Analysis of options for building telephony based on Microsoft Skype For Business
This post analyzes the options for building telephony based on Microsoft Skype For Business.
Good afternoon everyone. When building telephony in a company, in most cases, the choice lies among traditional telephone manufacturers, such as: Cisco / Avaya / Siemens (Unify) / Panasonic / NEC and others. This is primarily due to the fact that people choose telephony and look at classic manufacturers. But increasingly, companies in their requirements, among other things, indicate the possibilities of unified communications. Why not approach this issue differently, choose a unified communications system, and build a telephony system on its basis? In this article, I would like to consider the possibility of building a full-fledged telephony based on the Microsoft Skype For Business solution.
Microsoft initially came to the market with the unified communications system, even with the OCS product, then Lync, now renaming it Skype For Business. I'll make a reservation right away that the solution has almost nothing to do with the classic Skype. All the advantages of unified communications (any platform for all communications / video conferencing / collaboration with documents / instant messaging / integration with the Office suite / presence status) I will not describe in detail. Here we can only say that Microsoft has already proven that it is a world leader in this area, which is confirmed by a large number of independent studies, including the "magic" squares of Gartners. But as for the quality of telephony, while the solution is not so popular. If we consider Microsoft Skype For Business (hereinafter S4B), then it has a sufficient number of telephone functions that provide the necessary functionality for telephony, namely:
- Call transfer
- Call forwarding
- Simultaneous call
- Hunt groups
- Call pickup
- And others.

Moreover, from the point of view of configuring these functions, all this can be easily and simply configured via the S4B client, which makes the use of this functionality very convenient and intuitive. So why, after all, Microsoft S4B has not become so popular as a telephony, if there is everything for this. The main factors that influence this:
- Microsoft released a software platform with a software client, but they did not release telephones and solutions for interfacing with the telephone network. Microsoft's concept that telephones are the last century and you need to use software clients, and the interface with the telephone network is enough to be done via SIP directly, and the telecom operator must support all the specifics of MS S4B operation. This concept, like many others, is good on paper but not in real life. Until now, telephones are required, an interface with communication operators not only with those offered by Microsoft, but also with those with whom you have been working for a long time and through those channels that have been working for a long time with the preservation of the number.
- Microsoft entered this market as a UC solution and the telephony market cannot immediately accept that telephony is only part of UC. Not to mention the attitude of telephonists towards Microsoft itself.
With the help of partner solutions, you can solve the following tasks:
- IP Phones. A compatible phone is a phone that works directly with Microsoft Lync / Skype For Business. In this case, you shouldn't even try to connect a standard SIP phone to S4B, it just won't work, since Skype For Business works using its own protocol. Although the basis of this protocol is SIP. The advantage of such phones is the following (In terms of functions, I describe the functions of AudioCodes phones. For phones from other manufacturers, check on the Microsoft website):
- Independence from a multifunctional device, such as a computer or smartphone, when it can be busy with other applications, discharge, overload, etc.
- Full synchronization of status with Skype For Business and the ability to manage status directly from your phone
- Synchronizing your phonebook contacts with the S4B phonebook
- Ability to set up call forwarding from your phone and synchronize the forwarding status with Skype For Business.
- Support for call transfer / call pickup / group call / head-secretary filter / speed dial panel with presence indication MS S4B
- One of the important and convenient features is the Better Together driver, which allows you to use your IP phone as a headset. This allows you to dial via Skype For Business while talking on the phone / transferring an active call from the phone to the Skype For Business client / managing a phone call from the S4B client.

- An important aspect is Microsoft S4B interface with metro network... Here Microsoft suggests using various devices voice gateways and SBC (Session Border Controller), which are responsible for connecting Microsoft Skype For Business to an existing PBX or CO line. Moreover, the range of these devices is really very large, ranging from several analog lines to high-performance devices designed for several thousand simultaneous connections, providing carrier-class fault tolerance. Port options can be completely different: CO (FXS / FXO), E1, BRI, SIP. If we consider the SIP protocol, then it makes sense to highlight several points:
- Microsoft supports SIP over TCP and / or TLS. Microsoft does not support SIP over UDP. But besides this, Microsoft's implementation of the SIP protocol is very peculiar. To be more precise, Microsoft uses not very popular extensions of the SIP standards, but somewhere interprets these standards in its own way. Not every station is compatible with Microsoft S4B, and even if it is compatible, it has a number of limitations. All of these limitations are documented on the TechNet pages.
- If you need to use standard SIP, remove the restrictions on the integration of S4B and telephone exchanges, then an SBC device is used for this, which ensures full compatibility with Microsoft S4B and third-party telephone exchanges, converting dialects of the SIP protocol to meet the requirements that exist from different sides.
- Also, one of the important functions of SBC is to provide a secure connection to the SIP operator over the public Internet.

- Fault tolerance system for remote offices... If we consider Microsoft S4B as a telephony system, then ensuring the fault tolerance of remote offices immediately becomes an important point. In this case, Microsoft proposes to use the SBA solution, which ensures fault tolerance of remote offices at the time of the loss of the channel between the remote office and the central one. Also, AudioCodes offers a range of proprietary remote office resiliency solutions for Microsoft S4B, ranging from multi-person offices to large remote offices.
- Call recording system. If a company's security team has requirements for recording conversations, then Microsoft uses a partner solution for this task, such as AudioCodes SmartTAP. It allows you to record all conversations, invisibly from the user and save all conversations in a centralized way.

- Auto attendant system... Microsoft uses an Exchange server as its Auto Attendant system. Also, to solve these problems, you can use a third-party Auto Attendant, which can provide wider and more flexible functionality, including providing a dedicated Auto Attendant in remote offices. The main difference between the Auto Attendant adapted for Skype For Business from any other is that when distributing incoming calls according to various scenarios, the system takes into account the status of the Microsoft Skype For Business user.
- Contact center. As you know, contact centers are currently an important component of many companies and are often integrated into the telephone exchange. To implement the functionality of the contact center, partner solutions are also used, which provide a complete contact center solution for any business requirements of the customer. Moreover, the list of qualified contact center solutions is quite large, among which there are leading manufacturers of contact centers, including the leader of the contact center market - Genesys.
- Connection of analog telephones and faxes. Based on my personal experience, I can say that this task is still relevant for almost all companies. Microsoft Lync / S4B has a solution for connecting analog subscribers and faxes, moreover, AudioCodes pays a lot of attention to solving this problem, so we can say with confidence that if there is a problem to connect analog devices and faxes, then it can be solved.
I would also like to mention some things that can really be important, but at the same time not all of them notice:
- Microsoft uses the SILK codec in its Skype and Skype For Business solutions. This codec was taken from Skype and moved to Skype For Business. Why is it important. There are several reasons for this:
- a. SILK supports HD quality transmission, which ensures the best quality sound.
- b. SILK was developed to transmit voice information online via the public Internet and has proven itself in the Skype solution better than many other codecs. If we talk about standard IP telephony, then this is not an important factor, since phones, as a rule, are placed in a separate VLAN, where voice traffic is prioritized and quality problems do not arise. But for the technology of unified communications, this task becomes almost impossible, since the call can be made from any device and from any place (via the Internet, WiFi network, from a software client, and so on). It is at these times that it is important to have a codec that can adapt to the existing environment and provide optimal quality.
- Microsoft provides very strong quality analysis tools, such as DashBoard, that allow you to correctly analyze what is happening with the UC network and find and fix problems on the network in time.
- Microsoft is currently trying to be as multi-vendor company as possible and it does not give priority to one platform or another for the MS Lync / S4B client. Thus, a full-fledged client is available on almost all popular OS for PCs / tablets / smartphones - Windows / MacOS / Adroid / iOS / Windows phone. Not supported, perhaps only Linux.
- Microsoft has a fairly powerful interaction interface, both client and server. Thus, the end client can independently add almost any application for MS Lync, or integrate his system with MS Lync. Moreover, there are companies that offer ready-made integration solutions, for example, 1C integration with MS Lync / S4B.
What are the strengths I would highlight
- Unified solution for unified communications and telephony. One way or another, more and more companies are using MS Lync / Skype For Business as a unified communications system, while having a separate telephony system in parallel. So why spend on operating two systems when you can use one.
- Partner solutions program. Many believe that by making a partner solutions program, Microsoft complicates the process of integrating its system with third-party PBXs or when integrating with the PSTN. On the one hand, this is true, but on the other hand, Microsoft allows you to truly use best solution in its class. Moreover, Microsoft guarantees to work with them and provides support for its products when working with these solutions. This gives Microsoft more freedom of choice and flexibility than anyone else.
- Integration of telephony, unified communications and office applications. This is what makes your employees work easier and more efficiently. I realize there is some crazy Microsoft research that talks about how you can save many hours a month with Lync and Skype For Business. I do not argue against this analysis, but in my opinion, it is sometimes more important (especially in our realities) when this system allows you to save seconds, or even minutes at those moments when it is really necessary.
- Ease of use. I think no one will deny that, from the point of view of ease of use, Skype For Business is the most convenient system of unified communications and telephony on this system is also very convenient and easy to use. And the ability to use the phone as a headset for S4B simplifies operation.

Well, now you can talk about weaknesses Skype For Business as telephony:
- The first drawback and, probably, the main one is the usual amount of telephone functionality. Many telephonists are used to having 100,500 phone functions in their system. Indeed, this is a "huge advantage", but in fact, people use 5-10 functions, such as call pickup, transfer, forwarding, group call, Auto attendant. Basic functions in Skype For Business are available.
- Partner solutions. Skype For Business is not a telephony system as such, but a UC system from the very beginning. Moreover, it is a completely software product. In order to make a telephony system on Skype For Business, you need to use partner solutions, thereby obtaining a multi-vendor solution. But there is also a downside - Microsoft officially supports its system if it works with certified partner solutions. And at the moment there are more and more partner solutions and the customer is provided with a fairly large selection. And if we talk specifically about voice and telephony, then all tasks related to voice services can be closed by one manufacturer - AudioCodes, which covers all tasks related to voice.
), I would like to dwell on a modern, progressive and at the same time affordable solution based on Microsoft Skype for Bussiness (formerly MS Lync), which allows organizing corporate communications with great opportunities.
Recall that the solution Skype for business is a unified communications system that allows you to conduct telephone conversations, video and audio conferences, online meetings (webinars), messaging. Feature this decision, is tight integration with other MS-services, the main of which are Active Directory, Exchange, SharePoint.
Building a unified communications system with the development of technology and business informatization is becoming an increasingly complex process. If earlier it was enough to install a telephone exchange and user devices to organize communications in a company, then current business requirements force the use of a unified communication system built on various means of communication: chat, call, e-mail, webinar systems, video calls, etc.
That is why we will consider the general architecture of the solution, the design features and the dependence of the architecture and the implemented functions of the Skype for Business Server 2015 unified communications system.
To begin with, let's take a closer look at the functionality of the Skype for Business system (SfB below):
- Chat, presence monitoring
- Screen demonstration
- Integration with internal services based on Microsoft products (out of the box)
- Availability of API for integration with services of other vendors
Based on the above functions, we can safely say that SfB organizes a platform for all communications used in enterprises. But, it is important to note that Sfb, unlike others similar systems(Cisco Unified Communication Manager, Avaya, Siemens (Unify), was originally positioned as a unified communications system, so IP telephony is only a constituent element, not the core of the system, which affects the functionality. Despite this fact, SfB as a telephony system allows :
- Call transfer
- Call forwarding
- Simultaneous call
- Hunt groups
- Call pickup
In addition, since the IP telephony system is not the core of the system, SfB has a number of features in the implementation of the SIP communication protocol (using the protocol only over TCP or TLS), which affects the interfacing with other systems and communication operators, as well as the connection of user devices. Despite this, Microsoft's active work with partners allows us to build a full-fledged IP telephony system, for example, SBC (Session Border Controller) solutions from various vendors are used to connect with operators.
As we can see, the SfB system solves a wide range of business problems in the communication process, which is why the solution architecture is also non-trivial. SfB includes the following server roles:
|
Server role |
Description |
|
Front End Server |
Front End Server. Includes the following functionality: User authentication and registration Status information and address book Chats, group chats Audio conferencing, web conferencing Monitoring and CDR Telephony Central management console |
|
Back End Server |
Database server MS SQL Server. Serves as a storage for SfB service information, incl. user list, conference data, etc. |
|
Edge Server |
Edge server. Used to provide access to the unified communications system to external (outside the corporate environment) users |
|
Mediation Server | |
|
Video Interop Server |
Server role that allows you to integrate the SfB system with other vendor webinar systems (Cisco / Tandberg) |
|
Used for authentication external users and therefore protection against DDOS attacks |
|
|
Persistent Chat Server Roles |
Allows you to save the history of messages in chats and group messages |
Table of correspondence between functions and server roles:
|
Intracorporate communication, including encrypted |
Front End Server |
|
Possibility to connect to PSTN (using intermediaries) |
Mediation Server |
|
Chat, presence monitoring |
Front End Server, Persistent Chat Server Roles |
|
Video calls, online meetings |
Front End Server, Video Interop Server |
|
Screen demonstration |
Front End Server |
|
Integration with internal services based on Microsoft products (out of the box) |
Front End Server |
|
Availability of API for integration with services of other vendors. |
Front End Server, Video Interop Server |
|
Support for phones, software clients, mobile clients |
Front End Server, Edge Server, Director |
Understanding what server roles exist and what functions are responsible for, you can actually move on to building the architecture of the future unified communications system based on SfB. Before building the architecture, consider the restrictions on the overlapping of server roles, namely, the following roles should be placed separately:
- Director
- Video Interop Server
The Mediation Server in the Standard version of Sfb is combined with the Front End server, but in the Enterprise Edition it can be moved to a separate server. The rest of the roles can be combined or placed on separate servers.
Consider a possible architecture for an SfB solution for medium to large businesses (see Figure 1).
Figure 1 - An example of an architecture based on Skype for Business
This structure, according to Microsoft recommendations, depending on the server performance, is capable of serving up to 4000 clients. The diagram shows two SfB Standard Edition servers, each of which serves 2,000 employees, but user information is synchronized between both servers so that if one of the nodes fails, the service does not fail. In this configuration, it is recommended to use the Edge server as an edge server to connect external clients to the unified communications system. The Edge server is hosted in the DMZ. Also, to connect to the PSTN, it is proposed to use the SBC gateway (Session Border Controller), which allows you to connect external providers using available methods (FXO / E1 / SIP). The diagram also reflects two Office Web Apps server and Exchange UM: servers for integration with other Microsoft services.
Both Standard Edition central servers include the following roles:
- Front End Server.
- Back End Server.
- Mediation Server.
- Persistent Chat Server Roles.
This architecture will allow to implement all the functions presented in SfB, to ensure high service availability, high quality communication, the ability to communicate with the regions and the mobility of employees. In companies with a large number of people, the Enterprise version of SfB is used, in which Back End and Front End servers, Mediation servers are distributed, and pools of Edge servers are created.
For Small Business companies, cloud solutions based on SfB can be considered. We will write more about the architecture of the cloud solution in the next article.
At the moment, there are quite a few solutions for unified communications systems, but these technologies are available only to large corporations that can afford multimillion-dollar implementations of such systems. The Skype for Business product, especially the cloud version, is designed to make a unified communications solution widely available, and the process of employee interaction efficient, convenient and mobile.
System integration. Consulting
Before defining all the advantages of SIP technology or, as Microsoft called it, Skype Connect. It is necessary to give a clear definition of SIP technology, and how it can replace the telephone.
SIP is a special protocol for IP telephony. It allows us to use the telephony we are used to, but using the Internet. This technology is excellent for business, as it provides high quality communications and is significantly cheaper than conventional telephone networks. Now let's take a look at the advantages of SIP technology from Skype software.
What is Skype Connect
At its core, Skype took the standard SIP telephony protocol as a basis, but thanks to its technology, it somewhat supplemented it.
The thing is that the company has a lot of funds, respectively, and the equipment that is used to provide communication is an order of magnitude better than that of competitors. Also, due to the huge amount of resources, skype provides a low cost of tariffs when high quality service.
Easy company start
Organizing calls efficiently does not take much time, effort or money, and it does not require highly specialized knowledge. When setting up, everything is clear at an intuitive level. The great advantage of Microsoft IP telephony is a free call from a customer to your company. The fact is that a client can call your corporate number using his Skype client without spending any money.
Administrator help
Incredibly convenient feature for administrators - (formerly called skype to sip). At any time, you can receive all detailed information regarding your IP telephony. To do this, there is no need to constantly be at the workplace, you can view any information you are interested in on your home PC or laptop, on your tablet or phone. The gateway works quickly, accurately and stably, which system administrators will rightly appreciate.
Economy tariff
If your company's budget is small, then this is not such a serious problem. SIP Skype tariffs are calculated on a monthly subscription, which determines the maximum number of simultaneously open lines. The more expensive the subscription, the more operators will be able to work, but the cost does not affect the number of free minutes of conversation. In addition, the first time you connect, Skype gives you a whole month of free communication, and only starting from the second, a subscription fee is charged. You can test the network without fear of losing company funds.
How to use Sip Skype
If you use regular Skype, then registration in this program will not be something new for you. Let's look at everything in stages:
Create account (s). A standard procedure on any resource. You have a choice here. You can link an existing KM to a manager or create a new user. In fact, there are not so many conveniences, just one login and password for the manager and Skype. If you will use a gateway to control operators, it is better to register a new user.
Creation of SIP profiles. As soon as the program opens, use the "Functions" tab to connect to Skype connect, so you can create a SIP profile, and then immediately proceed to operation.
Payment. After registering and creating profiles, you need to pay a subscription fee. Choose a payment method convenient for you and enter the required amount, then activate the subscription.
Important! Do not top up your main Skype account, even if it is linked to Skype Manager. You will not be able to use these facilities for SIP telephony. It is possible to top up Skype using Skype Manager, but this function does not work in the opposite direction.
Enjoy your work in SIP Skype!
How the Trunk Ports of the Mediation Server of Skype for Business 2015 work.
This article focuses on the Skype for Business 2015 Mediation server, and keep in mind that all of the above can be applied to Lync 2013. One of the areas that will certainly be affected in any type of voice communication on a corporate scale is channels, or trunks, SIP (SIP Trunk). Therefore, let's go directly to a topic that can be very confusing when it comes to listening and sending ports on the server side of Skype for Business in connection with the configuration of trunk ports.

We will cover a number of issues related to configuring trunk ports:
Listening port for the IP / PSTN gateway (the listening side of the corporate PBX);
The port of the linked Mediation Server (the listening side of the Mediation Server).
Listening port for IP / PSTN gateway
The Skype for Business 2015 Mediation broker will have to send SIP (signals) and Media (sound) through a specific port to the SIP trunk created for the IP / PSTN gateway, or a specified range of ports on the mediation server. The default port for TLS is 5067 and the default port for TCP is 5066. Optionally, you can specify a TCP port range, such as 5070-5090. For simplicity, we will choose the port range 5068-5068. This means that Mediation Servers will not be located on a different TCP port when using SIP and Media for the next SIP hop; in this case, an IP / PSTN gateway other than 5068 is used.
We will not dwell on which IP / PSTN gateway is used. These can be various PBXs such as Cisco, Avaya, Nortel, or gateways such as Audio Codes, Dialogic, and Sonus.

Listening port
At the next hop, the IP / PSTN gateway sends SIP and Media to the port selected for this part of the trunk configuration. This tells the carrier that you will be sending TCP / SIP and Media data on port 5068. In addition, this means that the communication group must wait to receive TCP / SIP and Media data from the mediation pool on port 5068 (screen above) ...
How is this different from the case when we have a range of ports? Nothing, you just need to remember that by having a range, for example, 5070-5090, you are informing the service provider that you can send TCP / SI P and Media data through that specific range; however, on a specific trunk, you will send SIP and Media data on a specific port specified in the Listening port for IP / PSTN gateway section when configuring the trunk.

Configuring an IP / TCP gateway
A Mediation server can serve multiple connections over a SIP backbone created for an IP / PSTN gateway. In our example, the PBX is listening on TCP / 5068 and the Mediation Server is listening on TCP / 5068. In addition to these ports, the Mediation Server uses ports 60000-65536 (UDP) for audio traffic. Make sure the firewall ports 60000-65536 are open between the Mediation Server and the PBX (screen above).
Linked Mediation Server Port
The Associated Mediation Server port is the exact opposite of the listening port for the IP / PSTN gateway. This means that the Mediation Server is listening (not sending) TCP / SIP and Media packets on the specified port (in this case, port 5068).

Ports of receiving traffic
When the PBX transmits TCP / SIP and Media data to the Mediation Server, the service provider usually asks which port you want to receive traffic on. The screen above shows which ports these are. If you have a range of ports, this is fine, but remember that for each trunk you need to specify a specific port to send and receive SIP and Media traffic.
Understanding the intricacies of the ports for listening and sending TCP / SIP Media is not so difficult. Basically, these are two devices trying to communicate with each other and asking which port to forward traffic on. Unfortunately, there is no room for uncertainty in this area; you cannot say: "Configure any TCP or TLS protocol at your discretion and send data to any ports of your choice, and I will listen, waiting for them to appear ...".
Did you want to thoroughly study the operation of SIP trunks ports, but could not install Skype? In this case, I recommend that you look for a site whose specialists can offer you assistance not only in installing the program on your work computer, but may also help you master the basics of SFB. For example, this can be hlps.ru, where you will find the most comprehensive information on this topic.
As part of one project, a trunk was made at the test bench between Skype For Business 2015 (hereinafter referred to as Skype) and free version PBX (free license for 1 year) Vodia PBX, below is a description of the settings. The challenge is making Skype calls<—>Vodia, phone numbers Skype - 55xx, Vodia PBX - 57xx.
Vodia PBX Settings
To set up Vodia PBX you need:
- You can download the package with the Vodia server from the site - http://vodia.com/onefree;
- Next, you need to install the Vodia PBX package. I installed on Windows 10.
- On the vodia.com website, get a test license for 1 year and indicate it in the License section. If this is not done, Vodia services will not work correctly.
- In the Security-> General section, specify the login and password for the administrator. If necessary, you can create an additional account.
- In the SIP section, check the port numbers that are used for the SIP protocol.
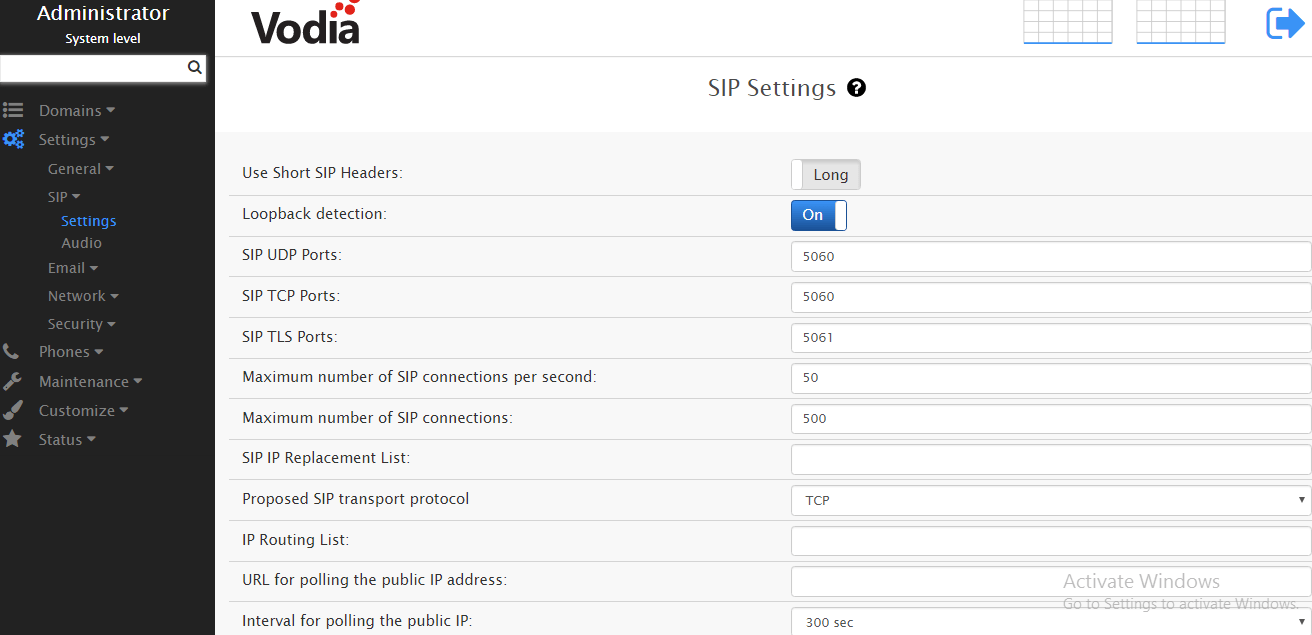


- In the settings of the WCFC.demo domain, in the Trunks section, create a new trunk by clicking the Add button. It is assumed that the trunk will use the TCP transport protocol, the Mediation server address is uc01.wcfc.local, and the TCP port is 5068.
Trunk settings are listed below:

In the trunk settings in the SIP Caller-ID Presentation section (see above), the following field values are indicated, by default the direct values of which are not displayed, so to find out their real values, you need to specify Other in the Value.

- In the settings of the WCFC.demo domain, in the Feauters-> Dial Plan section, you will need to create a new Dial Plan, specifying its name (for example, uc.demo). Within the framework of the stand, all calls should be sent over one trunk, I did not indicate specific ranges and left the * symbol, which means to route all outgoing calls to the "SIP Gateway" trunk.



- Settings in the domain WCFC.demo section Advanced-> General Settings

Free SIP client PhonerLite was used as a client

Skype setup
- Install Mediation Server;
- Create PSTN Gate and Trunks in the topology;
- Create Dial Plan;
- Create a Voice Policy;
- Configure trunk configuration;
- Configure Skype users;
- Have specialized licenses available.
1 Installing Mediation Server
Mediation Server is a role that is responsible for broadcasting a signal from the RTA or SILK format to the PSTN-understandable format - G711.
In order to check or install Mediation Server, you need to open the corresponding section in Topology Builder.

2 Create PSTN Gate
On the picture below, two gateways are created - the PSTN.WCFC.LOCAL gateway is Vodia, port 5060, the PBX.WCFC.LOCAL gateway is another IP-PBX. (After creating the gateways, do not forget to publish the updated topology).
The FQDN must be specified as the gateway name, which is correctly resolved in DNS Mediation by the north. Trunks are created automatically after the PSTN Gate is created.


3 Creating a Dial Plan
Dial Plan is a normalization rule that transforms telephone numbers into a single standard (E. 164). This applies to both incoming and outgoing numbers.
In real life, there are certainly more number formats than in the example below.
The rule shown in the image below keeps track of any four-digit numbers and adds a "+" sign to them.

On the test bench, everything is simplified, so it doesn't really matter what scope the routing rule will have. I created for users and named it "Internal Calls".
Policy settings:

- After the voice policy is created, you need to create a PSTN Usage to which you then bind specific routes. Initially I create empty PSTN Usage. In this example, two PSTN Usages are created. (In the PSTN Usage image, routes are already attached, initially this field will be empty).
- After creating the PSTN Usage, you need to create a route.
- The route is created based on which numbers need to be traced and to which PSTN gateway to route. In my case, it is necessary to track the numbers + 57xx called by Skype subscribers (already normalized after Dial Plan) and send them to the pstn.wcfc.local gateway. The Select button allows you to attach the route to the PSTN Usage created in the previous step.
As a result, two routes were created at the stand, one tracked + 57xx calls and sent to Vodia, the second route sent + 56xx calls to MX-One PBX.

5 Trunk configuration
Trunk settings:

In the Associated translation rule section, you can create rules for changing outgoing and called numbers when leaving the Skype trunk. For example, you can specify a rule in relation to outgoing numbers, the meaning of which is to remove the "+" sign from numbers. In fact, this is not necessary - Vodia will accept calls from + 55xx numbers.
6 Setting up Skype users
For users, you need to enable Enterprise Voice, assign a voice policy, as it is created for users, and assign a phone number.

After all the settings on Vodia and Skype are completed, audio calls can be made between users of the two systems. The only caveat is that Vodia in free mode can make no more than two simultaneous calls.
 Why does the blue screen turn on on the iPhone Blue screen on the iPhone 5s what to do
Why does the blue screen turn on on the iPhone Blue screen on the iPhone 5s what to do Everything you need to know about Apple Music
Everything you need to know about Apple Music How To Set Up An iPhone Like New From Zero - Detailed Instructions
How To Set Up An iPhone Like New From Zero - Detailed Instructions