Power supply and zeroing of CMOS memory
The section is still in work ...
The basics
What is a CPU?
CPU (from the English "Central Processing Unit") - central processing unit - a central processor, the main part of the architecture of a personal computer. Designed for computing general purpose(performs logical and arithmetic operations), input / output operations, as well as to control all other components of the computer. Physically it is realized, as a rule, in the form of a discrete microcircuit. This microcircuit is either installed in a special connector on motherboard(socket), or soldered directly on it.Motherboard form factor
Form factor of the motherboard (from the English "Form Factor") - the form factor - an industry standard that determines the overall dimensions of the motherboard, the number and location of its attachment points to the case, location on it various devices and connectors (socket central processing unit, slots for random access memory, bus interfaces, input / output ports, etc.), as well as the location and type of connector (or connectors) for connecting the power supply to it.With regard to ordinary (office or home) computers, the main modern form factors of the motherboard are: ATX, Micro ATX, Flex ATX and Mini-ITX.

Main modern motherboard form factors (dimensions in inches)
The retail market is mainly represented by ATX, Micro ATX and Mini-ITX boards.
Rarely, but there are other options. So, AMD, specifically for small-sized home computers, proposed the DTX / Mini-DTX form factor, which, unfortunately, has not received mass distribution. And EVGA has released several HPTX form factor boards aimed at wealthy enthusiast maniacs.
Professional form-factor E-ATX (Extended ATX) cards are practically not found on the market of non-professional computers, but sometimes their compatibility is indicated by manufacturers computer cases.
The table below shows the characteristics of modern motherboard form factors in descending order of their overall dimensions.
| Form Factor (standard) |
Dimensions, mm | Number of slots for cards enlargement |
|
| width | height | ||
| HPTX | 381 | 345 | up to 9 |
| E-ATX | 330 | 305 | 7 |
| ATX | 244 | 305 | 7 |
| Micro ATX | 244 | 244 | 4 |
| Flex ATX | 191 | 229 | 3 |
| DTX | 244 | 203 | 2 |
| Mini-DTX | 170 | 203 | 2 |
| Mini-ITX | 170 | 170 | 1 |
A few comments on the table.
In bold the main modern form factors of the motherboard are highlighted.
If a computer case is designed for a board of one form factor, then all the downstream ones will also fit into it.
It should also be noted that the form factor is of a recommendatory nature, so manufacturers can change the size of motherboards (usually in the direction of decreasing width), while declaring compatibility with the standard.
BIOS
What is BIOS?
BIOS (from English "Basic Input / Output System") - basic input / output system - software providing interaction operating system and hardware resources of the computer.The physical implementation of the BIOS is a set of microcircuits on the motherboard, plus a battery that powers the CMOS.
The BIOS program itself is stored on the chip Flash ROM(for older computers in EPROM or EEPROM). V modern computers this microcircuit, as a rule, is removable and lies in a special "crib".
What is EPROM?
EPROM (from English "Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory") - read-only memory, erasable, programmable - a permanent (non-volatile) memory chip, the contents of which are erased using an ultraviolet lamp. To write information into such a microcircuit, you need a special device - a programmer.What is ЕЕPROM?
ЕЕPROM (from English "Electrically Eraseble Programmable Read Only Memory") - read-only memory, electrically erasable, programmable - a permanent (non-volatile) memory chip whose contents are erased using an electrical signal. For recording, you also need a programmer.EPROM and ЕЕPROM are outdated types of microcircuits, and they are no longer used in modern computers for storing the BIOS program.
What is Flash ROM?
Flash ROM (from English "Flash Read Only Memory") - read-only memory, on flash chips - "flashable" permanent (non-volatile) memory. You can update information in such a microcircuit and by software(usually from DOS).What is CMOS?
CMOS (from the English "Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor") - memory for storing information about the current configuration (settings) of the computer hardware. The name comes from the technology for the production of transistors - the complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) structure. It is to save this information when the power is off that the same battery is used.What is CMOS Battery?
CMOS Battery (from the English "CMOS Battery") - CMOS battery - a power source needed to store information in CMOS when the computer's power is off.Some people mistakenly think that there is a battery on the board - no, there is an ordinary 3V lithium battery. Why does it last so long? Because the current required to power the CMOS chip is very small, and the battery itself is very high quality :)
Do I need to change the battery?
If the computer is already old (well, over eight years, for example), then the battery may be discharged. The first sign of this approaching is the lag of the system clock. This is not good, because if the battery is completely discharged CMOS data will be erased, and the computer will either turn on with CMOS settings reset to default values, or not turn on at all. Therefore, it is better to change the battery. Any type of CR2030 or CR2032 lithium power supply (this is preferred) will do.
Here it should be noted that without a battery, the CMOS data is erased (after a couple of seconds). Therefore, before replacing it is useful to remember or write down all the settings by going to BIOS Setup. Well, after replacement, respectively, restore them there.
The process of removing and reinstalling (after a couple of seconds) the battery can also be useful if you need to clear the CMOS (and most importantly, erase the password for entering BIOS Setup :), and no other means were found for this :)
For simpler and safer manipulations with CMOS data, it is recommended to use the CMOS De-Animator program - a utility that allows you to erase the CMOS checksum, reset all BIOS settings to default values, and also erase all BIOS passwords (if any). In addition, the program can save the current CMOS settings to a file, as well as restore them from a saved file. You can download this program from here.
What is Clear CMOS?
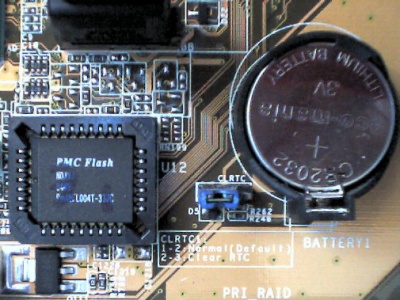
Clear CMOS (from the English "Clear CMOS") - clearing CMOS - erasing all information stored in the CMOS. All settings are then reset to some basic values (default values). A jumper (jumper) on the motherboard, located somewhere near the battery, is usually responsible for the implementation of this function. How to use this jumper should be indicated either in the description of the board, or directly on its PCB.
As a rule, to erase CMOS data, you need to rearrange the jumper to the adjacent position, turn on the computer, wait a couple of seconds, turn off the computer and rearrange the jumper back.
What is RTC?
RTC (from the English "Real Time Clock") - real time clock - electronic circuit, designed to take into account chronometric data ( current time, date, day of the week, etc.). It is a system consisting of an autonomous power source and a metering device.What is Clear RTC?
Clear RTC ("Clear Real Time Clock") - clear (reset) the real time clock. As applied to computers, it is generally the same as Clear CMOS.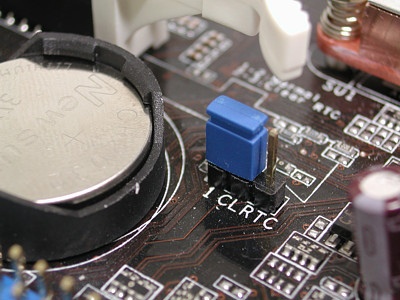
What is POST?
POST (from the English "Power On Self Test") - self-test when the power is turned on - checking the functioning hardware computer before loading the operating system. Performed by programs included in Motherboard BIOS boards.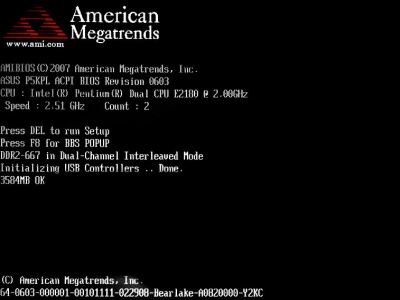
What are POST-Codes?
POST-Codes (from the English "Power On Self Test Codes") - self-test error codes (digital, in hexadecimal format). The meaning of these digital codes should be listed in the BIOS description of the motherboard.What is BIOS Setup?
BIOS Setup (from English "Basic Input / Output System Setup") - a program for setting the current configuration of the computer. The phrase "enter BIOS" implies launching this particular program :)
In general, it is more correct to say not BIOS Setup, but CMOS Setup, since it is not the BIOS program that is configured, but the CMOS data. Nevertheless, the phrase BIOS Setup is more common.
What is ESCD?
ESCD (Extended System Configuration Data) - extended system configuration data - are responsible for configuring Plug & Play devices. When changing the hardware configuration of the computer, for example, when replacing a video or sound card, they are subject to updating. For this, there is a corresponding item in the BIOS Setup.What is ACPI?
ACPI ("Advanced Configuration and Power Interface") is an advanced configuration and power management interface. ACPI replaces APM (Advanced Power Management) and defines a common interface for hardware discovery, power management, and configuration of the motherboard and other devices. ACPI's job is to provide interoperability between the operating system, hardware, and motherboard BIOS.BIOS Software Companies
BIOS software manufacturers:- Award Software, owned by Phoenix Technologies Ltd. (Award BIOS)
- American Megatrends Inc.(AMI BIOS)
- Phoenix Technologies Ltd.(Phoenix BIOS)
Download all required programs to work with BIOS, you can from the corresponding section of our file archive.
UEFI
What is EFI?
EFI (from the English "Extensible Firmware Interface") - an extensible firmware interface (firmware) - software that provides interaction between the operating system and firmware that directly control the hardware of the computer. The main purpose of EFI is to correctly initialize the existing hardware and transfer control to the operating system loader.The EFI specification was originally created for the first Intel systems- HP Itanium in the mid-1990s. The EFI 1.02 specification was released by Intel on December 12, 2000.
What is UEFI?
UEFI (from the English "Unified Extensible Firmware Interface") - unified extensible firmware interface (firmware) - EFI version for Intel x86, Intel x64 and ARM architectures. Positioned as a replacement for BIOS in personal computers.The Unified EFI Forum is currently developing UEFI. The last one, on this moment, UEFI 2.5 was adopted in April 2015.

In fact, EFI / UEFI is a kind of operating system, with its own services, drivers, support for drives and file systems (including FAT32) and with its own graphical shell (EFI shell). The shell can be used to run various EFI applications such as system setup, OS installation, diagnostics, firmware updates. EFI shell commands allow you to copy and / or move files and directories in supported file systems, load and unload drivers. The shell can also be used for, for example, CD / DVD playback or Internet access (without booting the "main" OS), provided that the EFI applications support these capabilities.

In other words, the EFI shell is a functional replacement for the textual BIOS interface and interpreter command line DOS.
You can download all the necessary programs for working with UEFI from the corresponding section of our file archive.
The material is still in work ...
To power the nonvolatile memory of the computer configuration ( CMOS) a lithium battery is installed on the system board. The term of her work is enough for several years. The message says about the need to replace it “CMOS Battery State Low” or “CMOS Checksum Error” during POST ( Power on self test) - self-test when turned on. The first signs of battery replacement may be the internal calendar clock stops or the settings are lost. SETUP when the machine is turned off.On older motherboards, the battery was usually a blue barrel soldered to the board. In recent years, they fail on motherboards. 286 and 386 machines. In this case, information is lost. CMOS, but what is much more dangerous, electrolyte can leak out, causing short circuits and erosion of the system board elements. The leaked battery must be evaporated, and the board in that place must be cleaned with a brush and rinsed. It can be difficult to find a new battery of the same size, but it can be replaced with any other one with the same voltage (usually 3-4.5 V). A new battery can be connected to the connector pins external battery(Ext. Bat.), Which is available on most motherboards (see Fig. 1b), by removing the power supply jumper from the internal battery and making sure to observe the polarity of the connection. There are external batteries for PCs, enclosed in plastic cases with connection wires. This body is fixed with Velcro in a convenient place. It is possible to use a simple and reliable self-made reusable option: two metal pushpins with soldered wires are stuck into a wooden clothespin, and they clamp a coin-cell battery (for example, type 2732), strictly observing the polarity. It is quite simple to fix such a structure in the case.
Note: Lithium batteries should never be charged; they tend to explode when charged and can damage the inside of the computer.
Modern motherboards often use a coin-cell battery in a special holder, which is easy to replace.
The external battery connector is also used for zeroing CMOS... Such a need may arise, for example, if you lose the input password in BIOS Setup (or if you need to reset it). Usually, for this, it is enough with the computer turned off for a few minutes to move the jumper to the position shown in Fig. 1c.
Rice. 1. Connecting an external battery and clearing CMOS: a - work from an internal battery, b - from an external one, c - resetting CMOS
Sometimes a separate jumper or switch is designed to reset the password (used if the password is not stored in CMOS and in NVRAM). In this case, by switching the jumper, the computer must be turned on - only then the password will be reset, after which the jumper must be returned to its original state.
ZeroingCMOS should be used with caution. Configuration information stored there is relatively easy to recover - problems can arise only with non-standard parameters of hard drives set manually. In addition to the Setup information, in CMOS the key for binding any application software to a specific motherboard can be written, and when zeroing CMOS the key will be lost. So, for example, it is easy to "kill" a legal copy of a package "1C-Accounting"... To insure against such troubles, after installing such protected products, you should save the contents in the file CMOS... This allows you to do, for example, a test package QAPlus.
However, there are times when these by regular means do not reset the password. Then there is another way: short-circuit the pins of the microcircuit CMOS memory with disconnected (!) power supply and disconnected battery. To do this, a piece of foil is applied from above to the microcircuit and gently smoothed with a fingernail to the leads along the perimeter of the case. In older motherboards286, 386 and some 486 chip CMOS memory It has 14 – 16 contacts. In these cases, it is sufficient to short-circuit the power contacts (usually 7 from 14 for 14-pin ICs and 8 from 16 for 16-pin ICs).
Periodic destruction of information CMOS on power-up may not be caused by the battery, but by insufficient signal delay Power good relative to the moment of establishing the supply voltage or, conversely, an excessive delay of this signal after turning on the source. Determining the cause is quite simple. If you hold down the Reset button before turning on the power and release it only after a few seconds, this in most cases simulates an increase in the signal delay. Power Good. If the data CMOS are still lost, you need to check the version of the shutdown delay. To do this, press the Reset button before turning off the power and hold it for a few more seconds - this simulates the acceleration of signal removal Power good... If, with this method of shutdown, the data CMOS are saved, the point is a large delay when turning off. In both cases, replacement or repair of the power supply is required.
Hello dear friends, everyone! Users, having set a password for Bios, often forget it. Only now it is impossible to enter the system without typing a password. How the reset occurs BIOS password decided to write in this article.
This is what the monitor looks like when prompted for a password:
Clear CMOS
Turn off the computer, unplug the power cable from the computer. Now find the Clear CMOS jumper on the motherboard (the Clear CMOS label is usually located near the battery, and the inscription can also be written in abbreviation). Now move the jumper to the adjacent place. After it has been moved, click on the "Power" button (turn on the computer). Now put the jumper back and you can turn on the computer.
After these steps, the password and default settings (Default) will be reset.
In the event that you have not found exactly where the Clear CMOS inscription is located, read the instructions for your motherboard, which they give when buying a computer. If it is absent (lost, thrown out), enter your motherboard model into the search engine and find the place where Clear CMOS is located.
How to reset the password on Bios using the battery located on the motherboard, read below.
Battery in motherboard
Reset BIOS Password If Clear CMOS is missing on the motherboard, then you need to remove the battery and wait 30 to 180 minutes... To do this, turn off the computer, pull out the power cable and on the motherboard, take out the battery (see the picture above for where it is located).
Use a small screwdriver to remove the battery. Just press the latch that is in the battery compartment and it will lift itself up. Remove the battery, press the Power button (the power cable should not be plugged in while pressing) and leave the computer in this state for 30 - 180 minutes.
From these actions, the password will be reset and the default settings will be restored (Default). When time has passed, you can put the battery back in and turn on the computer. After that, when the computer boots, the message “CMOS checksum error - Defaults loaded. Press "F1": to continue, "DEL": BIOS Setup "or" CMOS checksum Failure ".
The inscription may be different, but the meaning remains the same . In the figure below, you can see an example of such a message:
If you want to boot the computer with the default parameters (Defaults), then press the "F1" key. More experienced users can enter BIOS Setup by pressing the "Delete" key, where you can configure the BIOS. After setting, press "F10" and confirm the changes made with the "Enter" key.
Together with this article read: ""
Good luck! Try not to forget your BIOS passwords!
 The glass on the tablet cracked - what to do?
The glass on the tablet cracked - what to do? Autotransformers (latr)
Autotransformers (latr) What bulbs are better to put at home What is the difference between bulbs
What bulbs are better to put at home What is the difference between bulbs