What operations can be performed with folders. Basic operations with files and folders. Files and file system
Before starting to work on a PC, you should create a folder structure for saving files.
A folder is always created in the folder window in which it will be located. Follow these steps to create a folder.
- Open a folder window in which a new folder will be created.
- In an empty area of the window, right-click and execute the New - Folder command.
- Use the keyboard to enter the name of the folder to be created.
File creation
Usually, files are created using application programs (MS Word, MS Excel, etc.). However, some types of files can be created without running the corresponding program.
The file is created in the window of the folder in which it will be located. Follow these steps to create a file.
- Open a window of the folder in which the file will be created.
- In an empty area of the window, right-click and execute the New command and select the desired file type in the submenu that appears.
- Use the keyboard to enter the name of the file to be created.
- Double-click the left mouse button in an empty area of the window.
Renaming folders and files
Follow these steps to rename a folder or file.
- Right-click on the object icon and execute the Rename command.
- Double-click the left mouse button in an empty area of the window.
- Open a window of the folder in which the renamed object is located.
- Perform two or three single clicks with the left mouse button on the name of the object so that the cursor starts blinking in the name field.
- Enter a new name for the object using the keyboard.
- Double-click the left mouse button in an empty area of the window.
Moving and copying folders and files
Moving and copying folders and files can be done in two fundamentally different ways: by dragging and dropping and using the clipboard.
When dragging or dragging objects, follow these steps.
- If necessary, place windows on the screen so that both are visible at the same time.
- When moving - drag (drag) the object icon from the window of one folder to the window of another folder.
- When copying, drag (drag) the object icon from the window of one folder to the window of another folder while pressing the key.
Moving and copying folders and files can also be done by dragging objects with the right mouse button. In this case, after the end of the towing, select the required command in the appeared context menu: Move or Copy.
Follow these steps when moving and copying objects using the clipboard.
- Open a window of the folder from which the object will be moved or copied.
- When moving - select the object to be moved and move it to the clipboard in one of the following ways:
Copying folders and files to floppy disks can be done in another way. To do this, right-click on the object icon and execute the Send - Disk 3.5 (A :) command.
Deleting folders and files
Deleting folders and files can be done in several ways.
In the first method, follow these steps.
- Select the object icon and press a key on the keyboard.
In the second method, you should follow these steps.
- Right-click on the object icon and execute the Delete command.
- In the window that appears, click the Yes button.
In the third method, drag the icon of the object to be deleted to the Desktop on the Trash icon.
Recovering deleted folders and files. Setting up the shopping cart
Deleted folders and files are usually not destroyed, but placed in a special "Trash" folder.
To recover accidentally or mistakenly deleted folders and files, follow these steps.
- Right-click on the icon of the object to be restored and execute the Restore command.
This will restore the folder or file to the same folder from which it was deleted.
To restore a deleted object in any arbitrary folder, move it to the desired folder using one of the methods described above.
It should be noted that folders and files deleted from a floppy disk are not placed in a special folder "Recycle Bin" and, therefore, cannot be restored.
To avoid problems when restoring folders and files, you should check and, if necessary, change the settings for the special folder "Trash". To do this, right-click on the icon of the special folder "Trash" and run the Properties command.

Rice. 8. Dialog Box Properties: Trash
In the Properties: Recycle Bin dialog box (Fig. 8), you should pay attention to the absence of a check mark against the command Delete files immediately after deletion, without placing them in the recycle bin. If such a mark is set, restore deleted files it will be impossible. In the same dialog box, you can set the maximum basket size. Recommended volume - 10 ... 15% of the size of the hard disk.
- Open the special folder "Trash".
- Right-click on the icon of the object to be deleted and execute the Delete command.
- In the window that appears, click the Yes button.
In the second case, follow these steps.
- Right-click the item's Trash icon and run Empty Trash.
- In the window that appears, click the Yes button.
If desired, files and folders can be deleted without placing them in the trash. To do this, you can use any deletion method, however, any of them must be performed with a pressed keyboard key.
Actions with groups of folders and files
You can move, copy and delete not only individual folders and files, but also groups of folders and files. Only files and folders located in one window can be combined into a group. To combine files and folders into a group, you need to select them.
To select all the folders and files in a window, the easiest way is to execute the Edit - Select All command.
To select folders and files one after another in the window, you should first select the first object from the group, and then select the last object while holding down the keyboard key.
When selecting an arbitrary group of folders and files, select them while pressing the keyboard key.
When selecting all the folders and files of the window, except for some, you should first select the objects that are not to be selected, and then execute the Edit - Invert selection command.
The selected group of files can be moved, copied, deleted by any of the methods described above.
Search for folders and files
To search for a folder or file on your PC, open the Main windows menu and execute the command Search - Folders and files.
The search is performed in the Find: All Files window (Fig. 9). The search for folders and files can be performed according to the following criteria:
You can search for any one feature or for all features at the same time. The search result can be multiple objects.
From the search window, files can be moved, copied, deleted by any of the methods described above
Creating and using shortcuts
A shortcut is a special kind of file designed to quickly open other files, folders and launch programs. Shortcuts are usually placed on the Desktop.
Follow these steps to create a shortcut.
- Open the window of the folder containing the object for which the shortcut is being created.
- Drag an object to the Desktop while holding down the right mouse button.
- After towing, in the context menu that appears, execute the Create shortcut (s) command.
The shortcut can be renamed like a regular file.
You can change the shortcut icon if you want. To do this, follow these steps.
- Right-click on the shortcut icon and execute the Properties command.
- In the Properties: ... dialog box, go to the Shortcut tab.
- In the tab, click the Change icon button.
- In the Change Icon dialog box, select the desired icon.
- In the Change Icon dialog box, click OK.
- In the Properties: ... dialog box, click the OK button.
Double-clicking the left mouse button on the shortcut icon opens the window of the object for which this shortcut was created.
Renaming, changing the shortcut icon, copying, moving, or even deleting it does not affect the object for which it was created. In contrast, renaming or moving an object may result in the shortcut not working properly. Deleting the object for which the shortcut was created results in the complete inoperability of the shortcut.
Archiving files
Archiving is the process of reducing the size of files for easy storage and movement. Archiving is performed using special programs-archivators. Among the numerous archiving programs, the WinZip program has recently become the most popular. This program is not part of the standard Windows programs and must be preinstalled on your computer.
When archiving files, a new file, which is called archival. An archive file contains one or more compressed files.
For creating archive file follow these steps.
- Select files to be archived.
- Right-click on the selected icons and execute the Add to Zip command.
- In the Add window, in the Add to Archive field, enter the name of the archive file to be created.
- In the Action drop-down list, you can select the method of placing files in the archive: Add (adding, copying) or Move (moving).
- From the Compression drop-down list, you can select the compression rate for the files.
- In the Add window, click the Add or Move button, depending on the selected method of placing files in the archive.
- Close the WinZip window.
To add files to an existing archive, drag the icon onto the archive file icon.
To extract files from an archive, the easiest way is to open the archive file and drag the extracted file from the archive file window to the required folder window.
2 In Windows 95/98, almost all actions can be performed different ways... In this study guide only the most common and convenient options for actions using the windows of the special folder "My Computer" are given.
4 When copying items to a folder of another logical drive you do not need to keep the (Ctrl) key pressed.
5 To search for a file with the name Letter in JSC Zarya.doc, it is enough to indicate the name of the letter.
6 The search can be performed for the last period (several days or months) or for a specific period (from one date to another date).
7 The terms "compression", "packaging" are also used.
Copy and move
- 1 way. Place two windows on the desktop: copy source and destination. Select the necessary icons in the source window. Several icons are highlighted while holding down the Ctrl key. Drag the selected icons to the destination window, pointing to any of the selected icons. While pressing the Ctrl key, copying occurs, without it - moving elements (provided that the folders are on the same disk). excel print file zip
- Method 2. Select copied items. Select the Edit / Copy (Cut) menu. When you select "Cut", a move will occur. Open destination folder. Select the Edit / Paste menu.
Deleting files and folders
Deleting files is done by selecting items and pressing the Delete key. In this case, the marked items are moved to a special folder - the Recycle Bin. Emptying the trash will destroy files. There is also an operation to erase files, when special utilities fill the clusters that contained the files to be erased with random data.
Group operations with files
If you need to perform a copy or delete operation with a large number of files at the same time, it is not very convenient to select them while holding Ctrl. You can select a whole group of consecutive icons by clicking on the first of them and holding down the Shift key - on the last one. However, in this case, you need to arrange the icons in a certain way. To do this, open the folder with the files and go to the View / Arrange icons menu. There are 4 ways to organize icons in a folder: by name, by type, by size, by date. For example, you need to copy all files with the extension .txt. In this case, you should sort the icons by type, after which all files of type .txt will be grouped together and use the Shift key to select them. A similar technique is used to select "old" files (sort by date), "small" (sort by size) and in other standard situations.
If the window is not shown full information about files (extension, volume and date of creation), you should go to the window menu of the View / Table folder and all the characteristics of the files will be displayed in the window.
Renaming files and folders.
Renaming a file or folder is performed either through the Rename menu, invoked by a click right button mouse on the corresponding icon, or by clicking on the name of the selected icon.
Comment. Deleting or renaming is not possible if the specified file is already open by some application.
Archiving - data recoding in order to reduce their volume. Data compression is a data transcoding procedure performed in order to reduce their volume. It is used for more rational use of storage and data transmission devices.
Compression is lossless (when it is possible to restore the original data without distortion) or lossy (restoration is possible with distortions that are hardly noticeable to the human eye or ear). Lossless compression is commonly used in processing computer programs and data, less often - to reduce the volume of audio, photo and video information. Lossy compression is used to reduce the volume of audio, photo and video information, it is much more efficient than lossless compression. Compression is based on eliminating the redundancy of the information contained in the original data. An example of redundancy is the repetition of fragments in the text (for example, words of natural or machine language). This redundancy is usually eliminated by replacing the repeating sequence with a shorter value (code). Another type of redundancy is associated with the fact that some values in the compressed data occur more often than others, while it is possible to replace frequently occurring data with shorter codes, and rare data with longer ones (probabilistic compression). Compressing data that does not have the property of redundancy (for example, random signal or noise) is impossible without loss. Also, it is usually impossible to compress encrypted information.
When storing data, two problems are solved: how to save data in the most compact form and how to provide convenient and quick access to them (if access is not provided, then this is not storage). To provide access, the data must have an ordered structure. This generates address data. Without them, it is impossible to access the required data elements included in the structure.
Since address data is also sizeable and also needs to be stored, it is inconvenient to store data in small units such as bytes. It is inconvenient to store them in larger units (kilobytes, megabytes, etc.), since partial filling of one storage unit leads to storage inefficiency.
The unit of data storage is a variable length object called a file.
A file is a sequence of an arbitrary number of bytes with a unique proper name.
Usually, data belonging to the same type is stored in a separate file. In this case, the data type determines the file type.
Since there is no size limit in the file definition, you can imagine a file having 0 bytes (an empty file) and a file having any number of bytes.
In the definition of the file, special attention is paid to the name. It actually carries address data, without which the data stored in the file will not become information due to the lack of an access method to them. In addition to functions related to addressing, the file name can also store information about the type of data contained in it. This is important for automated tools for working with data, since they can automatically determine the appropriate method for extracting information from the file by the name of the file.
The file name consists of two parts: the actual name and the file extension.
The actual file name can consist of letters of the Russian and English alphabets, numbers and special characters... Moreover, its length should not exceed 256 characters.
Depending on the extension, all files are divided into two large groups: executable and non-executable.
Executable files are files that can be executed on their own, that is, they do not require any special programs to run them. They have the following extensions:
- - exe - ready-to-execute file (tetris.exe; winword.exe);
- - com - operating system file (command.com);
- - sys - operating system file (Io.sys);
- - bat - batch file of the MS-DOS operating system (autoexec.bat).
Non-executable files require the installation of special programs to run. So, for example, in order to view a text document, you need a text editor. By the extension of the non-executable file, one can judge the type of data stored in this file... You can concatenate multiple files into one using the cat (1) utility, short for "concatenate". This utility was originally designed to combine multiple text files into one, but it can be used for other purposes as well.
To combine two or more files into one, simply list the files after the cat command and redirect the output to a new file. The cat utility works with standard input and output, so you need to use shell characters to redirect. For example: $ cat file1 file2 file3> bigfile
This command will take the contents of files file1, file2 and file3 and concatenate them into bigfile.
The cat utility is also used to view the contents of files. Many users cat with the filename to view text files and then pipe the output through more or less:
$ cat file1 | more
Also, cat is often used to copy files. Any file can be copied by running:
$ cat / bin / bash> ~ / mybash
The file / bin / bash will be copied to your home directory under the name mybash.
The examples discussed here are just a few of the possible options using cat. Because cat provides extensive control over standard input and output, it is ideal for scripting and as part of more complex commands.
Course of the lesson
1. Organizational moment: greeting, checking attendance and readiness for class
2. Communication of the topic, purpose of the lesson, assessment criteria
Knowledge actualization (repetition of the studied material)
Currently, all operating systems for personal computers provide user interaction through a graphical interface.
This allows even a novice computer user to confidently work in the operating system environment (perform operations with files, run programs, and so on).
Explanation of the new material
Graphical interfaceallows for human-computer interaction in the form of a dialogue using windows, menus and controls (dialog panels, buttons, and so on).
Operating room Windows system has a fairly convenient graphical interface, built on the following basic elements:
Desktop
Task bar
Window
4. Dialogue components (menus, toolbars, buttons, ...)
Pictograms and Labels
Desktop (PC)- the initial state of the MS Windows dialog environment. The PC is displayed on the screen after starting MS Windows. On the "surface" of the PC there are shortcuts to the most frequently used applications, documents, folders, devices.







Files and file system
All programs and data are stored in the long-term (external) memory of the computer in the form of files.
Fileis a certain amount of information (program or data) that has a name and is stored in long-term (external) memory.
File name. The file name consists of two parts, separated by a period: the actual file name and the extension that determines its type (program, data, and so on). The actual name of the file is given by the user, and the file type is usually set by the program automatically when it is created (Table 4.2).
Different operating systems have different file name formats. In the MS-DOS operating system, the actual file name must contain no more than 8 letters of the Latin alphabet, numbers and some special characters, and the extension consists of three Latin letters, for example: proba.txt
In the operating system Windows name file can be up to 255 characters long, and you can use the Russian alphabet, for example: Information units.doc
File system. Each storage medium (floppy disk, hard disk or laser disk) can store a large number of files. The order in which files are stored on disk is determined by the file system used.
Each disk is divided into two areas: a file storage area and a directory. The directory contains the name of the file and an indication of the beginning of its placement on disk. If we draw the analogy of a disk with a book, then the file storage area corresponds to its content, and the directory corresponds to the table of contents. Moreover, the book consists of pages, and the disk - of sectors.
For discs with a small number of files (up to several dozen) can be used single-level file system, when the directory (disk table of contents) is a linear sequence of file names (Table 4.3). Such a catalog can be compared to the table of contents for a children's book, which contains only the titles of individual stories.
If hundreds and thousands of files are stored on the disk, then for the convenience of searching, it is used multilevel hierarchical file system which has a tree structure. Such a hierarchical system can be compared, for example, with the table of contents of this textbook, which is a hierarchical system of sections, chapters, paragraphs and paragraphs.
The initial, root directory contains subdirectories of the 1st level, in turn, each of the latter can contain subdirectories of the 2nd level, and so on. It should be noted that files can be stored in directories of all levels.
For example, the root directory can contain two subdirectories of the 1st level (Directory_1, Directory_2) and one file (File_1). In turn, the 1st level directory (Catalog_1) contains two subdirectories of the second level (Catalog_1.1 and Catalog_1.2) and one file (File_1.1) - Fig. 4.21.
File systemis a file storage and directory organization system.
Basic file operations.
In the process of working on a computer, the following operations are most often performed on files:
- copying (a copy of the file is placed in another directory);
- move (the file itself is moved to another directory);
- deletion (the file record is deleted from the directory);
- rename (file name changes).
The Windows graphical interface allows operations on files with the mouse using the Drag & Drop method. There are also specialized applications for working with files, the so-called file managers : Norton Commander, Windows Commander, File Explorer, etc.
In some cases, it becomes necessary to work with the interface command line... Windows provides an MS-DOS command line interface mode.
Summing up the results of the lesson
6. Reflection:
What did you remember during the lesson?
What did you like?
What are the difficulties?
7. Homework: records.
Computer objects Questions and tasks, Informatics Grade 6 Bosova Questions and tasks, Informatics Grade 6 Bosova answers to questions, Informatics Grade 6 Bosova GDZ, Informatics Grade 6 Bosova answersExercise 1
What is a file?
Solution
A file is an area on a medium, some kind of drive, containing logically combined information and named with a specific name.
Assignment 2
What are the parts of a file name?
Solution
The file name consists of two parts, separated by a period:
a) name - to the point;
b) expansion - after.
Assignment 3
What are the rules for writing the file name should be followed?
Solution
It is better to name the file in Latin letters, using no more than 9 symbols.
Assignment 4
Describe the file storage system on the disk.
Solution
Each disk is divided into two areas - a file storage area and a directory. The directory contains the name of the file and an indication of the beginning of its placement on disk. If we draw the analogy of a disk with a book, then the file storage area corresponds to its content, and the directory corresponds to the table of contents. Moreover, the book consists of pages, and the disk - of sectors.
Assignment 5
What actions can you take with files?
Solution
The file can be: opened, scanned for viruses, renamed, copied, sent by mail, deleted.
Assignment 6
What should be avoided when working with files?
Solution
1) delete the file without knowing exactly whether it should be done;
2) give the file a name that does not explain its content;
3) save the file in the folder where it will be difficult to find later;
4) delete or move files located in the folders of application programs - this may cause the programs to stop working.
Assignment 7
Name the properties of the operating system object "Desktop".
Solution
1) icons and shortcuts to Windows objects;
2) windows of open applications;
3) a taskbar containing a "Start" button, an indication panel and a number of Desktop toolbars;
4) the background of the Desktop, containing a uniform background, wallpaper or active elements of the desktop. In the course of work, there may be additional objects on the Desktop: folder windows, dialog boxes, application windows, etc.
Assignment 8
One of the actions in the context menu of an operating system object is always highlighted in bold. What is this action? Why was it chosen? How can you perform this action without a context menu?
Solution
In the context menu of an operating system object, the Open action is always highlighted in bold. This action is selected because the system considers this action to be the most likely to be performed for this object. This action without a context menu can be performed by pressing left button mice.
Assignment 9
As you know, actions on the main objects of the operating system can be performed in several ways: using menu commands; using the toolbar buttons duplicating menu commands; using the commands of the context menu; using the "Drag & Drop" technology. Why do you think so many methods are needed? Why didn't the developers give preference to one of them?
Solution
In Windows, for the convenience of users, a huge number of functions have been created, often interchangeable with each other. One person, for example, will select the context menu to control the object, the other will select the menu bar. Every person has a habit, who is used to acting in one way, will think that another way is inconvenient and does not need it at all.
Assignment 10
What
The purpose of the laboratory work
Studying the basic operations of working with objects of the operating system Windows XP (creating, moving, copying, deleting) files, folders, shortcuts.
software products
Equipment
Materials (edit): Handout.
Software products : operating system Windows XP.
Work order
1. Configure "My Computer":
Drive C: open a separate window for each folder,
Objects: in the form of a table;
Sorting by name;
Show all files;
Display file extensions and full path in header.
2. In the MY DOCUMENTS folder create the GROUP folder, in the GROUP folder create the NEW, TEST and EXECUTION folders.
3. In the EXECUTIVE folder, create shortcuts for the programs "My Computer", "Recycle Bin" and the FILES folder.
4. Copy 15 files into the FILES folder, no more than 30 Kb in size, of which: 5 - with the * .txt extension, 5 - with the * .bmp extension, 5 - with the * .doc extension.
5. Copy the 4 newest files to the TEST folder from the FILES folder.
6. Move the 2 largest files to the NEW folder from the FILES folder.
7. In the TEST folder, use the NOTEBOOK to create 3 text files, assign them attributes: 2 - read-only, 1 - hidden.
8. In the NEW folder, delete and restore 1 file.
9. Move the TEST and NEW folders to the EXECUTE folder.
10. Set the volume of the "BASKET" to 1%.
11. Find files created in the past month and containing the word MICROSOFT in the text.
12. Delete the created objects.
Report form
Protection order
LABORATORY WORK No. 2
Topic: “Operating system Windows XP.
Utilities, working with the clipboard "
The purpose of the laboratory work
Studying the basic operations of working with the utilities of the Windows XP operating system (text editors, graphics editor, data exchange between applications via the clipboard).
Used equipment, materials,
software products
Equipment: multimedia complex, personal computers.
Materials (edit): Handout.
Software products: Windows XP operating system, service Windows programs XP.
Work order
1. Create a document: picture and heading in PAINT, text in Wordpad (use tabs when creating text).
2. Paste a picture into the text via the clipboard.
Report
Sale of system blocks
No. Name Date Price, $
1 Samsung 01.03 204
2 X – Ring 02.05 250
3 Lizard 05.07 215
4 Sony 06.09 305
5 Fillips 07.11 202
Director Ivanov I.I.
Chief Accountant P.P. Petrov
- sin 54 o 25 ";
– ((18+9)/14,5*5)*8+15=;
- average value of numbers: 15; eighteen; 25.9; 134.8; 18.4; 125.1.
Report form
The results of the laboratory work are documented in electronic form in accordance with the assignment.
Protection order
The protection of the results of laboratory work is carried out orally and in writing (calculation results) with subsequent exposure assigned amount points in the point-rating system of assessment.
LABORATORY WORK No. 3
Topic: "The structure of the Word 2007 window. Basics of formatting
And editing a text document "
The purpose of the laboratory work
Studying the basic elements of the Word 2007 interface, as well as techniques for formatting and editing a text document.
Used equipment, materials,
software products
Equipment: multimedia complex, personal computers.
Materials (edit): Handout.
Software products: operating system Windows XP, text editor Word 2007.
Work order
(Text - four chapters with headings (chapter 1, 2, 3, 4) and subheadings (in which ...) in each chapter).
Format characters, paragraphs, and pages for text according to the following requirements:
1. Page settings: paper - 19.5 x 27.5 cm; margins - left, right - 1.5 cm each, top, bottom - 2 cm each; binding indent - 1.2 cm.
2. Text formatting:
2.1. Headings chapters (chapter one, second, third, fourth):
- font: ARIAL, style - bold, size - 22 pt, discharge - 5 pt, character scale 140%;
- paragraph: center alignment, before / after the paragraph - 6 points;
2.2. Subheadings chapters (in which ...):
- font: TIMES NEW ROMAN, style - italic, size - 18 pt, underline - words only;
- paragraph: indentation of the paragraph on the left / right - 2 cm each, alignment - in the center, line spacing - exactly 22 points, before / after the paragraph - 12 points;
2.3. Basic text:
- font: TIMES NEW ROMAN, size - 14 pt.
- paragraph: first line - indented by 1.8 cm, line spacing - 18 points, alignment - in width, before / after the paragraph - 4 points;
3. The first paragraph of each chapter: drop cap - 3 lines height, font - ARIAL, distance to the text - 0.4 cm.
4. The title of each chapter on new page; framing pages with a frame.
5. Arrange pagination (bottom center) and hyphenation.
6. Check spelling.
7. Header: on even pages - "Task by WORD"; on odd ones - his Surname I.O.
8. Divide the last chapter into two columns with a separator (no heading or subheading; do not include drop caps).
9. Insert 2 footnotes into the text - Yalo - Olya's name is the other way around, Gurd is the other way around.
Report form
The results of the laboratory work are documented in electronic form in accordance with the assignment.
Protection order
The defense of the results of laboratory work is carried out orally, followed by the setting of a set number of points in the point-rating system of assessment.
LABORATORY WORK No. 4
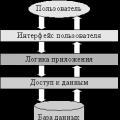 Architecture of a distributed control system based on a reconfigurable multi-pipeline computing environment L-Net "transparent" distributed file systems
Architecture of a distributed control system based on a reconfigurable multi-pipeline computing environment L-Net "transparent" distributed file systems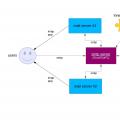 Email sending page Fill relay_recipients file with addresses from Active Directory
Email sending page Fill relay_recipients file with addresses from Active Directory Missing language bar in Windows - what to do?
Missing language bar in Windows - what to do?