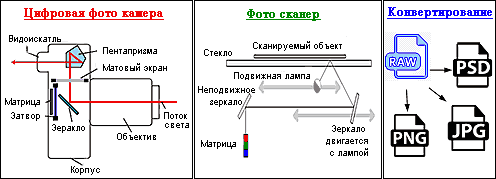
Fig.2 Methods of obtaining files of digital photos of raster formats.
You may need to change the photo file format for various reasons. For example, to reduce the size of photo files, to maintain maximum image quality, or to be able to work with layers. There are other reasons, but in any case, each photo file format should be used for its intended purpose.
Basic photo file formats
The file names of digital photos of any photo format, as well as other types of program files, consist of a variable part, a period and an extension. The extension of photo files is always unchanged and can consist of three or four characters, which determine the file type or format name. For example, jpeg, cr2, tiff, psd, gif (Fig. 3).

Fig. 3 The extension of the photo file indicates its format.
JPEG is considered the universal format for digital photo files. This is the most popular bitmap format used for saving photographs in different types photographic equipment. It is convenient to work with it in various photo editors and use it to view photos in all technical devices... Its main drawback is the loss of image quality when saving a file (Fig. 4).

Fig.4 Loss of image quality of a photo when saving its file in JPEG format.
In addition to the JPEG format, expensive photographic equipment often uses the RAW format. The file of this format contains the most full information about the image and about all the camera settings with which it was taken. This provides tremendous advantages in photo processing and allows you to eliminate many photography errors (Fig. 5).
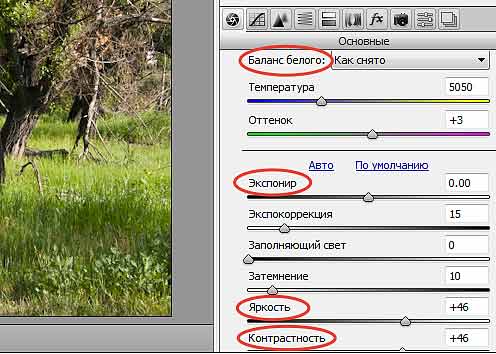
Fig. 5 Using special program in RAW photo files, you can change camera settings.
RAW format is the general name for several formats used in photographic equipment from different manufacturers. Each such format has its own characteristics and is not unified. In order to bring all existing RAW formats to a single standard, the DNG format was developed. In fact, this is the same RAW format, but its file size is smaller and there are no additional text files(fig. 6).
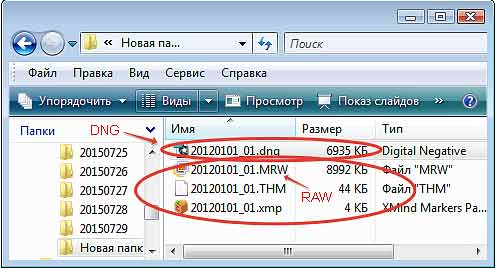
Fig.6 Files of the same photo in RAW and DNG format have different sizes and ways of storing text information.
In cases where it is necessary to preserve the results of color processing, layers, channels, masks or any other attributes of photo editing, the PSD format is used. This is the internal file format of Photoshop, in which all information about changes to photos after taking a photo should be saved (Fig. 7). The main disadvantage of this format is its limited use.
![]()
Fig. 7 In files PSD format conveniently store information about editing photos ( example file).
The TIFF format is another file format used for storing digital photographs. It allows you to preserve the maximum image quality, but at the same time the size of such a file will be the largest in comparison with the other listed formats (Fig. 8). In digital photography, it is used for high quality color work.
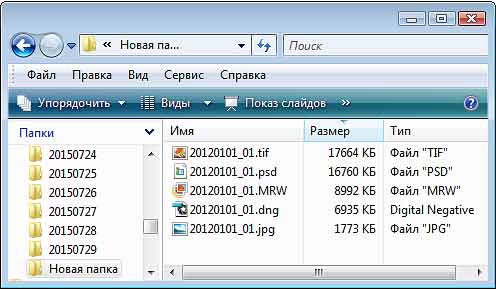
Fig.8 Comparison of file sizes of one photo saved in different photo formats.
The five file photo formats discussed above - JPG, RAW, DNG, PSD and TIFF are considered the main ones for storing, processing and viewing digital photos. But such formats are not suitable for effective display of photos to the viewer. To do this, you need to choose other formats designed for this purpose.
File formats for displaying photos
The main purpose of all photographs is to show them to the viewer. Unlike paper photographs, displaying many digital photographs can be made more accessible and interesting by using suitable file formats. For example, photos can be animated and posted on the Internet, you can add music, text and various special effects to them.
The most convenient way to show photos to a large number of viewers is to post them on the Internet - on photo sites, in social networks or (fig. 9). In this case, the format of photo files should be such that their sizes are as small as possible, and the image has good quality... There are three suitable formats for this.
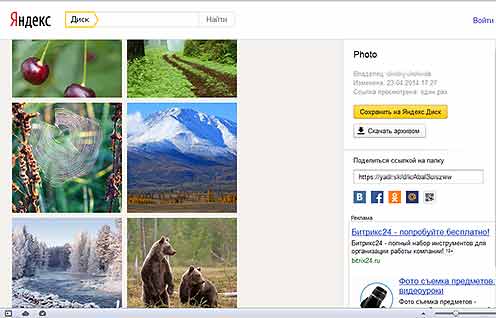
Fig.9 An example of placing digital photos in the cloud.
The main format for posting photos on the Internet is still the same JPEG, but with a high degree of information compression. For this purpose, it is ideal. A 600 by 900 pixel photo file in this format can be compressed to 50 - 70 kb and the image will look normal.
The second popular format that was created for the rapid transmission of bitmap images over networks is GIF. This format allows you to significantly compress digital photo files without losing image quality. In addition, in this format, you can save the animation and transparency of the image layer (Fig. 10). The main disadvantage of the GIF format is its limitations in color rendering.


Fig. 10 GIF photo file with animation.
(hover over the image)
For better color reproduction on the Internet, the PNG format was developed. This format has a higher compression rate without losing the quality of graphic information, unlike the JPEG format, and can store an unlimited number of colors, unlike the GIF format. In addition, PNG files can be used as an alternative to the format for editing photos.
Using all of the above formats, photo files can be stored and viewed individually. But there is also another way. If the photos are combined and saved in video format, they become one file. At the same time, you can make a beautiful slideshow with music, text and special effects from them. Several formats are suitable for this purpose: MPEG4, MOV, AVI, WMV, FLV (Fig. 11). But this is not all the formats.
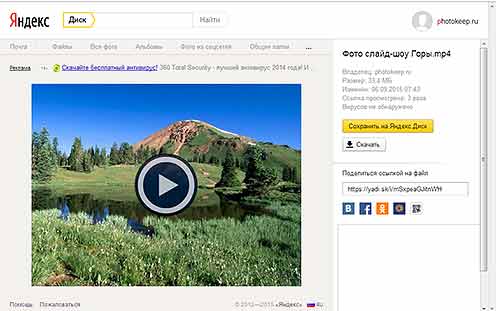
Fig. 11 An example of a slideshow of photos in MPEG4 file format.
()
To store and view digital photos in one file, you can also use the most popular book PDF format... In this format, photos can be stored as in one photo album. This makes it possible to create an interactive menu for them. quick search or view photos as a slideshow (Fig. 12).
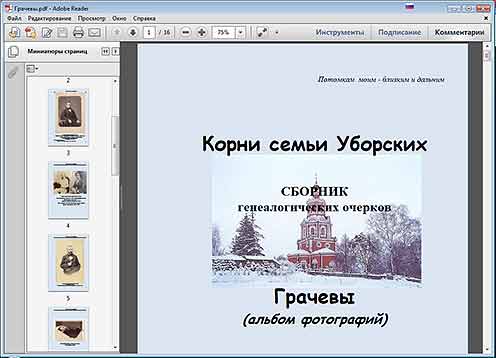
Fig. 12 An example of storing digital photos in a PDF file.
()
That's probably all there is to it for a general overview of the file formats in which digital photos should be stored. When choosing formats for some specific purposes, you need to know more about them - features, advantages, disadvantages. Read more about each such format in the following articles.
 Odnoklassniki: Registration and profile creation
Odnoklassniki: Registration and profile creation E is. E (functions E). Expressions in terms of trigonometric functions
E is. E (functions E). Expressions in terms of trigonometric functions Social networks of Russia Now in social networks
Social networks of Russia Now in social networks