How to find out what processor is on the computer? How to find out what processor is on your computer: a few simple methods
The processor is the main computing component of a laptop and computer, so it is advisable for the user to remember its model and specifications. You can find out this information using standard Windows tools or special monitoring software.
Using built-in tools
You can see which processor is on the laptop even before the system starts. The boot screen usually displays information about the CPU: model, power, frequency. The window disappears very quickly, but if you press the Pause Break key, the download will pause and you can overwrite the information about the installed hardware.
Another method that works Windows boot- check the BIOS. To get into the BIOS, press the Delete key when booting the laptop. If you cannot enter the BIOS with the Delete key, you will have to check other options - F1, Esc. The basic I/O system should have a section with a name like "System Info". Sometimes the necessary information is located on the "Main" tab. 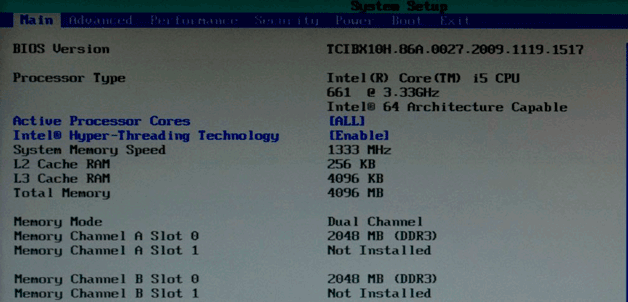
If you can't get into the BIOS, don't worry. You can also view CPU information on a booted system. Method one:
You can find out the model and number of cores in the "System Information" window:
You can check this information in Device Manager:
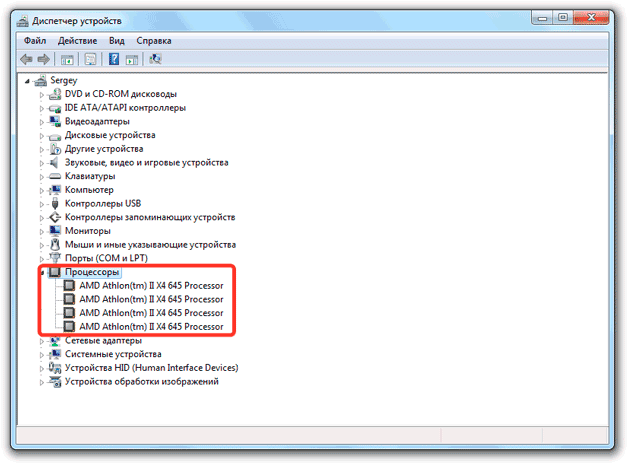
The number of devices in the expanded section shows the number of cores. In the example shown, the CPU has four cores. You can check the specifications again on the manufacturer's website or using the DirectX diagnostic tool:
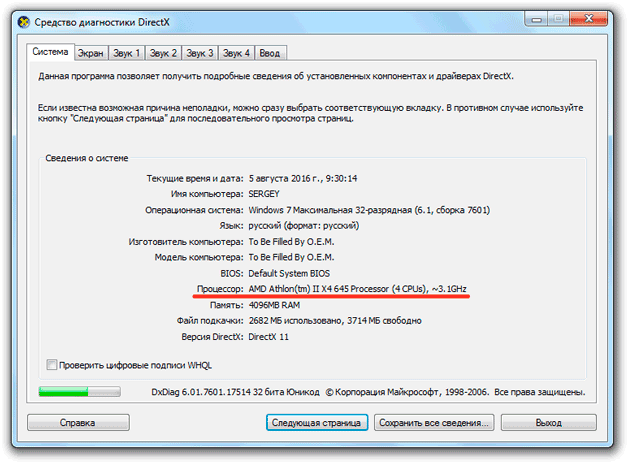
Using the built-in Windows tools, you can find out only the most general parameters of the processor. If you need all the technical specifications, there are two options: look at the specification on the manufacturer's website or use special laptop monitoring software.
Use of third party software
There are many programs that show what hardware is on a laptop. You can find both free options (Speccy, CPU-Z) and shareware utilities (AIDA64, demo access for 30 days). Between themselves, these programs differ in the amount of information provided: if the free CPU-Z shows a little more than the built-in windows tools, then AIDA64 produces a huge array of characteristics. Let's see how to use these three programs.
CPU-Z
When you run the utility, the CPU tab immediately opens, which displays basic information about the processor. 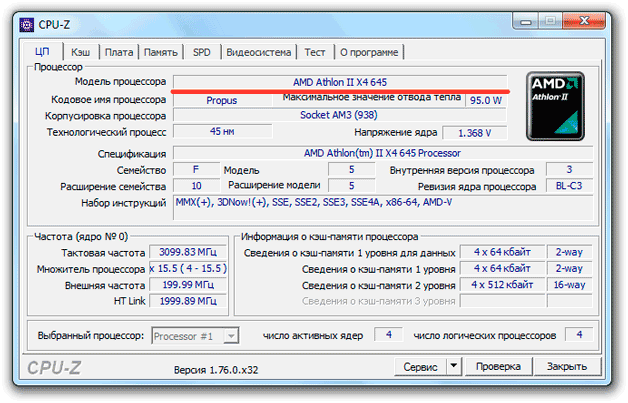
What you can learn:
- Model.
- clock frequency.
- The number of active cores and other information.
This should be enough to get a rough idea of the CPU installed in the laptop.
Speccy
The program from the developers from the Piriform studio, like CPU-Z, is distributed free of charge, but it shows much more information. 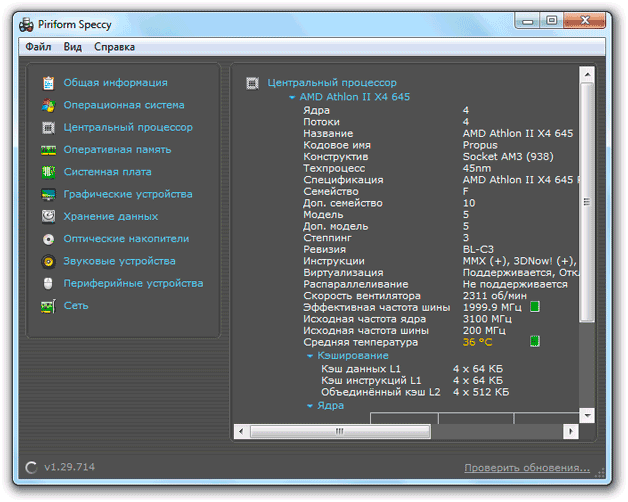
On the "Central Processing Unit" tab, you can see everything from the model to the temperature and fan speed. Half of the parameters will not tell anything to non-specialists, but the temperature display is a definite plus.
AIDA64 Extreme
In AIDA64's powerful diagnostic utility, processor information is located on the "Motherboard" tab in the "CPU" section. 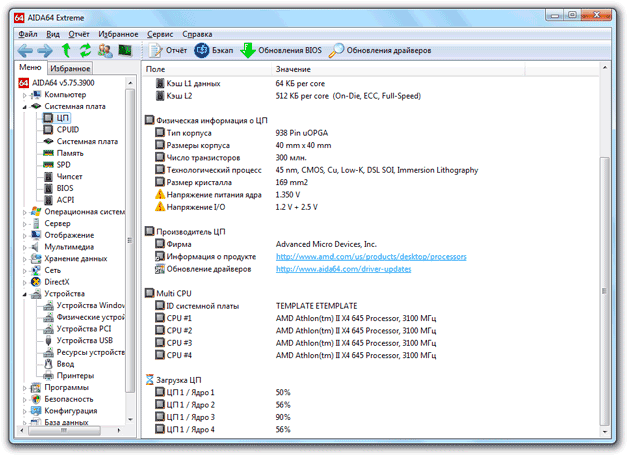
Here you will find many useful information, including die size, number of transistors, and load information for each core individually. It is noteworthy that the window displays a link to a web page with specifications on the manufacturer's website - this is very convenient, you can immediately check the correctness of the information provided by the AIDA64 program.
Processor replacement
If you are going to upgrade a laptop, then pay attention not only to which processor is currently in the laptop, but also to which socket is used to connect. A socket is a socket on the system board where the processor is installed. They can be different, so it is important to know which socket is on motherboard before buying new hardware, otherwise there is a risk that you simply won't be able to install the processor. 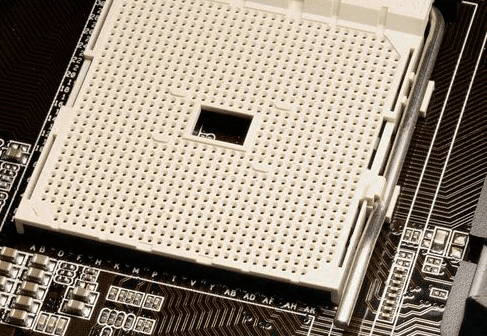
With built-in Windows tools you can't see which socket is in use. Only computer monitoring programs - Speccy, AIDA64, CPU-Z will help you find out this information. In order not to get confused in the characteristics, use the following brief instructions for each utility:
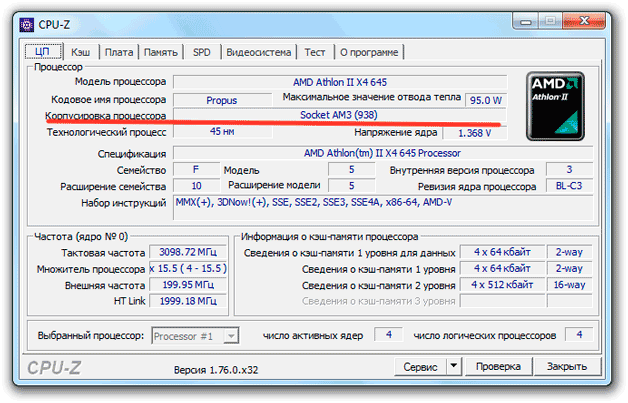
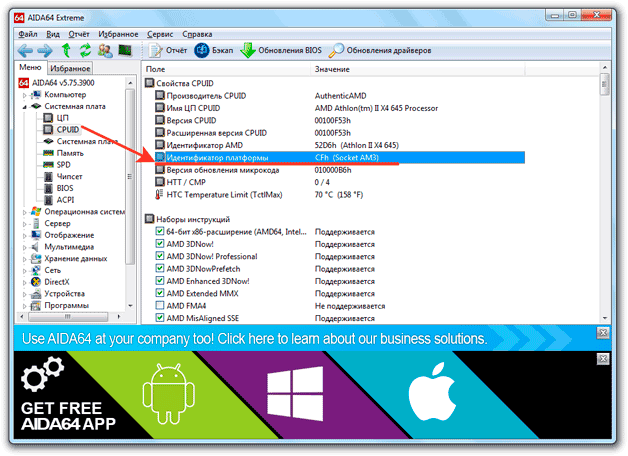
AIDA64 has another way to find out which socket is in use. Open the "Motherboard" subsection and in the "Physical Information" field, look at the number of CPU sockets. This line will indicate not only the number of sockets, but also their type.
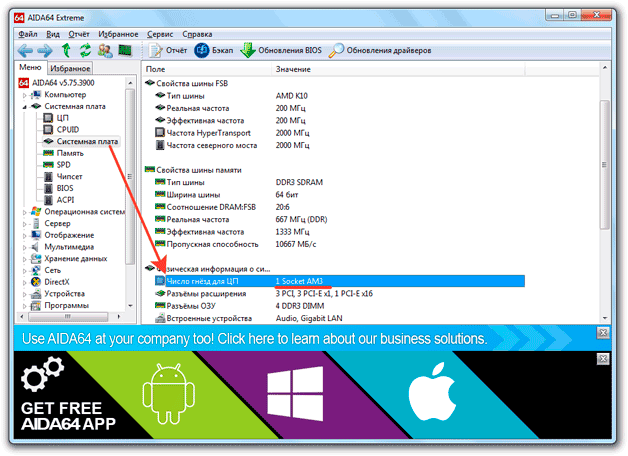
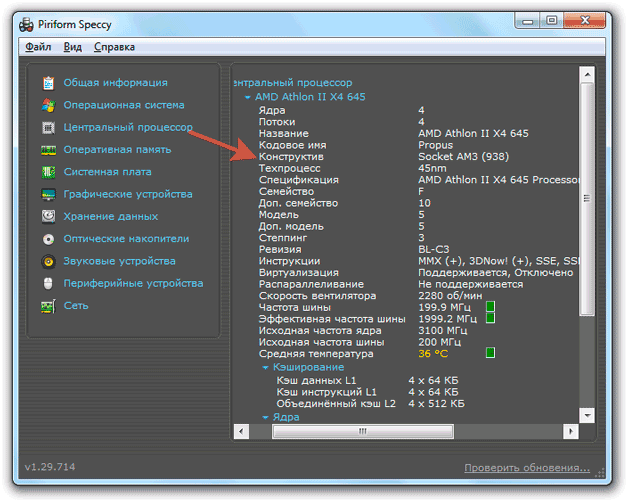
It is recommended to use several methods at once in order to find out for sure which socket is used to connect the processor to the laptop motherboard. You can also check the information on the CPU manufacturer's website.
When writing down information about a socket, be extremely careful. Every single sign has meaning. Case in point: there is Socket-AM3 and Socket-AM3+. You cannot install a Socket-AM3+ processor in Socket-AM3 - it simply will not work due to lack of compatibility. But in Socket-AM3+, you can put a CPU with a Socket-AM3 interface, because the new socket supports old hardware.
When buying a desktop PC or laptop, it is quite natural to ask how to find out which processor is installed on the computer, since in most cases, along with the volume random access memory this plays a key role in ensuring the speed of the entire system. There are many methods to solve this problem, but let's focus on the simplest and most accessible to a user with any level of knowledge.
How to find out what processor is on your computer: the easiest way
To begin with, we immediately note that only the most simple and quick methods calling certain settings, parameters and information that consists in using the Run console, called through the Win + R combination. It can also be launched through the Start menu, and access to the parameters can also be obtained from the Control Panel. But I don't think it's the best. The best way, especially since in the tenth version of Windows it is not so easy to get to it (unless, of course, you know that you can use the control command to quickly call it).
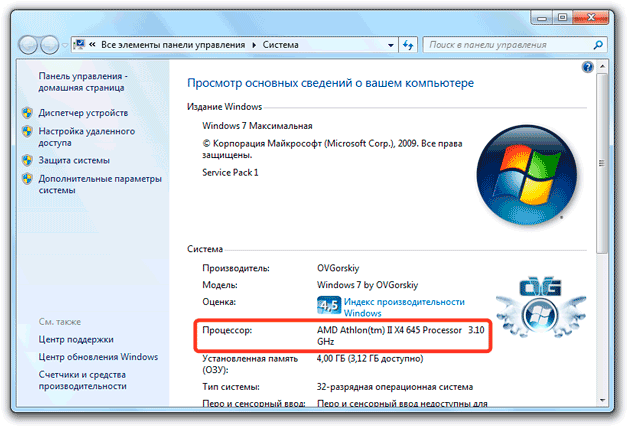
So, the user is faced with the problem of how to find out which processor is on the computer. In the simplest case, to obtain general information, you can use the properties section, which is called from the menu when you right-click on the computer icon present on the "Desktop" (in Windows 10 it is not there, so you need to use "Explorer"). The version is indicated here operating system, RAM and CPU information. If multiple clock speeds are specified, this corresponds to the number of cores.
How to find out what processor is on your computer: system information
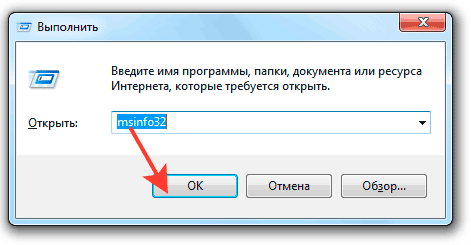
More advanced specifications can be obtained from the system information section, which is launched through the msinfo32 line.
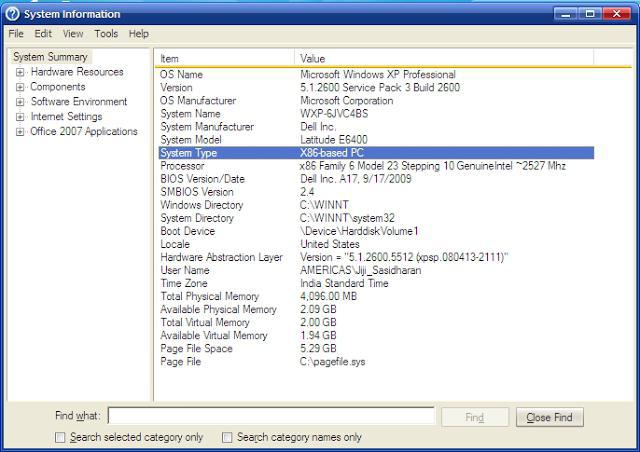
Here, along with the model, you can get information about the number of cores and the computational threads corresponding to each core.
Using Device Manager Information
Another easy way to help solve the problem of how to find out which processor is on your computer is to use the standard Device Manager.
The devmgmt.msc command is responsible for launching it, although many users prefer to call it from the Control Panel or system administration tools. Here you just need to refer to the corresponding line to view the general data. But in the properties of the device you can also find information about installed driver, and sometimes identify hardware problems.
DirectX Data
Not all users know that the problem of how to find out which processor is on the computer is completely elementary solved through the DirectX bridge dialog.

It can be accessed through the dxdiag command. By the way, you can’t call it in any other way (even through the “Control Panel” or through the settings in Windows 10).
Specialized utilities
If the problem of how to find out which processor is on the computer is especially acute, you can use special programs.
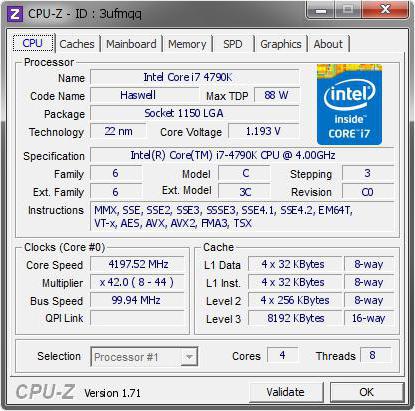
Rightfully one of the most popular is the CPU-Z utility, which serves the most full information and about the central processor, and about all other "iron" components of the system. If you use the CPU-Z application, you can get information regarding the video card and GPU. As is already clear, there are enough funds.
Conclusion
In principle, all means are good, but to get the most complete information, it is still better to use the DirectX dialog or special utilities operating on the CPU-Z type. If you don’t like any of the methods, you can find the special identifiers DEV and VEN in the “Device Manager” in the description of the processor, and then use them to search for information of interest on the Internet or on the official website of the equipment manufacturer.
But, as practice shows (and statistics also confirm this), most users, in order not to get into the jungle of settings and system parameters, prefer to use the CPU-Z program, especially since it can be found even in the form of a portable version that does not require installation or integration into the system through a standard installer. Frankly, there is some common sense in this - both faster and easier.
The processor is a key element of the PC. The better it is, the more productive the computer. The processor can be integrated into the motherboard. This is typical for netbooks, weak PCs. Their power is sufficient for office work, Internet surfing and watching videos in average quality. External processors are much more productive than integrated ones. They are recommended to choose when buying a PC.
Classification
The price of a processor directly depends on its power:
- Up to 100$. They have 2 cores and are suitable for games that do not require processing scenes with many objects on the monitor, simple mathematical operations.
- From $100 to $200. They have two or four cores. Optimal for most games, resource-intensive applications, 3D modeling.
- From $200 to $250. They have 4 cores, have higher performance than devices from the previous category.
- Above $300. Have 6 or more cores. Suitable for any kind of games and applications.
Today, only 2 manufacturers produce CPUs for personal computers: AMD" and " Intel". Devices « Intel» more powerful, « AMD" - cheaper.
Processors from the same manufacturer that have the same architecture and similar power are combined in a series. The series is reflected in the device name:

Processors of the same series usually differ in clock speed.
Characteristics
Consider some characteristics of the processor:
Instruction
So, you asked yourself a question: how to find out what processor I have, and to be more precise, what processor is installed in your PC or laptop. To get a response, you need to do the following:
- Click the left mouse button on " My computer».
- Click right key mouse without removing the cursor from the shortcut.
- In the appeared context menu click " Control».
- Will be open Computer management". Click on " Device Manager».
- Find the section " Processors”, 2 times left-click on it.
- In the opened window " Processors» It is possible to find out the name of your central processor, its capacity, clock frequency and other characteristics.
This algorithm is valid for all Windows versions, starting with the "seven".
Now let's look at how to find out the processor of your own computer in more old system, for example, in Windows XP:
- Press the " Start».
- Click on " Control Panel».
- Go to the section " System».
- You will see information about all system properties. Among them will be data on the central processor installed in the PC, its characteristics.
Special applications
There are many applications designed to show information about the OS and devices. One of them is considered CPU-Z. By installing it, you will be able to get detailed information about RAM modules, motherboard, video card, CPU.
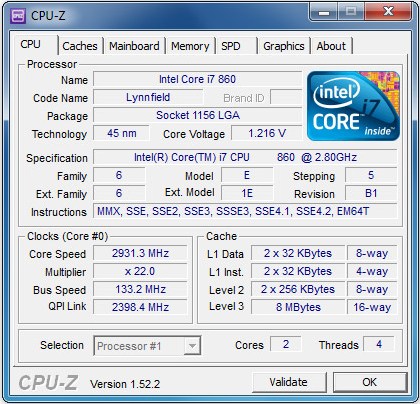
Processor details are shown in the " CPU". The device model is written in the field " Name". In field " Specification» it is possible to find out the clock frequency in the field « Nuclei» - the number of cores. How to learn architecture? The architecture of the processor is determined by whether it is 32-bit or 64-bit. The bit depth along with the type of socket, the size of the cache is indicated in the appropriate section.
Program " Everest» ( AID64) provides the user personal computer similar possibilities.
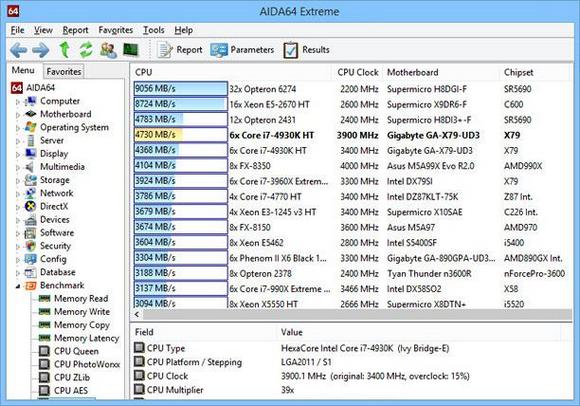
Which of the two applications to choose - it's up to you. They are both free and feature rich. It is worth noting that AID64 is more popular than CPU-Z. However, this does not mean that CPU-Z is a useless program.
Conclusion
The processor is one of the main elements of computer performance, so you need to be able to choose it correctly. It depends on what tasks it will be possible to perform. If the processor is already installed, then its characteristics can be found independently from the information about the OS or using special applications.
Related videos
The computer processor is its most important component, which performs all the calculations necessary for the operation of a particular program. For example, when downloading an application such as Microsoft Word the work of the processor is minimal and consists only in creating, running and maintaining the application as a process or task. Much more heavily load the processor with applications that actively conduct various calculations. For example, Excel spreadsheets with a large number of complex formulas, modern archivers and, of course, various audio and video file transcoders.
Media content transcoding operations are very popular among home computer users, and when they are going to compress or convert their favorite movie to another format, they are faced with the question of how to find out what processor I have installed and how many hours such an operation will take.
First, let's look at two main characteristics of processors that determine the speed of their work and performance of various tasks. To make the physical meaning of the characteristics more clear, let's imagine them as water flowing out of a hole in a virtual reservoir.
- core frequency. Determines the number of operations that the processor can perform per unit of time. In the reservoir example, the processor core frequency can be represented as the size of the hole from which water flows. The larger the hole, the faster the water will flow out.
- Number of Cores. A few years ago, the era of multi-core computers began. An increase in the number of cores allows parallelization of tasks in optimized programs, due to which an increase in performance is achieved. Using the example of a barrel of water, we can imagine that we add another one of the same size to one hole from which water flows out and we get twice the rate of emptying the tank. This will correspond to the use of dual-core processors in computers. Processors with four cores are gradually becoming affordable.
Using Device Manager Data
Device Manager can be launched either using the Windows GUI or via the command line. 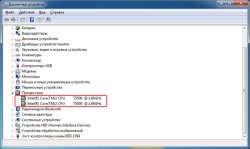
Using the CPU-Z Utility
The free CPU-Z utility allows you to get more complete information about the type of processor installed in your computer: its model and code designation, the type of socket for which it is designed, frequency, number of cores, cache sizes, and sets of supported instructions. You can get the listed data as follows. 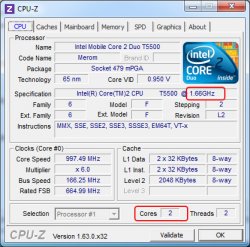
There are other ways to determine the processor installed in the computer. For example, through Computer BIOS. But they are not as simple and convenient as the ones above.
 Tcpdump - a useful guide with examples
Tcpdump - a useful guide with examples Key management Key distribution involving a key distribution center
Key management Key distribution involving a key distribution center Which files infect macro viruses
Which files infect macro viruses