Ide connector on the power supply. SATA Molex adapter: what is it
We provide reference data on color coding and the location of the wires in the sockets and plugs of the PC. The pinout and connection of the wires of the power supply and other main computer modules must be carried out accurately and accurately in order to prevent short circuits during operation. Let's find out what voltage is applied and on which wires.

Color coding
In ordinary PC power supplies, 9 colors are used, denoting the role of wires:
- Black- common wire, also known as ground or GND
- White- voltage -5V
- Blue- voltage -12V
- Yellow- supplies + 12V
- Red- supplies + 5V
- Orange- supplies + 3.3V
- Green- responsible for turning on (PS-ON)
- Gray- POWER-OK (POWERGOOD)
- Purple- standby power supply 5VSB
All computer connectors - name and photo
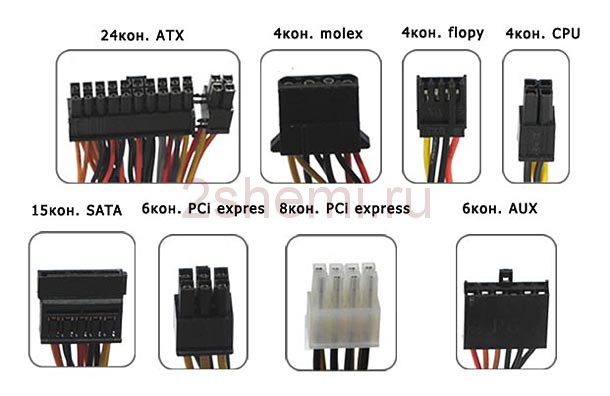
In total, when the power supply unit operates, 8 types of connectors are used, their type and names are shown in the photo. To turn on the AT-ATX power supply, you need to close the GND and PWR SW connectors. It will work as long as they are closed. If you use it separately, put a button on these contacts.
Power supply connector wire pinout
Pinout for the sata and esata hard drive power connector

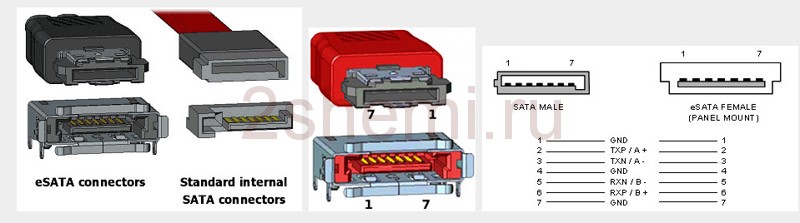
Diagram of the pinout of the power supply pins of the video card
![]()
How to get a different voltage from a PSU
| POSITIVE | ZERO | DIFFERENCE |
| +12 | +12 | |
| +5 | -5 | +10 |
| +12 | +3.3 | +8.7 |
| +3.3 | -5 | +8.3 |
| +12 | +5 | +7 |
| +5 | +5 | |
| +3.3 | +3.3 | |
| +5 | +3.3 | +1.7 |
There are situations when the connected device requires such a voltage for its operation that the power supply unit is not capable of producing. In these cases, you have to be perverted. Let's say our additional device (let it be lighting) operates on a voltage of 8.7 volts. We can get it by a combination of wires that give out + 12V and + 3.3V. For convenience, all possible combinations are shown in the table.
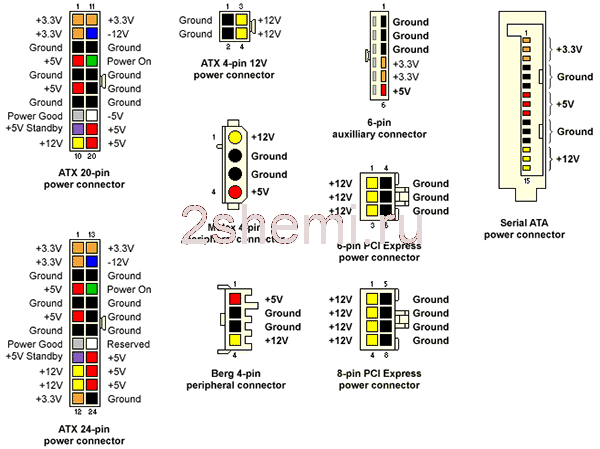
The ATX specification requires the power supply to produce three main outputs, +3.3 V (± 0.165 V), +5 V (± 0.25 V) and +12 V (± 0.60 V). Low-power −12 V (± 1.2 V) and 5 VSB (standby) (± 0.25 V) supplies are also required. A −5 V output was originally required because it was supplied on the ISA bus, but it became obsolete with the removal of the ISA bus in modern PCs and has been removed in later versions of the ATX standard.
Originally the motherboard was powered by one 20-pin connector. Current version of ATX12V 2.x power supply provides two connectors for the motherboard: a providing additional power to the CPU, and a main, an extension of the original 20-pin version.
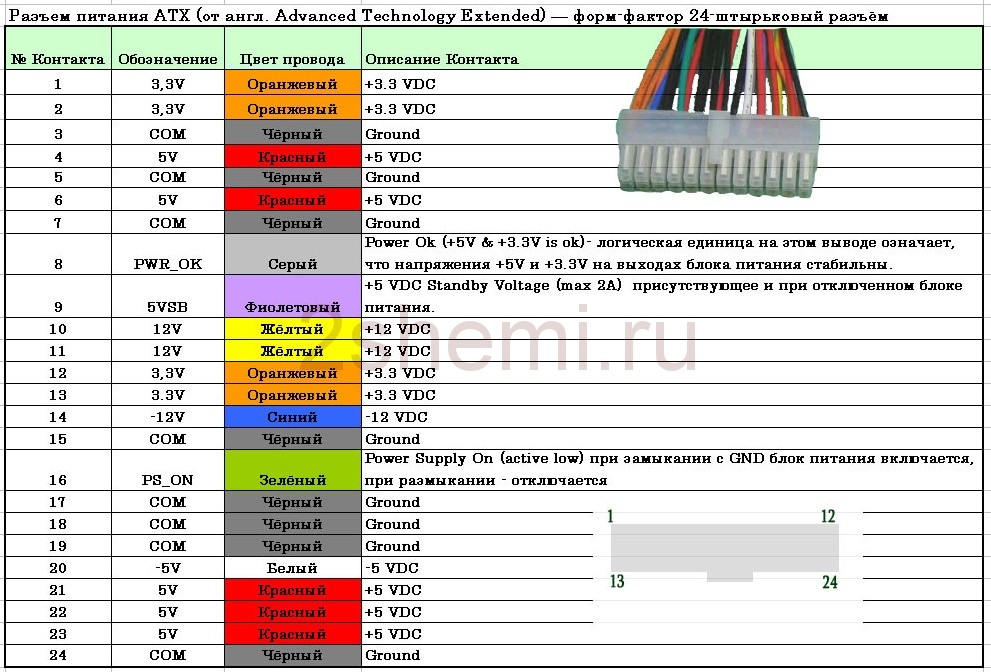
ATX connector pinout
| Pin | Name | Color | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.3V | Orange | +3.3 VDC | |
| 2 | 3.3V | Orange | +3.3 VDC | |
| 3 | COM | Black | Ground | |
| 4 | 5V | Red | +5 VDC | |
| 5 | COM | Black | Ground | |
| 6 | 5V | Red | +5 VDC | |
| 7 | COM | Black | Ground | |
| 8 | PWR_OK | Gray | Power Ok is a status signal generated by the power supply to notify the computer that the DC operating voltages are within the ranges required for proper computer operation (+5 VDC when power is Ok) | |
| 9 | 5VSB | Purple |
5 VDC Standby Voltage (max 10mA) 500mA or more typical |
|
| 10 | 12V | Yellow | +12 VDC (may sometimes have a colored stripe to indicate which rail it "s on) | |
| 11 | 3.3V | Orange | +3.3 VDC | |
| 12 | -12V | Blue | -12 VDC | |
| 13 | COM | Black | Ground | |
| 14 | / PS_ON | Green | Power Supply On (active low). Short this pin to GND to switch power supply ON, disconnect from GND to switch OFF. | |
| 15 | COM | Black | Ground | |
| 16 | COM | Black | Ground | |
| 17 | COM | Black | Ground | |
| 18 | -5V | White | -5 VDC (2002 v1.2 made optional, 2004 v2.01 removed from specification) | |
| 19 | 5V | Red | +5 VDC | |
| 20 | 5V | Red | +5 VDC |
/ PS_ON activated by pressing and releasing the power button while the power supply is in standby mode.
Activating / PS_ON turns on the power supply.
In several power supply units pin-12 may be Brown (not Blue), pin-18 may be Blue (not White), and pin-8 may be White (not Gray). In addition, some PSU violate color coding of wires.
Pin 9 (standby) supply 5V even when PSU is turned off. Pin 14 goes from 0 to 3.7 when PSU switch is turned on.
Shorting pin 14 (/ PS_ON) to GND (COM) causes power supply to switch ON and PWR_OK to change to + 5V.
This article promises to be quite explanatory and theoretical. Today we will consider in detail the subject so relevant in our time of technology - an adapter. This will be an adapter SATA Molex("SATA Molex"). In this article you will find answers to your questions, for example, what it is, what it is intended for, what function it performs, and others.
SATA Molex
Let's start with the fact that SATA (sata) is just an abbreviation, but somewhat incomprehensible. In relation to computer technology, the decryption will be as follows - Serial Ata The Acronym. To put it simply and clearly, SATA is a serial interface that appeared in 2003. It replaced the IDE (IDE) connector, which was later renamed to PATA (pata) - parallel ATA, since it was a faster connector, involving data transfer at a speed of up to one and a half gigabits per second. This also explains the physical change of the hard drive connector itself, as a result of which a need arose for a special device. Here we are talking specifically about the SATA power adapter (SATA). It is needed to connect new hard drives to old computers that do not have such a connector.
Why do you need a SATA Molex adapter ("SATA Molex")?
Today, all modern ones have a Molex connector. Despite this, the SATA Molex adapter itself ("SATA Molex") is relevant and in high demand to this day. Why? For example, you want to install on your Personal Computer additional equipment in the form of hard drives (or in the form of an additional CD-ROM drive). However, the available free ones are already taken. What will you do in such a situation? The SATA Molex adapter ("SATA Molex") will come to your rescue. 
What it is?
In fact, the SATA Molex adapter is the simplest device, which consists of two connectors for connecting to connectors, interconnected by four lengths of cable. Previously, devices with a Molex connector were powered by four following contacts: + 5V; Earth; Earth; +12. The SATA power connector has fifteen pins. It is divided into five groups and has a + 3.3V sequence; Earth; + 5V; Earth; + 12V.
There is also a less common SATA Molex adapter ("SATA Molex") for connecting power to a laptop CD-ROM drive. This device has a more compact connector due to the fact that it has only six + 5V contacts (instead of fifteen) and ground.
Pinout
Let's take a closer look at the Molex SATA adapter. The pinout of this device, like the connector itself, is pretty simple.
The first group of contacts in the SATA connector is a voltage of +3.3 volts. This group is not used in the adapter, since the Molex connector does not have such a voltage at all.
The second group of SATA contacts is earth.
The third group of contacts of the connector has a voltage of +5 volts. It should be noted that it is combined with the first contact.
The fourth group of contacts of the connector is ground, it is combined with the third contact of Molex (molex).
The fifth group of contacts of the SATA connector (+12 volts) is combined with the fourth contact of the Molex connector.

The adapter can be purchased at any computer store or in the radio parts department. These devices have completely different lengths: from a few centimeters to several tens of centimeters. The most common adapters cost around one dollar. Also, there are not only one-to-one adapters on sale. There are adapters from one Molex connector to several SATA connectors. This is very convenient in cases when your power supply has already run out of all free connectors, while there is one Molex (molex) available and complete, but you need to turn on several SATA devices. The device already described in the article will help you here.
 How to deactivate the "You've received a call" service from MTS?
How to deactivate the "You've received a call" service from MTS? Factory reset and hard reset Apple iPhone
Factory reset and hard reset Apple iPhone Factory reset and hard reset Apple iPhone
Factory reset and hard reset Apple iPhone